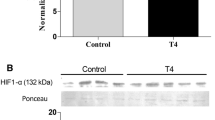
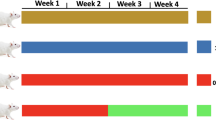
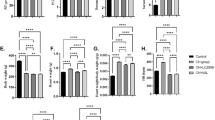
Abstract
Hyperthyroidism is associated with the alteration in molecular pathways involved in the regulation of mitochondrial mass and apoptosis, which contribute to the development of cardiac hypertrophy. Diminazene (DIZE) is an animal anti-infection drug that has shown promising effects on improving cardiovascular disease. The aim of the present study was to investigate the therapeutic effect of DIZE on cardiac hypertrophy and the signaling pathways involved in this process in the hyperthyroid rat model. Twenty male Wistar rats were equally divided into four groups: control, hyperthyroid, DIZE, and hyperthyroid + DIZE. After 28 days of treatment, serum thyroxine (T4) and thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) level, cardiac hypertrophy indices, cardiac damage markers, cardiac malondialdehyde (MDA), and superoxide dismutase (SOD) level, the mRNA expression level of mitochondrial and apoptotic genes were evaluated. Hyperthyroidism significantly decreased the cardiac expression level of SIRT1/PGC1α and its downstream involved in the regulation of mitochondrial biogenesis, mitophagy, and antioxidant enzyme activities including TFAM, PINK1/MFN2, Drp1, and Nrf2, respectively, as well as stimulated mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis by reducing Bcl-2 expression and increasing Bax expression. Treatment with DIZE significantly reversed the downregulation of SIRT1, PGC1α, PINK1, MFN2, Drp1, and Nrf2 but did not significantly change the TFAM expression. Moreover, DIZE suppressed apoptosis by normalizing the cardiac expression levels of Bax and Bcl-2. DIZE is effective in attenuating hyperthyroidism-induced cardiac hypertrophy by modulating the mitophagy-related pathway, suppressing apoptosis and oxidative stress.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used and analyzed in this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Amini N, Badavi M, Mard SA, Dianat M, Moghadam MT (2022) Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Archives Pharmacol 395(6):691–701
Araujo A, Ribeiro M, Enzveiler A, Schenkel P, Fernandes T, Partata W et al (2006) Mol Cell Endocrinol 249(1-2):133–139
Barreto-Chaves M, Senger N, Fevereiro MR, Parletta AC, Takano APC (2020) Endocr Connect 9(3):R59–R69
Bektur Aykanat NE, Şahin E, Kaçar S, Bağcı R, Karakaya Ş, Burukoğlu Dönmez D et al (2021) Can J Physiol Pharmacol 99(11):1226–1233
Bereda G (2022) J Biomed Biol Sci 1(2):1–11
Boťanská B, Dovinová I, Barančík M (2022) Cells. 11(7):1203
Castardeli C, Sartório CL, Pimentel EB, Forechi L, Mill JG (2018) Biomed Pharmacother 107:212–218
Chen Y, Zeng M, Zhang Y, Guo H, Ding W, Sun T (2021) Nlrp3 deficiency alleviates angiotensin II-induced cardiomyopathy by inhibiting mitochondrial dysfunction. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2021:10
Chistiakov DA, Shkurat TP, Melnichenko AA, Grechko AV, Orekhov AN (2018) Ann Med 50(2):121–127
Coutinho DC, Santos-Miranda A, Joviano-Santos JV, Foureaux G, Santos A, Rodrigues-Ferreira C et al (2022) Diminazene aceturate, an angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) activator, promotes cardioprotection in ischemia/reperfusion-induced cardiac injury. Peptides 151:170746
Cui Y-K, Hong Y-X, Wu W-Y, Han W-M, Wu Y, Wu C et al (2022) Eur J Pharmacol 920:174858
da Silva Oliveira GL, de Freitas RM (2015) Pharmacol Res 102:138–157
Elnakish MT, Ahmed AA, Mohler PJ, Janssen PM (2015) Role of oxidative stress in thyroid hormone-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and associated cardiac dysfunction: an undisclosed story. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2015:16
Freitas F, Estato V, Carvalho V, Carvalho Torres R, Lessa M, Tibiriçá E (2013) Microcirculation 20(7):590–598
Freitas F, Estato V, Lessa M, Tibiriçá E (2015) Fundam Clin Pharmacol 29(1):31–40
Fukuchi M, Shimabukuro M, Shimajiri Y, Oshiro Y, Higa M, Akamine H, Komiya I, Takasu N (2002) Life Sci 71(9):1059–1070
Gao L, Liu Y, Guo S, Xiao L, Wu L, Wang Z et al (2018) LAZ3 protects cardiac remodeling in diabetic cardiomyopathy via regulating miR-21/PPARa signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis 1864(10):3322–3338
Ghahremani R, Damirchi A, Salehi I, Komaki A, Esposito F (2018) Life Sci 213:102–108
Goffart S, von Kleist-Retzow J-C, Wiesner RJ (2004) Cardiovasc Res 64(2):198–207
Guan X, Wang L, Liu Z, Guo X, Jiang Y, Lu Y et al (2016) J Mol Cell Cardiol 99:207–217
Hashem H, Saad S (2020) Egypt J Histol 43(3):791–807
Hassan MQ, Akhtar MS, Akhtar M, Ali J, Haque SE, Najmi AK (2015) Redox Rep 20(6):275–281
Hu LW, Benvenuti LA, Liberti EA, Carneiro-Ramos MS, Barreto-Chaves MLM (2003) Am J Phys Regul Integr Comp Phys 285(6):R1473–R1R80
Ikeda M, Ide T, Fujino T, Arai S, Saku K, Kakino T et al (2015) PLoS One 10(3):e0119687
Kane LA, Lazarou M, Fogel AI, Li Y, Yamano K, Sarraf SA et al (2014) J Cell Biol 205(2):143–153
Khamis T, Alsemeh AE, Abdullah DM (2022) Sci Rep 12(1):1–13
Khatua TN, Dinda AK, Putcha UK, Banerjee SK (2016) Biochem Biophys Rep 5:77–88
Kulemina LV, Ostrov DA (2011) J Biomol Screen 16(8):878–885
Lei MY, Cong L, Liu ZQ, Liu ZF, Ma Z, Liu K et al (2022) Environ Toxicol 37(2):282–298
Liang H, Ward WF (2006) PGC-1α: a key regulator of energy metabolism. Adv Physiol Educ 30(4):145–151
Lu Z, Wu D, Wang Z, Zhang H, Du Y, Wang G (2022) BMC Pharmacol Toxicol 23(1):1–12
Ma K, Chen G, Li W, Kepp O, Zhu Y, Chen Q (2020) Front Cell Dev Biol 8:467
Ma Z, Liu Z, Xue Y, Zhang H, Xiong W, Zhou H, et al (2021) Metformin collaborates with PINK1/Mfn2 overexpression prevented isoproterenol-induced cardiomyocyte injury by improving mitochondrial function. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-680629/v1
Mahmud T, Khan Q, Saad S (2021) Cureus 13(4):14517
Maity S, Kar D, De K, Chander V, Bandyopadhyay A (2013) J Endocrinol 217(2):215–228
Maulik SK, Kumar S (2012) Toxicol Mech Methods 22(5):359–366
Mishra P, Paital B, Jena S, Swain SS, Kumar S, Yadav MK et al (2019) Sci Rep 9(1):1–16
Mishra P, Samanta L (2012) Oxidative stress and heart failure in altered thyroid states. Sci World 2012:17
Oh C-M, Ryu D, Cho S, Jang Y (2020) Korean Circ J 50(5):395–405
Ortega-Molina A, Efeyan A, Lopez-Guadamillas E, Muñoz-Martin M, Gómez-López G, Cañamero M et al (2012) Cell Metab 15(3):382–394
Palikaras K, Lionaki E, Tavernarakis N (2015) Cell Death Differ 22(9):1399–1401
Palikaras K, Tavernarakis N (2014) Exp Gerontol 56:182–188
Picca A, Lezza AMS (2015) Mitochondrion. 25:67–75
Rigatto K, Casali K, Shenoy V, Katovich M, Raizada M (2013) Eur J Pharmacol 713(1-3):89–93
Rosner B (2005) Fundamentals of biostatistics. 6th ed. Brooks/Cole, Boston
Senger N, Parletta CA, Marques BV, Akamine EH, Diniz GP, Campagnole-Santos MJ et al (2021) J Cell Physiol 236(4):3059–3072
Shackebaei D, Feizollahi F, Hesari M, Bahrami G (2016) Int Cardiovasc Res J 10(2)
Sinha K, Das J, Pal PB, Sil PC (2013) Arch Toxicol 87:1157–1180
Soni SK, Basu P, Singaravel M, Sharma R, Pandi-Perumal SR, Cardinali D et al (2021) Cell Mol Life Sci 78(6):2503–2515
Tang J, Lu L, Liu Y, Ma J, Yang L, Li L et al (2019) J Cell Biochem 120(6):9747–9757
Taylor PN, Albrecht D, Scholz A, Gutierrez-Buey G, Lazarus JH, Dayan CM et al (2018) Nat Rev Endocrinol 14(5):301–316
Teixeira RB, Barboza TE, de Araújo CC, Siqueira R, de Castro AL, Bonetto JHP et al (2018) J Biosci 43(5):887–895
Vásquez-Trincado C, García-Carvajal I, Pennanen C, Parra V, Hill JA, Rothermel BA et al (2016) J Physiol 594(3):509–525
Velkoska E, Patel S, Griggs K, Burrell L (2016) PLoS One 11(8):e0161760
Velkoska E, Patel S, Griggs K, Pickering R, Tikellis C, Burrell L (2015) PLoS One 10(3):e0118758
Wan X, Wen J-j, Koo S-J, Liang LY, Garg NJ (2016) PLoS Pathog 12(10):e1005954
Wen S, Unuma K, Funakoshi T, Aki T, Uemura K (2021) Sci Rep 11(1):24129
Xiong W, Ma Z, An D, Liu Z, Cai W, Bai Y et al (2019) Front Physiol 10:411
Xu W, Hou D, Jiang X, Lu Z, Guo T, Liu Y et al (2012) J Cell Physiol 227(9):3243–3253
Yang D, Liu H-Q, Liu F-Y, Guo Z, An P, Wang M-Y et al (2022) Front Cardiovasc Med 8:2190
Yang H, Yang R, Liu H, Ren Z, Wang C, Li D et al (2016) OncoTargets Ther 9:5329
Yao X, Cao Y, Lu L, Xu Y, Chen H, Liu C et al (2022) Parasit Vectors 15(1):1–12
Yin F, Spurgeon HA, Rakusan K, Weisfeldt ML, Lakatta EG (1982) Am J Phys Heart Circ Phys 243(6):H941–H9H7
Yu H, Guo Y, Mi L, Wang X, Li L, Gao W (2011) J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther 16(2):205–211
Funding
The study was funded by the vice-chancellor for research and technology, Hamadan University of Medical Sciences (no. 140110138754). The authors would like to thank Hamadan University of Medical Sciences for funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FSH and FRA conceived the project. FSH, FRA, MZ, and SR participated in data extraction and analysis, prepared figures, and wrote the manuscript. FRA and AK revised the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript. The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethical approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of Hamadan University of Medical Sciences (ethics committee permission no. IR.UMSHA.REC.1401.772).
Consent for publication
None.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shokri, F., Zarei, M., Komaki, A. et al. Effect of diminazene on cardiac hypertrophy through mitophagy in rat models with hyperthyroidism induced by levothyroxine. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 397, 1151–1162 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02680-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02680-6