Abstract
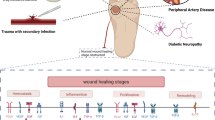
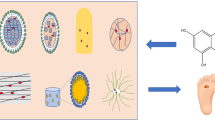
Diabetic foot wounds (DFUs) are counted as one of the most common microvascular complications associated with poorly controlled and chronic diabetes mellitus. It confers a serious challenge to clinical practice, surmounting hyperglycemia-induced disturbance in angiogenesis and endothelial dysfunction, with limited fruitful intervention to control the manifestations of DFUs. Resveratrol (RV) can improve endothelial function and has strong pro-angiogenic properties for the treatment of diabetic foot wounds. The present study aims to design an RV-loaded liposome-in-hydrogel system to effectively heal diabetic foot ulcers. A thin-film hydration method was used to prepare RV-loaded liposomes. Liposomal vesicles were assessed, for various characteristics such as particle size, zeta potential, and entrapment efficiency. The best-prepared liposomal vesicle was then incorporated into 1% carbopol 940 gel to develop a hydrogel system. The RV-loaded liposomal gel showed improved skin penetration. To assess the efficacy of the developed formulation, a diabetic foot ulcer animal model was used. The topical application of the developed formulation significantly reduced blood glucose and increased glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) to improve ulcer healing as well as wound closure on day 9. Faster re-epithelization, proliferation of fibroblast, formation of collagen, and reduced inflammatory cell infiltration at the wound site were also noted. Results indicate that RV-loaded liposomes in hydrogel-based wound dressing significantly accelerate wound healing in diabetic foot ulcers by restoring the altered wound healing process in diabetics.
Graphical Abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Greaves NS, Ashcroft KJ, Baguneid M, Bayat A (2013) Current understanding of molecular and cellular mechanisms in fibroplasia and angiogenesis during acute wound healing. J Dermatol Sci 72:206–217
World Health Organisation Global report on diabetes 2016 Available from World Health Organization Global report on diabetes
Zheng Y, Ley SH, Hu FB (2018) Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat Rev Endocrinol 14(2):88–98
Bus S, Van Netten S, Lavery L, Monteiro-Soares M, Rasmussen A, Jubiz Y, Price P (2016) IWGDF guidance on the prevention of foot wounds in at-risk patients with diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 32(S1):16–24
Moeini M, Shahriari M, Yousefi H, Esfandiari J, Babaahmadi M (2017) An investigation on the wound severity and its association with predisposing factors in patients with diabetic foot. Journal of Clinical Nursing and Midwifery 5:4
Bashmakov YK, Assaad-Khalil S, Petyaev IM (2011) Resveratrol may be beneficial in treatment of diabetic foot syndrome. Med Hypotheses 77(3):364–367
Jhaveri A, Deshpande P, Pattni B, Torchilin V (2018) Transferrin-targeted, Resveratrol -loaded liposomes for the treatment of glioblastoma. J Control Release 277:89–101
Ndiaye M, Philippe C, Mukhtar H, Ahmad N (2011) The grape antioxidant Resveratrol for skin disorders: promise, prospects, and challenges. Arch Biochem Biophys 508(2):164–170
Eroğlu İ, Gökçe EH, Tsapis N, Tanrıverdi ST, Gökçe G, Fattal E, Özer Ö (2015) Evaluation of characteristics and in vitro antioxidant properties of RSV loaded hyaluronic acid–DPPC microparticles as a wound healing system. Colloids Surf, B 126:50–57
Gokce EH, Tanrıverdi ST, Eroglu I, Tsapis N, Gokce G, Tekmen I, Fattal E, Ozer O (2017) Wound healing effects of collagen-laminin dermal matrix impregnated with Resveratrol loaded hyaluronic acid-DPPC microparticles in diabetic rats. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 119:17–27
Hecker A, Schellnegger M, Hofmann E, Luze H, Nischwitz SP, Kamolz LP, Kotzbeck P (2022) The impact of Resveratrol on skin wound healing, scarring, and aging. Int Wound J 19(1):9–28
Yao H, Lu H, Zou R, Chen X, Xu H. 2020 Preparation of encapsulated resveratrol liposome thermosensitive gel and evaluation of its capability to repair sciatic nerve injury in rats Journal of Nanomaterials
Hussain Z, Thu HE, Shuid AN, Katas H, Hussain F (2018) Recent advances in polymer-based wound dressings for the treatment of diabetic foot wound: an overview of state of the art curr drug targets 19(5):527–550
Boateng J, Catanzano O (2015) Advanced therapeutic dressings for effective wound healing—a review. J Pharm Sci 104:3653–3680
Bhattarai N, Gunn J, Zhang M (2010) Chitosan-based hydrogels for controlled, localized drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 62:83–99
Stern D, Cui H (2019) Crafting polymeric and peptidic hydrogels for improved wound healing. Adv Healthc Mater 8:190010414
Dickinson LE, Gerecht S (2016) Engineered biopolymeric scaffolds for chronic wound healing. Front Physiol 7:341
Pitorre M, Gondé H, Haury C, Messous M, Poilane J, Boudaud D, Kanber E, Ndombina GA, Benoit JP, Bastiat G (2017) Recent advances in nanocarrier-loaded gels: which drug delivery technologies against which diseases? J Control Release 28(266):140–155
Hurler J, Sørensen KK, Fallarero A, Vuorela P, Škalko-Basnet N (2013) Liposomes-in-hydrogel delivery system with mupirocin: in vitro antibiofilm studies and in vivo evaluation in mice burn model. Biomed Res Int 1:2013
Grijalvo S, Mayr J, Eritja R, Díaz D (2016) Biodegradable liposome-encapsulated hydrogels for biomedical applications: A marriage of convenience. Biomater Sci 4:555–574
Banerjee R (2013) Overcoming the stratum corneum barrier: A nano approach. Drug Deliv Transl Res 3:205–208
Gao W, Vecchio D, Li J, Zhu J, Zhang Q, Fu V, Li J, Thamphiwatana S, Lu D, Zhang L (2014) Hydrogel containing nanoparticle-stabilized liposomes for topical antimicrobial delivery. ACS Nano 8(3):2900–2907
Paveli´c, Ž.; Škalko-Basnet, N.; Schubert, R. 2001 Liposomal gels for vaginal drug delivery Int J Pharm 219 139 149
Lu KJ, Wang W, Xu XL, Jin FY, Qi J, Wang XJ, Kang XQ, Zhu ML, Huang QL, Yu CH, You J (2019) A dual deformable liposomal ointment functionalized with retinoic acid and epidermal growth factor for enhanced burn wound healing therapy. Biomaterials Science 7(6):2372–2382
Salem HF, Kharshoum RM, Mahmoud M, Azim SA, Ebeid EZ (2018) Development and characterization of a novel nano-liposomal formulation of alendronate sodium loaded with biodegradable polymer. Ars Pharmaceutica (internet) 59(1):9–20
Ternullo S, Basnet P, Holsæter AM, Flaten GE, de Weerd L, Škalko-Basnet N (2018) Deformable liposomes for skin therapy with human epidermal growth factor: The effect of liposomal surface charge. Eur J Pharm Sci 125:163–171
Mulani H, Bhise KS (2017) QbD Approach in the formulation and evaluation of Miconazole Nitrate loaded ethosomal cream-o-gel. International Research Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 8:1
Nawaz A, Latif MS, Alnuwaiser MA, Ullah S, Iqbal M, Alfatama M, Lim V (2022) Synthesis and characterization of chitosan-decorated nanoemulsion gel of 5-Fluorouracil for topical delivery. Gels 8:412
Jangde R, Srivastava S, Singh MR, Singh D (2018) In vitro and In vivo characterization of quercetin loaded multiphase hydrogel for wound healing application. Int J Biol Macromol 115:1211–1217
Ansari MD, Ahmed S, Imam SS, Khan I, Singhal S, Sharma M, Sultana Y (2019) CCD based development and characterization of nano-transethosome to augment the antidepressant effect of agomelatine on Swiss albino mice. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology 54:101234
Lau TW, Lam FF, Lau KM, Chan YW, Lee KM, Sahota DS, Ho YY, Fung KP, Leung PC, Lau CB (2009) Pharmacological investigation on the wound healing effects of Radix rehmanniae in an animal model of diabetic foot ulcer. J Ethnopharmacol 123(1):155–162
Daburkar M, Lohar V, Rathore AS, Bhutada P, Tangadpaliwar S (2014) An in vivo and in vitro investigation of the effect of Aloe vera gel ethanolic extract using animal model with diabetic foot ulcer. J Pharm Bio Sci 6(3):205
Malviya VK, Goyal S, Bansal V, Jaiswal K (2022) Clinical uses of NPWT with irrigation of normal saline in diabetic foot ulcer: outcome assessed by DEPA score. J Cutan Aesthet Surg 15:58–64
Younes NA, Albsoul AM (2004) The DEPA scoring system and its correlation with the healing rate of diabetic foot ulcers. J Foot Ankle Surg 43(4):209–213
Fathalla D, Youssef EMK, Soliman GM (2020) Liposomal and ethosomal gels for the topical delivery of anthralin: preparation, comparative evaluation and clinical assessment in psoriatic patients. Pharmaceutics 12(5):446
Wang W, Lu KJ, Yu CH, Huang QL, Du YZ (2019) Nano-drug delivery systems in wound treatment and skin regeneration. Journal of Nanobiotechnology 17(1):1–5
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Faculty of Pharmacy, Integral University, for providing all necessary facilities related to the present work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PK make a substantial contribution to conception and design. SP and AS participated in the analysis and interpretation of data. SP and MS carried out the acquisition of data and wrote the paper with input from all authors. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The study was approved by the Faculty of Pharmacy, Integral University, Lucknow, India (CPCSEA approval#-IU/IAEC/19/17). All animal experiments were performed strictly in humane as possible and complied with the guidelines for animal care with the approval of the Institutional Animal Ethical Committee (IAEC).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pandey, S., Shamim, A., Shaif, M. et al. Development and evaluation of Resveratrol-loaded liposomes in hydrogel-based wound dressing for diabetic foot ulcer. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 396, 1811–1825 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02441-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02441-5