Abstract
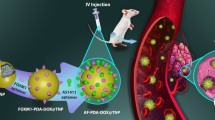
Applying nanotechnology to design drug delivery systems is a promising turning point in cancer treatment strategies. In the current study, Lawson, a nonpolar anticancer phytochemical, was entrapped into β-cyclodextrin polymer to evaluate its selective cytotoxicity in several types of human cancer cell lines including MCF-7, AGS, A549, and PC3. The Lawson-loaded β-cyclodextrin nanocarriers (LB-NCs) were produced by applying a high-energy ultrasound-mediated homogenization technique. The LB-NCs were characterized by applying dynamic light scattering (DLS), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), zeta potential, and field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) analysis. Also, the selective cytotoxic impact of the LB-NCs was studied by conducting the MTT assay on human MCF-7, AGS, A549, and PC3 cancer cell lines. Finally, the type of cellular death was evaluated by measuring the cell cycle status and apoptotic gene expression profile of the treated MCF-7 cells by conducting flow cytometry and Q-PCR methods, respectively. The synthesized negatively charged (− 23.8 mV) nanoparticles (348.12 nm) exhibited apoptotic activity in the human breast MCF-7 cancer cells by upregulating the apoptotic gene expression profile (Caspase 3, 8, and 9). The LB-NCs exhibited a significant selective cytotoxic effect on the human cancer cell lines compared with the normal HUVEC cells. However, variable toxic intensities were detected depending on the cancer cell type. Selective cancer cell-depended anticancer activity of the produced LB-NCs has the potential to be considered their safe efficient targeted anticancer activity. However, studying the animal cancer models has to be conducted to verify their selective toxicity and clarify the cellular death mechanism.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Alagheband Y et al (2022) Design and fabrication of a dual-drug loaded nano-platform for synergistic anticancer and cytotoxicity effects on the expression of leptin in lung cancer treatment. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 73:103389
Alam J et al (2022) Curcumin encapsulated into biocompatible co-polymer PLGA nanoparticle enhanced anti-gastric cancer and anti-Helicobacter Pylori effect. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev APJCP 23(1):61
Archontaki H, Vertzoni M, Athanassiou-Malaki M (2002) Study on the inclusion complexes of bromazepam with β-and β-hydroxypropyl-cyclodextrins. J Pharm Biomed Anal 28(3–4):761–769
Arima H et al (1998) Enhancing effect of hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin on cutaneous penetration and activation of ethyl 4-biphenylyl acetate in hairless mouse skin. Eur J Pharm Sci 6(1):53–59
Arima H et al (2001) Comparative studies of the enhancing effects of cyclodextrins on the solubility and oral bioavailability of tacrolimus in rats. J Pharm Sci 90(6):690–701
Asadi M et al (2018) Expression level of caspase genes in colorectal cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev APJCP 19(5):1277
Azar LK et al (2022) Design and development of nanostructured co delivery of artemisinin and chrysin for targeting hTERT gene expression in breast cancer cell line: possible clinical application in cancer treatment. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev APJCP 23(3):919
Baca JM et al (2022) Cells electric charge analyses define specific properties for cancer cells activity. Bioelectrochemistry 144:108028
Barani M et al (2018) Lawsone-loaded Niosome and its antitumor activity in MCF-7 breast cancer cell line: a nano-herbal treatment for cancer. DARU J Pharm Sci 26:11–17
Chang Y-L et al (2017) Theophylline exhibits anti-cancer activity via suppressing SRSF3 in cervical and breast cancer cell lines. Oncotarget 8(60):101461
Chen Z, Wu D (2014) Monodisperse BSA-conjugated zinc oxide nanoparticles based fluorescence sensors for Cu2+ ions. Sens Actuators B Chem 192:83–91
Gadade DD, Pekamwar SS (2020) Cyclodextrin based nanoparticles for drug delivery and theranostics. Adv Pharm Bull 10(2):166
Ghafaripour H et al (2023) Lawsone encapsulated polylactic-co-glycolic acid nanoparticles modified with chitosan-folic acid successfully inhibited cell growth and triggered apoptosis in Panc-1 cancer cells. IET Nanobiotechnol 17(5):425–437
Hashemy SI, Seyedi SMR (2021) ROS impacts on cell cycle checkpoint signaling in carcinogenesis. Handbook of oxidative stress in cancer: mechanistic aspects. Springer, Singapore, pp 1–19
Hassani N et al (2022) The effect of dual bioactive compounds artemisinin and metformin co-loaded in PLGA-PEG nano-particles on breast cancer cell lines: potential apoptotic and anti-proliferative action. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 194(10):4930–4945
Hazell S et al (2020) Financial toxicity in lung cancer: an assessment of magnitude, perception, and impact on quality of life. Ann Oncol 31(1):96–102
Herdiana Y et al (2021) Chitosan-based nanoparticles of targeted drug delivery system in breast cancer treatment. Polymers 13(11):1717
Hussain A et al (2020) Metallodrug-driven combination chemotherapy in cancer treatment. Combination therapy against multidrug resistance. Elsevier, Academic Press, pp 95–110
Iqbal H et al (2021) Breast cancer inhibition by biosynthesized titanium dioxide nanoparticles is comparable to free doxorubicin but appeared safer in BALB/c mice. Materials 14(12):3155
Iqbal H et al (2022) pH-responsive albumin-coated biopolymeric nanoparticles with lapatinab for targeted breast cancer therapy. Biomater Adv 139:213039
Jafari-Gharabaghlou D et al (2023) Potentiation of folate-functionalized PLGA-PEG nanoparticles loaded with metformin for the treatment of breast cancer: possible clinical application. Mol Biol Rep 50(4):3023–3033
Jiang H et al (2023) Drug-induced oxidative stress in cancer treatments: angel or devil? Redox Biol 63:102754
Jin L et al (2018) Breast cancer lung metastasis: molecular biology and therapeutic implications. Cancer Biol Ther 19(10):858–868
Kannan K, Jain SK (2000) Oxidative stress and apoptosis. Pathophysiology 7(3):153–163
Khatamian N et al (2022) Pinus morrisonicola needles essential oil nanoemulsions as a novel strong antioxidant and anticancer agent. Inorg Nano-Metal Chem 52(2):253–261
Kimchy AV et al (2022) Breast cancer metastasis to the gastrointestinal tract with unusual endoscopic and histologic presentations. ACG Case Rep J 9(12):e00938
Li H et al (2023) β-cyclodextrin-based nanosponges for crocetin delivery: physicochemical characterization, aqueous solubility, and bioactivity. J Mol Liq 83:122235
Liu Y et al (2023) Formation of pre-metastatic niches induced by tumor extracellular vesicles in lung metastasis. Pharmacol Res 188:106669
Long J et al (2024) Combating multidrug resistance of breast cancer with ginsenoside Rh2-irrigated nano-in-thermogel. Int J Pharm 650:123718
McMillan DC et al (2004) Role of oxidant stress in lawsone-induced hemolytic anemia. Toxicol Sci 82(2):647–655
Moshfegh A et al (2019) Phytochemical analysis, antioxidant, anticancer and antibacterial properties of the Caspian Sea red macroalgae, Laurencia caspica. Iran J Sci Technol Trans A Sci 43:49–56
Perlikos F, Harrington KJ, Syrigos KN (2013) Key molecular mechanisms in lung cancer invasion and metastasis: a comprehensive review. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 87(1):1–11
Peters JM, Gonzalez FJ (2018) The evolution of carcinogenesis. Toxicol Sci 165(2):272–276
Pourgholi A et al (2021) Anticancer potential of silibinin loaded polymeric nanoparticles against breast cancer cells: insight into the apoptotic genes targets. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev APJCP 22(8):2587
Rachmawati H, Edityaningrum CA, Mauludin R (2013) Molecular inclusion complex of curcumin–β-cyclodextrin nanoparticle to enhance curcumin skin permeability from hydrophilic matrix gel. AAPS PharmSciTech 14:1303–1312
Ravichandran R (2009) Nanoparticles in drug delivery: potential green nanobiomedicine applications. Int J Green Nanotechnol Biomed 1(2):B108–B130
Real DA et al (2021) Cyclodextrin-modified nanomaterials for drug delivery: classification and advances in controlled release and bioavailability. Pharmaceutics 13(12):2131
Rogovskii VS (2022) The therapeutic potential of urolithin A for cancer treatment and prevention. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 22(9):717–724
Saadaoui S et al (2017) Performance of natural-dye-sensitized solar cells by ZnO nanorod and nanowall enhanced photoelectrodes. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 8(1):287–295
Sadeghzadeh F et al (2023) In vitro and in vivo study on the anticancer effects of anethole-loaded bovine serum albumin nanoparticles surface decorated with chitosan and folic acid. Cancer Nanotechnol 14(1):24
Seyedi SMR, Asoodeh A, Darroudi M (2022) The human immune cell simulated anti-breast cancer nanorobot: the efficient, traceable, and dirigible anticancer bio-bot. Cancer Nanotechnol 13(1):1–24
Shen X et al (2020) PLGA-based drug delivery systems for remotely triggered cancer therapeutic and diagnostic applications. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 8:381
Soltani M et al (2015a) Transcriptional analysis of VEGF-D and TGFβ genes in MCF7 cells exposed to saponin isolated from Holothuria leucospilota (sea cucumber). Rep Biochem Mol Biol 4(1):25
Soltani M et al (2015b) Putative mechanism for apoptosis-inducing properties of crude saponin isolated from sea cucumber (Holothuria leucospilota) as an antioxidant compound. Iran J Basic Med Sci 18(2):180
Stetefeld J, McKenna SA, Patel TR (2016) Dynamic light scattering: a practical guide and applications in biomedical sciences. Biophys Rev 8(4):409–427
Vaquero-Siguero N et al (2022) Modeling colorectal cancer progression reveals niche-dependent clonal selection. Cancers 14(17):4260
Veisi A et al (2020) Role of crocin in several cancer cell lines: an updated review. Iran J Basic Med Sci 23(1):3
Vysyaraju NR et al (2022) Olaparib@ human serum albumin nanoparticles as sustained drug-releasing tumour-targeting nanomedicine to inhibit growth and metastasis in the mouse model of triple-negative breast cancer. J Drug Target 30(10):1088–1105
Wang W, Zou W (2020) Amino acids and their transporters in T cell immunity and cancer therapy. Mol Cell 80(3):384–395
Wang J et al (2021) Preparation of nanoparticles of β-cyclodextrin-loaded scutellarein anti-tumor activity research by targeting integrin α v β3. Cancer Nanotechnol 12:1–15
Wang Y et al (2023) Albumin-based nanodevices for breast cancer diagnosis and therapy. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 79:104072
Wilken R et al (2011) Curcumin: a review of anti-cancer properties and therapeutic activity in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Cancer 10(1):1–19
Wongsa P, Phatikulrungsun P, Prathumthong S (2022) FT-IR characteristics, phenolic profiles and inhibitory potential against digestive enzymes of 25 herbal infusions. Sci Rep 12(1):6631
Yasamineh S et al (2022) An overview on nanoparticle-based strategies to fight viral infections with a focus on COVID-19. J Nanobiotechnol 20(1):1–26
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Islamic Azad University, Tehran, Iran, and therefore is appreciated by the author.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ali Kadhim Alwan Alboabdullah: Methodology, Investigation and Writing-Original draft. Mohammad Taghi Goodarzi and Masoud Homayouni Tabrizi: Supervision, Data curation, Conceptualization, Validation and Writing- Reviewing and Editing. The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Alboabdullah, A.K.A., Goodarzi, M.T. & Homayouni Tabrizi, M. The Lawson-loaded β-cyclodextrin nanocarriers (LB-NCs) a novel targeted cancer cell in stomach and breast cancer as a drug delivery system. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-024-03042-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-024-03042-6