Abstract
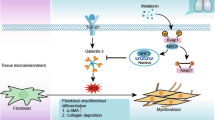
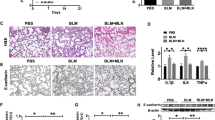
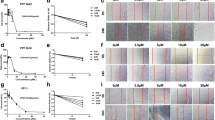
Pulmonary fibrosis (PF) is a devastating lung disease that leads to impaired lung function and ultimately death. Several studies have suggested that melatonin, a hormone involved in regulating sleep–wake cycles, may be effective in improving PF. Ramelteon, an FDA-approved melatonin receptor agonist, has shown promise in exerting an anti-PF effect similar to melatonin. However, further investigations are required for illuminating the extent on its therapeutic benefits and the underlying molecular mechanisms. In this work, a mouse lung fibrosis model was built through intratracheal administration of bleomycin (BLM). Subsequently, the mice were administrated Ramelteon for a duration of 3 weeks to explore its efficacy and mechanism of action. Additionally, we utilized a TGF-β1-induced MRC-5 cell model to further investigate the molecular mechanism underlying ramelteon’s effects. Functionally, Ramelteon partially abrogated TGF-β1-induced pulmonary fibrosis and reduced fibroblast proliferation, extracellular matrix deposition, and differentiation into myofibroblasts. In vivo experiments, ramelteon attenuated BLM-induced pulmonary fibrosis and collagen deposition. Mechanistically, ramelteon exerts its beneficial effect by alleviating translocation and expression of YAP1, a core component of Hippo pathway, from cytoplasm to nucleus; however, overexpression of YAP1 reversed this effect. In conclusion, our findings indicate that ramelteon can improve PF by regulating Hippo pathway and may become a potential candidate as a therapy to PF.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Amati F, Stainer A, Polelli V, Mantero M, Gramegna A, Blasi F, Aliberti S (2023) Efficacy of pirfenidone and nintedanib in interstitial lung diseases other than idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a systematic review. Int J Mol Sci 24(18):7849
Armagan I, Asci H, Erzurumlu Y, Ozkula S, Hasseyid N, Doguc DK, Okuyucu G, Varel A (2023) Ramelteon and mechanism of its restorative effect in an experimental lung disease model. Toxicol Mech Method 33:239–247
Bian FH, Lan YW, Zhao SY, Deng ZC, Shukla S, Acharya A, Donovan J, Le T, Milewski D, Bacchetta M, Hozain AE, Tipograf Y, Chen YW, Xu Y, Shi DL, Kalinichenko VV, Kalin TV (2023) Lung endothelial cells regulate pulmonary fibrosis through FOXF1/R-Ras signaling. Nat. Commun 14(20):2560
Buysse D, Bate G, Kirkpatrick P (2005) Fresh from the pipeline: Ramelteon. Nat Rev Drug Discov 4:881–882
Chen YZ, Zhao XG, Sun J, Su W, Zhang L, Li YN, Liu YQ, Zhang LJ, Lu YJ, Shan HL, Liang HH (2019) YAP1/Twist promotes fibroblast activation and lung fibrosis that conferred by miR-15a loss in IPF. Cell Death Differ 26:1832–1844
Cuesta VMM, Fernandez DI, Ibanez SA, de Francisco GA, Iribarnegaray JM, Hernandez-Rubio JC, Mezquida JPR, Luz VP, Hernandez RL, Gafas AD, Jover AS, Martinez JMC (2022) Antifibrotics and lung transplantation: a Spanish multicentre case-controlled study. Respirology 27:1054–1063
Ghaderi A, Okhovat MA, Lehto J, De Petris L, Doulabi EM, Kokhaei P, Zhong W, Rassidakis GZ, Drakos E, Moshfegh A, Schultz J, Olin T, Osterborg A, Mellstedt H, Hojjat-Farsangi M (2023) A small molecule targeting the intracellular tyrosine kinase domain of ROR1 (KAN0441571C) induced significant apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) Cells. Pharmaceutics 15(16):1148
Haak AJ, Ducharme MT, Diaz Espinosa AM, Tschumperlin DJ (2020) Targeting GPCR signaling for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis therapies. Trends Pharmacol Sci 41:172–182
Huang LS, Sudhadevi T, Fu PF, Punathil-Kannan PK, Ebenezer DL, Ramchandran R, Putherickal V, Cheresh P, Zhou G, Ha AW, Harijith A, Kamp DW, Natarajan V (2020) Sphingosine kinase 1/S1P signaling contributes to pulmonary fibrosis by activating Hippo/YAP pathway and mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in lung fibroblasts. Int J Mol Sci 21:2064
Lan YJ, Cheng MH, Ji HM, Bi YQ, Han YY, Yang CY, Gu X, Gao J, Dong HL (2023) Melatonin ameliorates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis via activating NRF2 and inhibiting galectin-3 expression. Acta Pharmacol Sin 44:1029–1037
Li XY, Zhang F, Qu LL, Xie Y, Ruan YN, Guo ZW, Mao YW, Zou Q, Shi MJ, Xiao Y, Wang YY, Zhou YX, Guo B (2021) Identification of YAP1 as a novel downstream effector of the FGF2/STAT3 pathway in the pathogenesis of renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis. J Cell Physiol 236:7655–7671
Li TY, Su W, Li LL, Zhao XG, Yang N, Gai JX, Lv X, Zhang J, Huang MQ, Zhang Q, Ji WH, Song XY, Zhou YH, Li XL, Shan HL, Liang HH (2022) Critical role of PAFR/YAP1 positive feedback loop in cardiac fibrosis. Acta Pharmacol Sin 43:2862–2872
Liu YL, Wang LX, Du N, Yin XL, Shao HT, Yang L (2021) Ramelteon ameliorates LPS-induced hyperpermeability of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) by activating Nrf 2. Inflammation 44:1750–1761
Liu YY, Chen SY, Yu L, Deng Y, Li DF, Yu X, Chen DD, Lu Y, Liu SM, Chen RC (2022) Pemafibrate attenuates pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting myofibroblast differentiation. Int Immunopharmacol 108:108728
Luo JH, Zhang ZG, Sun HQ, Song J, Chen XZ, Huang JX, Lin XP, Zhou RX (2020) Effect of melatonin on T/B cell activation and immune regulation in pinealectomy mice. Life Sci 242:117191
Martinez FJ, Collard HR, Pardo A, Raghu G, Richeldi L, Selman M, Swigris JJ, Taniguchi H, Wells AU (2017) Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers 3:17074
Mia MM, Singh MK (2022) New insights into Hippo/YAP signaling in fibrotic diseases. Cells-Basel 11:2065
Miyamoto M (2009) Pharmacology of Ramelteon, a selective MT1/MT2 receptor agonist: a novel therapeutic drug for sleep disorders. Cns Neurosci Ther 15:32–51
Nambara S, Masuda T, Nishio M, Kuramitsu S, Tobo T, Ogawa Y, Hu QJ, Iguchi T, Kuroda Y, Ito S, Eguchi H, Sugimachi K, Saeki H, Oki E, Maehara Y, Suzuki A, Mimori K (2017) Antitumor effects of the antiparasitic agent ivermectin via inhibition of Yes-associated protein 1 expression in gastric cancer. Oncotarget 8:107666–107677
Pandi-Perumal SR, Seils LK, Kayumov L, Ralph MR, Lowe A, Moller H, Swaab DF (2002) Senescence, sleep, and circadian rhythms. Ageing Res Rev 1:559–604
Salloum S, Jeyarajan AJ, Kruger AJ, Holmes JA, Shao T, Sojoodi M, Kim MH, Zhuo Z, Shroff SG, Kassa A, Corey KE, Khan SK, Lin WY, Alatrakchi N, Schaefer EAK, Chung RT (2021) Fatty acids activate the transcriptional goactivator YAP1 to promote liver fibrosis via p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. Cell Mol Gastroenter 12:1297–1310
Sateia MJ, Kirby-Long P, Taylor JL (2008) Efficacy and clinical safety of ramelteon: an evidence-based review. Sleep Med Rev 12:319–332
Shochet GE, Bardenstein-Wald B, McElroy M, Kukuy A, Surber M, Edelstein E, Pertzov B, Kramer MR, Shitrit D (2021) Hypoxia inducible factor 1A supports a pro-fibrotic phenotype loop in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Int J Mol Sci 22:3331
Stroethoff M, Christoph I, Behmenburg F, Raupach A, Bunte S, Senpolat S, Heinen A, Hollmann MW, Mathes A, Huhn R (2018) Melatonin receptor agonist Ramelteon reduces ischemia-reperfusion injury through activation of mitochondrial potassium channels. J Cardiovasc Pharm 72:106–111
Sun J, Jin TZ, Niu ZH, Guo JY, Guo YY, Yang RX, Wang QQ, Gao HY, Zhang YH, Li TY, He WX, Li ZX, Ma WC, Su W, Li LL, Fan XX, Shan HL, Liang HH (2022) LncRNA DACH1 protects against pulmonary fibrosis by binding to SRSF1 to suppress CTNNB1 accumulation. Acta Pharm Sin B 12:3602–3617
Wang XP, Wang GY, Qu JW, Yuan ZQ, Pan RG, Li KW (2020) Calcipotriol inhibits NLRP3 signal through YAP1 activation to alleviate cholestatic liver injury and fibrosis. Front Pharmacol 11:200
Wu XL, Lu SS, Liu MR, Tang WD, Chen JZ, Zheng YR, Ahsan A, Cao M, Jiang L, Hu WW, Wu JY, Chen Z, Zhang XN (2020a) Melatonin receptor agonist ramelteon attenuates mouse acute and chronic ischemic brain injury. Acta Pharmacol Sin 41:1016–1024
Wu GC, Peng CK, Liao WI, Pao HP, Huang KL, Chu SJ (2020b) Melatonin receptor agonist protects against acute lung injury induced by ventilator through up-regulation of IL-10 production. Resp Res 21:65
Yang WJ, Zhang Y, Lu DH, Huang TF, Yan KS, Wang WW, Gao J (2022) Ramelteon protects against human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cell injury induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) via activating nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)/heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) pathway. Bioengineered 13:1518–1529
Yu FX, Zhao B, Panupinthu N, Jewell JL, Lian I, Wang LH, Zhao JG, Yuan HX, Tumaneng K, Li HR, Fu XD, Mills GB, Guan KL (2012) Regulation of the Hippo-YAP pathway by G-protein-coupled receptor signaling. Cell 150:780–791
Zhan P, Lu X, Li Z, Wang WJ, Peng K, Liang NN, Wang Y, Li J, Fu L, Zhao H, Xu DX, Tan ZX (2022) Mitoquinone alleviates bleomycin-induced acute lung injury via inhibiting mitochondrial ROS-dependent pulmonary epithelial ferroptosis. Int. Immunopharmacol 113(10):109359
Zhang HM, Zhang YQ (2014) Melatonin: a well-documented antioxidant with conditional pro-oxidant actions. J Pineal Res 57:131–146
Zhao XG, Sun J, Su W, Shan HT, Zhang BW, Wang YN, Shabanova A, Shan HL, Liang HH (2018a) Melatonin protects against lung fibrosis by regulating the Hippo/YAP pathway. Int J Mol Sci 19:1118
Zhao XG, Sun J, Chen YZ, Su W, Shan HT, Li Y, Wang YN, Zheng N, Shan HL, Liang HH (2018b) lncRNA PFAR promotes lung fibroblast activation and fibrosis by targeting miR-138 to regulate the YAP1-Twist axis. Mol Ther 26:2206–2217
Zheng YG, Pan DJ (2019) The Hippo signaling pathway in development and disease. Dev Cell 50:264–282
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Shenzhen University Health Science Center for instrumental support.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U21A20339, 32171127) and the Outstanding Youth Scientific Fund Project of Heilongjiang Province (JQ2022H001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Haihai Liang and Lei Zhang conceived and designed the study. Lei Zhang performed cell experiments, analyzed the data. Ting Cheng was involved in the animal and cell experiments. Wenxian Chen, Changsheng Zhong, and Mengyang Li assisted the animal experiments. Yilin Xie assisted the cell experiments. Qin Deng and Huifang Wang assisted some Immunohistochemistry experiments. Zhenbo Yang and Jin Ju assisted some Western Blotting experiments. The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All animal experiments performed the standards of the Ethics Committee of the College of Pharmacy, Harbin Medical University (Ethical approval number: IRB3035621).
Competing interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Cheng, T., Chen, W. et al. Preventive effects of Ramelteon on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02867-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02867-x