Abstract
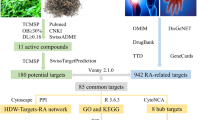
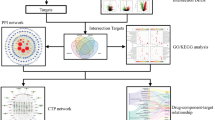
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that is associated with systemic complications. Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is the most common pulmonary complication and second leading cause of death in patients with RA. In this study, we used network pharmacology and experimental validation to identify the targets and pathways of quercetin (Que) in the treatment of RA-associated ILD (RA-ILD). A total of 32 potential targets of Que for RA-ILD treatment were screened from six databases, and 10 core targets were screened using protein–protein interaction network analysis. Gene Ontology (GO), Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analysis, and molecular docking were employed to explore the potential mechanisms of Que in RA-ILD treatment. The results suggested the IL-17 signaling pathway as an important pathway through which Que alleviates RA-ILD. Subsequently, LPS (1 µg/ml) was used to establish an inflammation model on RAW 264.7 cells, and different concentrations of Que (25, 50, and 100 µM) were used for intervention. Que significantly reduced the expression levels of IL-17, TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β in RAW 264.7 cells. Our findings suggest that Que alleviates RA-ILD by regulating the IL-17 signaling pathway and reducing inflammation.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the present study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Aumiller V, Balsara N, Wilhelm J, Gunther A, Konigshoff M (2013) WNT/beta-catenin signaling induces IL-1beta expression by alveolar epithelial cells in pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 49:96–104. https://doi.org/10.1165/rcmb.2012-0524OC
Baowen Q, Yulin Z, Xin W, Wenjing X, Hao Z, Zhizhi C et al (2010) A further investigation concerning correlation between anti-fibrotic effect of liposomal quercetin and inflammatory cytokines in pulmonary fibrosis. Eur J Pharmacol 642:134–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2010.05.019
Batiha GE, Beshbishy AM, Ikram M, Mulla ZS, El-Hack MEA, Taha AE et al (2020) The pharmacological activity, biochemical properties, and pharmacokinetics of the major natural polyphenolic flavonoid: quercetin. Foods 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9030374
Bilgici A, Ulusoy H, Kuru O, Celenk C, Unsal M, Danaci M (2005) Pulmonary involvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 25:429–435. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-004-0472-y
Ceylan H (2021) Identification of hub genes associated with obesity-induced hepatocellular carcinoma risk based on integrated bioinformatics analysis. Med Oncol 38:63. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-021-01510-0
Ceylan H (2022) Integrated bioinformatics analysis to identify alternative therapeutic targets for Alzheimer’s disease: insights from a synaptic machinery perspective. J Mol Neurosci 72:273–286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-021-01893-9
Chin CH, Chen SH, Wu HH, Ho CW, Ko MT, Lin CY (2014) cytoHubba: identifying hub objects and sub-networks from complex interactome. BMC Syst Biol 8(Suppl 4):S11. https://doi.org/10.1186/1752-0509-8-S4-S11
Cho ML, Yoon CH, Hwang SY, Park MK, Min SY, Lee SH et al (2004) Effector function of type II collagen-stimulated T cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients: cross-talk between T cells and synovial fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum 50:776–784. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.20106
Cutolo M, Soldano S, Montagna P, Sulli A, Seriolo B, Villaggio B et al (2009) CTLA4-Ig interacts with cultured synovial macrophages from rheumatoid arthritis patients and downregulates cytokine production. Arthritis Res Ther 11:R176. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar2865
d’Alessandro M, Perillo F, Metella Refini R, Bergantini L, Bellisai F, Selvi E et al (2020) Efficacy of baricitinib in treating rheumatoid arthritis: modulatory effects on fibrotic and inflammatory biomarkers in a real-life setting. Int Immunopharmacol 86:106748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106748
Dawson JK, Fewins HE, Desmond J, Lynch MP, Graham DR (2001) Fibrosing alveolitis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis as assessed by high resolution computed tomography, chest radiography, and pulmonary function tests. Thorax 56:622–627. https://doi.org/10.1136/thorax.56.8.622
Demir Y, Ceylan H, Turkes C, Beydemir S (2022) Molecular docking and inhibition studies of vulpinic, carnosic and usnic acids on polyol pathway enzymes. J Biomol Struct Dyn 40:12008–12021. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2021.1967195
Deng JL, Xu YH, Wang G (2019) Identification of potential crucial genes and key pathways in breast cancer using bioinformatic analysis. Front Genet 10:695. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2019.00695
Diesler R, Cottin V (2022) Pulmonary fibrosis associated with rheumatoid arthritis: from pathophysiology to treatment strategies. Expert Rev Respir Med 16:541–553. https://doi.org/10.1080/17476348.2022.2089116
Ding P, Liu J, Li Q, Lu Q, Li J, Shi R et al (2021) Investigation of the active ingredients and mechanism of hudi enteric-coated capsules in DSS-induced ulcerative colitis mice based on network pharmacology and experimental verification. Drug Des Devel Ther 15:4259–4273. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S326029
Du H, Zhang X, Zeng Y, Huang X, Chen H, Wang S et al (2019) A novel phytochemical, DIM, inhibits proliferation, migration, invasion and TNF-alpha induced inflammatory cytokine production of synovial fibroblasts from rheumatoid arthritis patients by targeting MAPK and AKT/mTOR signal pathway. Front Immunol 10:1620. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.01620
Fazeli MS, Khaychuk V, Wittstock K, Han X, Crocket G, Lin M et al (2021) Rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: epidemiology, risk/prognostic factors, and treatment landscape. Clin Exp Rheumatol 39:1108–1118. https://doi.org/10.55563/clinexprheumatol/h9tc57
Gao L, Cao M, Li JQ, Qin XM, Fang J (2021) Traditional Chinese medicine network pharmacology in cardiovascular precision medicine. Curr Pharm Des 27:2925–2933. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612826666201112142408
Habib HM, Eisa AA, Arafat WR, Marie MA (2011) Pulmonary involvement in early rheumatoid arthritis patients. Clin Rheumatol 30:217–221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-010-1492-5
Hohmann MS, Habiel DM, Coelho AL, Verri WA Jr, Hogaboam CM (2019) Quercetin enhances ligand-induced apoptosis in senescent idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis fibroblasts and reduces lung fibrosis in vivo. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 60:28–40. https://doi.org/10.1165/rcmb.2017-0289OC
Hyldgaard C, Hilberg O, Pedersen AB, Ulrichsen SP, Lokke A, Bendstrup E et al (2017) A population-based cohort study of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: comorbidity and mortality. Ann Rheum Dis 76:1700–1706. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-211138
Iqbal K, Kelly C (2015) Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: a perspective review. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis 7:247–267. https://doi.org/10.1177/1759720X15612250
Italiani P, Boraschi D (2014) From monocytes to M1/M2 macrophages: phenotypical vs. functional differentiation. Front Immunol 5:514. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2014.00514
Jakobsson PJ, Robertson L, Welzel J, Zhang M, Zhihua Y, Kaixin G et al (2022) Where traditional Chinese medicine meets Western medicine in the prevention of rheumatoid arthritis. J Intern Med 292:745–763. https://doi.org/10.1111/joim.13537
Juge PA, Lee JS, Lau J, Kawano-Dourado L, Rojas Serrano J, Sebastiani M et al (2021) Methotrexate and rheumatoid arthritis associated interstitial lung disease. Eur Respir J 57. https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.00337-2020
Kapellos TS, Iqbal AJ (2016) Epigenetic control of macrophage polarisation and soluble mediator gene expression during inflammation. Mediators Inflamm 2016:6591703. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/6591703
Kim GW, Lee NR, Pi RH, Lim YS, Lee YM, Lee JM et al (2015) IL-6 inhibitors for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: past, present, and future. Arch Pharm Res 38:575–584. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-015-0569-8
Kotake S, Udagawa N, Takahashi N, Matsuzaki K, Itoh K, Ishiyama S et al (1999) IL-17 in synovial fluids from patients with rheumatoid arthritis is a potent stimulator of osteoclastogenesis. J Clin Invest 103:1345–1352. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI5703
Li Y, Yao J, Han C, Yang J, Chaudhry MT, Wang S et al (2016) Quercetin, inflammation and immunity. Nutrients 8:167. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8030167
Li J, Wei Y, Li X, Zhu D, Nie B, Zhou J et al (2017) Herbal formula Xian-Fang-Huo-Ming-Yin regulates differentiation of lymphocytes and production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in collagen-induced arthritis mice. BMC Complement Altern Med 17:12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-016-1526-x
Li X, Bechara R, Zhao J, McGeachy MJ, Gaffen SL (2019) IL-17 receptor-based signaling and implications for disease. Nat Immunol 20:1594–1602. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-019-0514-y
Li Q, Liu Y, Yang M, Jin L, Wu Y, Tang L et al (2022) Mechanism of Radix Scutellariae in the treatment of influenza A based on network pharmacology and molecular docking. Ann Transl Med 10:351. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm-22-1176
Lipinski CA, Lombardo F, Dominy BW, Feeney PJ (2001) Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 46:3–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0169-409x(00)00129-0
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Lubberts E (2008) IL-17/Th17 targeting: on the road to prevent chronic destructive arthritis? Cytokine 41:84–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2007.09.014
Ma L, Lu H, Chen R, Wu M, Jin Y, Zhang J et al (2020) Identification of key genes and potential new biomarkers for ovarian aging: a study based on RNA-sequencing data. Front Genet 11:590660. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2020.590660
Mamani-Matsuda M, Kauss T, Al-Kharrat A, Rambert J, Fawaz F, Thiolat D et al (2006) Therapeutic and preventive properties of quercetin in experimental arthritis correlate with decreased macrophage inflammatory mediators. Biochem Pharmacol 72:1304–1310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2006.08.001
Massi A, Bortolini O, Ragno D, Bernardi T, Sacchetti G, Tacchini M et al (2017) Research progress in the modification of quercetin leading to anticancer agents. Molecules 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22081270
Migita K, Tsuji Y, Hisatomi K, Shigeno R, Izumi Y, Iwanaga N et al (2017) Acute exacerbation of rheumatoid interstitial lung disease during the maintenance therapy with certolizumab pegol. Mod Rheumatol 27:1079–1082. https://doi.org/10.3109/14397595.2015.1059008
Mori S, Cho I, Koga Y, Sugimoto M (2008) Comparison of pulmonary abnormalities on high-resolution computed tomography in patients with early versus longstanding rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 35:1513–1521
Morikawa K, Nonaka M, Narahara M, Torii I, Kawaguchi K, Yoshikawa T et al (2003) Inhibitory effect of quercetin on carrageenan-induced inflammation in rats. Life Sci 74:709–721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2003.06.036
Raza K, Falciani F, Curnow SJ, Ross EJ, Lee CY, Akbar AN et al (2005) Early rheumatoid arthritis is characterized by a distinct and transient synovial fluid cytokine profile of T cell and stromal cell origin. Arthritis Res Ther 7:R784-795. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar1733
Roubille C, Haraoui B (2014) Interstitial lung diseases induced or exacerbated by DMARDS and biologic agents in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic literature review. Semin Arthritis Rheum 43:613–626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semarthrit.2013.09.005
Ru J, Li P, Wang J, Zhou W, Li B, Huang C et al (2014) TCMSP: a database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines. J Cheminform 6:13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1758-2946-6-13
Shaw M, Collins BF, Ho LA, Raghu G (2015) Rheumatoid arthritis-associated lung disease. Eur Respir Rev 24:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1183/09059180.00008014
Shen P, Lin W, Deng X, Ba X, Han L, Chen Z et al (2021) Potential implications of quercetin in autoimmune diseases. Front Immunol 12:689044. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.689044
Shi MJ, Yan XL, Dong BS, Yang WN, Su SB, Zhang H (2020) A network pharmacology approach to investigating the mechanism of Tanshinone IIA for the treatment of liver fibrosis. J Ethnopharmacol 253:112689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2020.112689
Smolen JS, Schoels MM, Nishimoto N, Breedveld FC, Burmester GR, Dougados M et al (2013) Consensus statement on blocking the effects of interleukin-6 and in particular by interleukin-6 receptor inhibition in rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory conditions. Ann Rheum Dis 72:482–492. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202469
Spagnolo P, Distler O, Ryerson CJ, Tzouvelekis A, Lee JS, Bonella F et al (2021) Mechanisms of progressive fibrosis in connective tissue disease (CTD)-associated interstitial lung diseases (ILDs). Ann Rheum Dis 80:143–150. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-217230
Stewart LK, Soileau JL, Ribnicky D, Wang ZQ, Raskin I, Poulev A et al (2008) Quercetin transiently increases energy expenditure but persistently decreases circulating markers of inflammation in C57BL/6J mice fed a high-fat diet. Metabolism 57:S39-46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2008.03.003
Suganthy N, Devi KP, Nabavi SF, Braidy N, Nabavi SM (2016) Bioactive effects of quercetin in the central nervous system: focusing on the mechanisms of actions. Biomed Pharmacother 84:892–908. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2016.10.011
Terasaki Y, Terasaki M, Kanazawa S, Kokuho N, Urushiyama H, Kajimoto Y et al (2019) Effect of H(2) treatment in a mouse model of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. J Cell Mol Med 23:7043–7053. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14603
Turesson C, O’Fallon WM, Crowson CS, Gabriel SE, Matteson EL (2002) Occurrence of extraarticular disease manifestations is associated with excess mortality in a community based cohort of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 29:62–67
Wang L, Wang Z, Yang Z, Yang K, Yang H (2021a) Study of the active components and molecular mechanism of Tripterygium wilfordii in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Front Mol Biosci 8:664416. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2021.664416
Wang X, Wang ZY, Zheng JH, Li S (2021b) TCM network pharmacology: a new trend towards combining computational, experimental and clinical approaches. Chin J Nat Med 19:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1875-5364(21)60001-8
Xiang J, Cheng S, Feng T, Wu Y, Xie W, Zhang M et al (2016) Neotuberostemonine attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by suppressing the recruitment and activation of macrophages. Int Immunopharmacol 36:158–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2016.04.016
Xie Y, Mai CT, Zheng DC, He YF, Feng SL, Li YZ et al (2021) Wutou decoction ameliorates experimental rheumatoid arthritis via regulating NF-kB and Nrf2: integrating efficacy-oriented compatibility of traditional Chinese medicine. Phytomedicine 85:153522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153522
Xu J, Zhao Y, Aisa HA (2017) Anti-inflammatory effect of pomegranate flower in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages. Pharm Biol 55:2095–2101. https://doi.org/10.1080/13880209.2017.1357737
Xu D, Hu MJ, Wang YQ, Cui YL (2019) Antioxidant activities of quercetin and its complexes for medicinal application. Molecules 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061123
Yang Z, Han R, Yin H, Li J, Cao Y, Guo R et al (2022) Mechanism of Lycopodii herba for RA-ILD using integrated metabolomics and network pharmacology. Anal Biochem 648:114679. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2022.114679
Yap HY, Tee SZ, Wong MM, Chow SK, Peh SC, Teow SY (2018) Pathogenic role of immune cells in rheumatoid arthritis: implications in clinical treatment and biomarker development. Cells 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7100161
Yuan K, Zhu Q, Lu Q, Jiang H, Zhu M, Li X et al (2020) Quercetin alleviates rheumatoid arthritis by inhibiting neutrophil inflammatory activities. J Nutr Biochem 84:108454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2020.108454
Yue SJ, Liu J, Feng WW, Zhang FL, Chen JX, Xin LT et al (2017) System pharmacology-based dissection of the synergistic mechanism of Huangqi and Huanglian for diabetes mellitus. Front Pharmacol 8:694. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2017.00694
Zhan TW, Tian YX, Wang Q, Wu ZX, Zhang WP, Lu YB et al (2018) Cangrelor alleviates pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting GPR17-mediated inflammation in mice. Int Immunopharmacol 62:261–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2018.06.006
Zhang J, Wang D, Wang L, Wang S, Roden AC, Zhao H et al (2019) Profibrotic effect of IL-17A and elevated IL-17RA in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and rheumatoid arthritis-associated lung disease support a direct role for IL-17A/IL-17RA in human fibrotic interstitial lung disease. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 316:L487–L497. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.00301.2018
Zhang Q, Li X, Li J, Hu Y, Liu J, Wang F et al (2021a) Mechanism of anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects of QingXiaoWuWei Decoction based on network pharmacology, molecular docking and in vitro experiments. Front Pharmacol 12:678685. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.678685
Zhang Q, Liao Y, Liu Z, Dai Y, Li Y, Li Y et al (2021b) Interleukin-17 and ischaemic stroke. Immunology 162:179–193. https://doi.org/10.1111/imm.13265
Zheng Z, Guo M, Zhu W, Cheng W, Kong L, Liu Y et al (2022) Identification of JUN as determinant of osteoarthritis and its inhibition by the Chinese herbal formulae Zhuanggu Huoxue Tang. Comput Biol Med 148:105786. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105786
Zhou Y, Zhou B, Pache L, Chang M, Khodabakhshi AH, Tanaseichuk O et al (2019) Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets. Nat Commun 10:1523. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09234-6
Ziolkowska M, Koc A, Luszczykiewicz G, Ksiezopolska-Pietrzak K, Klimczak E, Chwalinska-Sadowska H et al (2000) High levels of IL-17 in rheumatoid arthritis patients: IL-15 triggers in vitro IL-17 production via cyclosporin A-sensitive mechanism. J Immunol 164:2832–2838. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.164.5.2832
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82074358) and the Postgraduate Research and Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (KYCX22_1947).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jing Wang and Zhichao Wang conceptualization, conceptualized and designed the project, performed the experiments, and wrote the manuscript. Yang Zhao and Le Bai provided technical support. Yun Wei and Tongxing Huang revised revisions of the manuscript. Xianmei Zhou and Yong Xu supervised the study. The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Wang, Z., Zhao, Y. et al. Molecular mechanism of quercetin in treating RA-ILD based on network pharmacology, molecular docking, and experimental validation. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 397, 3077–3092 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02772-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02772-3