Abstract
Intravenous lipid emulsion (ILE) has been widely used as an effective antidote in both veterinary and human medicine for the treatment of acute intoxications caused by drugs and pesticides with high lipid solubility. This study was conducted to investigate the effect of ILE co-administration on the kinetic dispositions of ivermectin (IVM) and carprofen (CRP) following intravenous bolus administration at subtoxic doses in rabbits.
Twenty-four male New Zealand rabbits weighing 2.78 ± 0.2 kg were used in this study. Rabbits were divided into four groups (Group 1: IVM and Group 2: IVM + ILE or Group 3: CRP and Group 4: CRP + ILE), each group consisting of 6 animals. In the IVM study, Group 1 received IVM (0.6 mg/kg) alone while Group 2 received IVM (0.6 mg/kg) and ILE (2.5 ml/kg). In the CRP study, Group 3 received CRP (12 mg/kg) alone while Group 4 received CRP (12 mg/kg) and ILE (2.5 ml/kg). In both drug groups, ILE was administered 3 times as an i.v. bolus at the 10th min and repeated 4th and 8th h after the drug administration. Blood samples were collected from the auricular vein at various times after drug administration. The drug concentrations in plasma samples were determined by high-pressure liquid chromatography. Kinetic parameters were calculated using a non-compartmental model for both CRP and IVM.
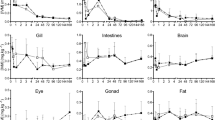
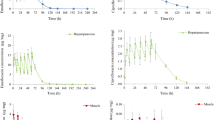
The C0 and area under the concentration–time curve from zero up to ∞ (AUC0–∞) values were significantly greater with ILE co-administration (2136 ng/ml and 360.84 ng.d/ml) compared to the IVM alone (1340.63 ng/ml and 206 ng.d/ml), respectively. Moreover, the volume of distribution (Vdss) and clearance (Cl) of IVM were reduced by approximately 42% and 46% with ILE co-administration compared to IVM alone resulting in a reduction of the distribution and slower elimination, respectively. Similar differences in C0, and Vdss values were also observed in CRP with ILE co-administration compared to CRP alone. ILE co-administration changed significantly the kinetic profile of both IVM and CRP in rabbits, supporting the lipid sink theory in which highly lipid-soluble compounds are absorbed into the lipid phase of plasma from peripheral organs such as the heart and brain affected by the acute toxicity of the compounds.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
This paper was summarized from the PhD thesis dissertation of Mrs. Busra Aslan Akyol at Balikesir University.
References
Anastassiades M, Lehotay SJ, Štajnbaher D, Schenck FJ (2003) Fast and easy multiresidue method employing acetonitrile extraction/partitioning and “dispersive solid-phase extraction” for the determination of pesticide residues in produce. J AOAC Int 86:412–431. https://doi.org/10.1093/jaoac/86.2.412
Armstrong S, Tricklebank P, Lake A, Frean S, Lees P (1999) Pharmacokinetics of carprofen enantiomers in equine plasma and synovial fluid–a comparison with ketoprofen. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 22:196–201. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2885.1999.00202.x
Bischoff K, Smith MC, Stump S (2014) Treatment of pieris ingestion in goats with intravenous lipid emulsion. J Med Toxicol 10:411–414. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13181-014-0426-z
Bosch L, Bersenas AM, Bateman S (2018) Acute polyneuromyopathy with respiratory failure secondary to monensin intoxication in a dog. J Vet Emerg Crit Care 28:62–68. https://doi.org/10.1111/vec.12684
Bramante CT, Huling JD, Tignanelli CJ, Buse J, Liebovitz DM, Nicklas JM, Cohen K, Puskarich MA, Belani HK, Proper JF, Siegel LK, Klatt NR, Odde DJ, Luke DG, Anderson B, Karger AB, Ingraham NE, Hartman KM, Rao V, Hagen AA, Patel B, Fenno SL, Avula N, Reddy NV, Erickson SM, Lindberg S, Fricton R, Lee S, Zaman A, Saveraid HG, Tordsen WJ, Pullen MF, Biros M, Sherwood NE, Thompson JL, Boulware DR, Murray A (2022) Randomized trial of metformin, ivermectin, and fluvoxamine for Covid-19. N Engl J Med 387:599–610. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2201662
Bruenisholz H, Kupper J, Muentener CR, Dally A, Kraemer T, Naegeli H, Schwarzwald CC (2012) Treatment of ıvermectin overdose in a miniature shetland pony using ıntravenous administration of a lipid emulsion. J Vet Intern Med 26:407–411. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1939-1676.2011.00865.x
Caly L, Druce JD, Catton MG, Jans DA, Wagstaff KM (2020) The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro. Antiviral Res 178:104787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104787
Cavana P, Iuliano A, Cagnotti G (2020) Use of intravenously lipid emulsion for treatment of baclofen toxicosis in a cat. Pak Vet J 40:133-135. https://doi.org/10.29261/pakvetj/2019.123
Cave G, Harvey MG (2014) Should we consider the infusion of lipid emulsion in the resuscitation of poisoned patients? Crit Care 18:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-014-0457-5
Chumbler NS, Schildt JC, Mawby DI, Papich MG (2020) Use of intravenous lipid therapy in a cat with carprofen overdose. Clin Case Rep 8:653–657. https://doi.org/10.1002/ccr3.2772
Ciechanowicz S, Patil V (2012) Intravenous lipid emulsion – rescued at LAST. Br Dent J 212:237–241. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bdj.2012.187
Clarke DL, Lee JA, Murphy LA, Reineke EL (2011) Use of intravenous lipid emulsion to treat ivermectin toxicosis in a Border Collie. J Am Vet Med Assoc 239:1328–1333. https://doi.org/10.2460/javma.239.10.1328
Curry SL, Cogar SM, Cook JL (2005) Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs: a review. J Am Anim Hosp Assoc 41:298–309. https://doi.org/10.5326/0410298
DailyMed (2022) Stromectol-ıvermectin tablet. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/DailyMed-STROMECTOL-ivermectin tablet (nih.gov). Accessed 19 June 2023
DeMel D, Gleeson M, Schachterle K, Thomer A (2022) Successful treatment of ivermectin overdose in a bearded dragon (Pogona vitticeps) using gastric lavage and intravenous lipid emulsion. J Vet Emerg Crit Care 32:680–684. https://doi.org/10.1111/vec.13218
DrugBank (2023a) Drugbank online: carprofen. https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB00821. Accessed 19 June 2023
DrugBank (2023b) Drugbank online: ivermectin. https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB00602. Accessed 19 June 2023
Ellsworth H, Stellpflug SJ, Cole JB, Dolan JA, Harris CR (2013) A Life-Threatening flecainide overdose treated with ıntravenous fat emulsion. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 36:87–89. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-8159.2012.03485.x
Enokiya T, Zhang E, Ikemura K, Muraki Y, Iwashita Y, Iwamoto T, Imai H, Maruyama K, Okuda M (2017) Effect of lipid emulsion infusion on paliperidone pharmacokinetics in the acute overdose rat model: a potential emergency treatment for paliperidone intoxication. Eur J Pharm Sci 109:217–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2017.08.010
Escajeda JT, Katz KD, Rittenberger JC (2015) Successful treatment of metoprolol-induced cardiac arrest with high-dose insulin, lipid emulsion, and ECMO. Am J Emerg Med 33:1111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajem.2015.01.012
Farah R, Kazzi Z, Brent J, Burkhart K, Wax P, Aldy K, Toxicology ınvestigators consortium FACT study group (2022) ıvermectin associated adverse events in the treatment and prevention of COVID-19 reported to the FACT pharmacovigilance project. Clin Toxicol 60:942-946. https://doi.org/10.1080/15563650.2022.2070187
Fernandez AL, Lee JA, Rahilly L, Hovda L, Brutlag AG, Engebretsen K (2011) The use of intravenous lipid emulsion as an antidote in veterinary toxicology. J Vet Emerg Crit Care 21:309–320. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-4431.2011.00657.x
Fettiplace MR, Pichurko AB (2021) Heterogeneity and bias in animal models of lipid emulsion therapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Toxicol 59:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1080/15563650.2020.1814316
Finn SDH, Uncles DR, Willers J, Sable N (2009) Early treatment of a quetiapine and sertraline overdose with Intralipid®. Anaesthesia 64:191–194. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2044.2008.05744.x
Foster RT, Jamali F (1987) High-performance liquid chromatographic assay of ketoprofen enantiomers in human plasma and urine. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 416:388–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-4347(87)80525-X
French D, Smollin C, Ruan W, Wong A, Drasner K, Wu AH (2011) Partition constant and volume of distribution as predictors of clinical efficacy of lipid rescue for toxicological emergencies. Clin Toxicol 49:801–809. https://doi.org/10.3109/15563650.2011.617308
Ghezzi P, Melillo G, Meazza C, Sacco S, Pellegrini L, Asti C, Porzio S, Marullo A, Sabbatini V, Caselli G, Bertini R (1998) Differential contribution of R and S ısomers in ketoprofen anti-inflammatory activity: role of cytokine modulation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 287:969–974
Gokbulut C, Nolan AM, McKellar QA (2001) Plasma pharmacokinetics and faecal excretion of ivermectin, doramectin and moxidectin following oral administration in horses. Equine Vet J 33:494–498. https://doi.org/10.2746/042516401776254835
Goodrich LR, Nixon AJ (2006) Medical treatment of osteoarthritis in the horse–a review. Vet J 171:51–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tvjl.2004.07.008
Hartmann T, Schmitt J (2004) Lipophilicity–beyond octanol/water: a short comparison of modern technologies. Drug Discov Today Technol 1:431–439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ddtec.2004.10.006
Harvey M, Cave G, Hoggett K (2009) Correlation of plasma and peritoneal diasylate clomipramine concentration with hemodynamic recovery after intralipid infusion in rabbits. Acad Emerg Med 16:151–156. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1553-2712.2008.00313.x
Heinonen JA, Litonius E, Salmi T, Haasio J, Tarkkila P, Backman JT, Rosenberg PH (2015) Intravenous lipid emulsion given to volunteers does not affect symptoms of lidocaine brain toxicity. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 116:378–383. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcpt.12321
Herring JM, McMichael MA, Corsi R, Wurlod V (2015) Intravenous lipid emulsion therapy in three cases of canine naproxen overdose. J Vet Emerg Crit Care 25:672–678. https://doi.org/10.1111/vec.12307
Jourdan G, Boyer G, Raymond-Letron I, Bouhsira E, Bedel B, Verwaerde P (2015) Intravenous lipid emulsion therapy in 20 cats accidentally overdosed with ivermectin. J Vet Emerg Crit Care 25:667–671. https://doi.org/10.1111/vec.12371
Kidwell JH, Buckley GJ, Allen AE, Bandt C (2014) Use of IV lipid emulsion for treatment of ivermectin toxicosis in a cat. J Am Anim Hosp Assoc 50:59–61. https://doi.org/10.5326/JAAHA-MS-5951
Krolewiecki A, Lifschitz A, Moragas M, Travacio M, Valentini R, Alonso DF, Solari R, Tinelli MA, Cimino RO, Alvarez L, Fleitas PE, Ceballos L, Golemba M, Fernandez F, Oliveira DF, Astudillo G, Baeck I, Farina J, Cardama GA, Mangano A, Spitzer E, Gold S, Lanusse C (2021) Antiviral effect of high-dose ivermectin in adults with COVID-19: a proof-of-concept randomized trial. EclinicalMedicine 37:100959. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100959
Lanusse C, Lifschitz A, Virkel G, Alvarez L, Sanchez S, Sutra JF, Galtier P, Alvinerie M (1997) Comparative plasma disposition kinetics of ivermectin, moxidectin and doramectin in cattle. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 20:91–99. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2885.1997.00825.x
Lees P, Aliabadi FS, Landoni MF (2002) Pharmacodynamics and enantioselective pharmacokinetics of racemic carprofen in the horse. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 25:433–448. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2885.2002.00436.x
Lees P, Delatour P, Foster AP, Foot R, Baggo D (1996) Evaluation of carprofen in calves using atissue cage model of inflammation. Br Vet J 152:199–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0007-1935(96)80074-1
Lees P, McKellar Q, May SA, Ludwig B (1994) Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of carprofen in the horse. Equine Vet J 26:203–208. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2042-3306.1994.tb04370.x
Lipscomb VJ, Pead MJ, Muir P, AliAbadi FS, Lees P (2002) Clinical efficacy and pharmacokinetics of carprofen in the treatment of dogs with osteoarthritis. Vet Rec 150:684–689. https://doi.org/10.1136/vr.150.22.684
Litonius E, Tarkkila P, Neuvonen PJ, Rosenberg PH (2012) Effect of intravenous lipid emulsion on bupivacaine plasma concentration in humans. Anaesthesia 67:600–605. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2044.2012.07056.x
Lockwood PW, Johnson JC, Katz TL (2003) Clinical efficacy of flunixin, carprofen and ketoprofen as adjuncts to the antibacterial treatment of bovine respiratory disease. Vet Rec 152:392–394. https://doi.org/10.1136/vr.152.13.392
Mansa S, Palmér E, Grøndahl C, Lønaas L, Nyman G (2007) Long-term treatment with carprofen of 805 dogs with osteoarthritis. Vet Rec 160:427–430. https://doi.org/10.1136/vr.160.13.427
McKellar QA, Delatour P, Lees P (1994) Stereospecific pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of carprofen in the dog. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 17:447–454. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2885.1994.tb00276.x
McKellar QA, Gokbulut C (2012) Pharmacokinetic features of the antiparasitic macrocyclic lactones. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 13:888–911. https://doi.org/10.2174/138920112800399194
Mealey KL, Matthews NS, Peck KE, Burchfield ML, Bennett BS, Taylor TS (2004) Pharmacokinetics of R (–) and S (+) carprofen after administration of racemic carprofen in donkeys and horses. Am J Vet Res 65:1479–1482. https://doi.org/10.2460/ajvr.2004.65.1479
Means C, Wismer T (2018) An overview of trends in animal poisoning cases in the United States: 2011 to 2017. Vet Clin Small Animl Pract 48:899–907. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cvsm.2018.07.010
Naggie S, Boulware DR, Lindsell CJ, Stewart TG, Slandzicki AJ, Lim SC, Cohen J, Kavtaradze D, Amon AP, Gabriel A, Gentile N, Felker M, Jayaweera D, McCarthy MW, Sulkowski M, Rothman RL, Wilson S, Delong A, Remaly A, Wilder R, Collins S, Dunsmore SE, Adam SJ, Thicklin F, Hanna GJ, Ginde AA, Castro M, McTigue K, Shenkman E, Hernandez, (2023) Effect of higher-dose ıvermectin for 6 days vs placebo on time to sustained recovery in outpatients with COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial. J Am Med Assoc 329:888–897. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2023.1650
Õmura S, Crump A (2004) The life and times of ivermectin—a success story. Nat Rev Microbiol 2:984–989. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro1048
Ozcan MS, Weinberg G (2014) Intravenous lipid emulsion for the treatment of drug toxicity. J Intensive Care Med 29:59–70. https://doi.org/10.1177/0885066612445978
Parton K, Balmer TV, Boyle J, Whittem T, MacHon R (2000) The pharmacokinetics and effects of intravenously administered carprofen and salicylate on gastrointestinal mucosa and selected biochemical measurements in healthy cats. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 23:73–79. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2885.2000.00253.x
Pollio D, Michau TM, Weaver E, Kuebelbeck KL (2018) Electroretinographic changes after intravenous lipid emulsion therapy in a dog and a foal with ivermectin toxicosis. Vet Ophthalmol 21:82–87. https://doi.org/10.1111/vop.12410
Popp M, Stegemann M, Metzendorf MI, Gould S, Kranke P, Meybohm P, Skoetz N, Weibel S (2021) Ivermectin for preventing and treating COVID-19. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 7:1–156. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD015017.pub2
Robben JH, Dijkman MA (2017) Lipid therapy for intoxications. Vet Clin-Small Anim Pract 47:435–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cvsm.2016.10.018
Rothschild L, Bern S, Oswald S, Weinberg G (2010) Intravenous lipid emulsion in clinical toxicology. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med 18:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1757-7241-18-51
Saqib M, Abbas G, Mughal MN (2015) Successful management of ivermectin-induced blindness in an African lion (Panthera leo) by intravenous administration of a lipid emulsion. BMC Vet Res 11:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12917-015-0603-6
Sauerbrey M (2008) The onchocerciasis elimination program for the Americas (OEPA). Ann Trop Med Parasitol 102:25–29. https://doi.org/10.1179/136485908X337454
Shi K, Xia Y, Wang Q, Wu Y, Dong X, Chen C, Tang W, Zhang Y, Luo M, Wang X, Papadimos T, Xu X (2013) The effect of lipid emulsion on pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of bupivacaine in rats. Anesth Analg 116:804–809. https://doi.org/10.1213/ANE.0b013e318284123e
Sines D (2016) Moxidectin intoxication in a dog—a patient care report. Vet Nurs 7:182–186. https://doi.org/10.12968/vetn.2016.7.3.182
Sirianni AJ, Osterhoudt KC, Calello DP, Muller AA, Waterhouse MR, Goodkin MB, Weinberg GL, Henretig FM (2008) Use of lipid emulsion in the resuscitation of a patient with prolonged cardiovascular collapse after overdose of bupropion and lamotrigine. Ann Emerg Med 51:412–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annemergmed.2007.06.004
Soraci A, Benoit E, Jaussaud P, Lees P, Delatour P (1995) Enantioselective glucuronidation and subsequent biliary excretion of carprofen in horses. Am J Vet Res 56:358–361
Turner-Lawrence DE, Kerns W (2008) Intravenous fat emulsion: a potential novel antidote. J Med Toxicol 4:109–114. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03160965
Van de Velde M, Wouters PF, Rolf N, Van Aken H, Flameng W, Vandermeersch E (1996) Long-chain triglycerides improve recovery from myocardial stunning in conscious dogs. Cardiovasc Res 32:1008–1015. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6363(96)00165-4
Vanek VW, Seidner DL, Allen P, Bistrian B, Collier S, Gura K, Miles JM, Valentine CJ, Kochevar M, American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (ASPEN) board of directors (2012) ASPEN position paper: clinical role for alternative intravenous fat emulsions. Nutr Clin Pract 27:150-192. https://doi.org/10.1177/0884533612439896
Weinberg G (2006) Lipid rescue resuscitation from local anaesthetic cardiac toxicity. Toxicol Rev 25:139–145. https://doi.org/10.2165/00139709-200625030-00001
Weinberg G, Di Gregorio G, Hiller D, Hewett A, Sirianni A (2009) Reversal of haloperidol-induced cardiac arrest by using lipid emulsion. Ann Intern Med 150:737–738. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-150-10-200905190-00023
Weinberg G, Ripper R, Feinstein DL, Hoffman W (2003) Lipid emulsion infusion rescues dogs from bupivacaine-induced cardiac toxicity. Reg Anesth Pain Med 28:198–202. https://doi.org/10.1053/rapm.2003.50041
Weinberg GL, VadeBoncouer T, Ramaraju GA, Garcia-Amaro MF, Cwik MJ (1998) Pretreatment or resuscitation with a lipid infusion shifts the dose-response to bupivacaine-induced asystole in rats. Anesthesiology 88:1071–1075. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000542-199804000-00028
Williams K, Wells RJ, McLean MK (2015) Suspected synthetic cannabinoid toxicosis in a dog. J Vet Emerg Crit Care 25:739–744. https://doi.org/10.1111/vec.12378
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge with pleasure the technical assistance of Asst. Prof. Dr. Eyup Tolga Akyol, Dr. Fazilet Sen and Dr. Nurullah Guclu in the animal experiment phase of the study.
Funding
This study was supported by the Scientific Research Committee of Balikesir University (Balikesir, Turkey) as a research project (project no: 2021/009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.G. supervised and designed the experiments; C.G. and B.A.A. performed the experiment, analysed the results and drafted the manuscript; C.G. and B.A.A. wrote the main manuscript text and C.G. prepared figures 1-3. All authors reviewed the manuscript. The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Approval was granted by the Animal Experiments Local Ethics Committee of Balikesir University (2021/2–2).
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Akyol, B.A., Gokbulut, C. The effect of intravenous lipid emulsion (ILE) on the pharmacokinetic/toxicokinetic dispositions of ivermectin and carprofen in rabbits. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 397, 1841–1852 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02738-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02738-5