Abstract
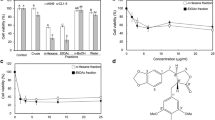
Lung cancer is one of the deadliest cancers in the world. Introducing new promising agents can help the chemotherapeutic management of cancer. In the knowledge of oncology, plants are of special interest as a rich source of new antineoplastic and chemotherapeutic agents. Grandivittin (GRA) is one of the main constituents of Ferulago trifida Boiss. with established medicinal, phytochemical, and pharmacological properties. This study aimed to isolate and evaluate the antineoplastic potential of grandivittin and its underlying mechanisms in human lung cancer A549 cells. The viability of the A549 cells after being treated with 0.1, 0.4, 0.7, 1, and 1.3 mM of GRA for three following days was measured using the MTT method. The early apoptosis and late apoptosis were assessed by fluorescence‐activated cell sorter analysis through annexin V/PI staining. The expression of apoptotic agents’ genes (caspase 3, caspase 9, Bcl2, Bax, and P53) was evaluated by the RT-PCR method. GRA increased apoptotic cells and decreased cell viability in a dose- and time-dependent manner, in which only 50% of cells survived at a dose of 0.7 mM. The expression of Bax, P53, caspase 3, and caspase 9 genes in the A549 cells was significantly upregulated after GRA treatment compared to control cells (P < 0.05). On the other hand, Bcl2 was significantly downregulated after GRA treatment (P < 0.05). The results indicated that GRA can activate cell death in A549 lung carcinoma cells by inducing both DNA toxicity p53 and cascade-dependent pathways. Therefore, GRA may be a potential new therapeutic agent for the treatment of lung cancer.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the analyzed data generated during the present study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ahmadi F, Valadbeigi S, Sajjadi S, Shokoohinia Y, Azizian H, Taheripak G (2016) Grandivittin as a natural minor groove binder extracted from Ferulago macrocarpa to ct-DNA, experimental and in silico analysis. Chem Biol Interact 258:89–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2016.08.020
Basile A, Sorbo S, Spadaro V, Bruno M, Maggio A, Faraone N et al (2009) Antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of coumarins from the roots of Ferulago campestris (Apiaceae). Molecules 14(3):939–952. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14030939
Bulbul A, Husain H (2018) First-line treatment in EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer: is there a best option? Front Oncol 8:94. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2018.00094
Filiz B, Songül K, Bostanlık D, Gül F, Sibel KC (2016) Anticancer effect of Ferulago mughlea Peşmen (Apiaceae) on cancer cell proliferation. Iranian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research: IJPR 15(3):501 (PMID: 27980585)
Gajra A, Marr AS, Ganti AK (2014) Management of patients with lung cancer and poor performance status. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 12(7):1015–1025. https://doi.org/10.6004/jnccn.2014.0098
Goodarzi S, Tavakoli S, Abai MR, Amini Z, Vatandoost H, Yassa N et al (2019) Strong insecticidal potential of methanol extract of Ferulago trifida fruits against Anopheles stephensi as malaria vector. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(8):7711–7717. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04149-7
HAJI AA, Aghel N, Etemadi R (2002) Chemical and biological study of essential oil of Ferulago macrocarpa (Fenzi) Boiss
Harada M, Kotake Y, Ohhata T, Kitagawa K, Niida H, Matsuura S et al (2014) YB-1 promotes transcription of cyclin D1 in human non-small-cell lung cancers. Genes Cells 19(6):504–516. https://doi.org/10.1111/gtc.12150
Hatami E, Nagesh PK, Jaggi M, Chauhan SC, Yallapu MM (2020) Gambogic acid potentiates gemcitabine induced anticancer activity in non-small cell lung cancer. European journal of pharmacology 888:173486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173486
Hsuuw YD, Chang CK, Chan WH, Yu JS (2005) Curcumin prevents methylglyoxal-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in mouse embryonic stem cells and blastocysts. J Cell Physiol 205(3):379–386. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.20408
Hutchinson BD, Shroff GS, Truong MT, Ko JP. 40 2019 ‘Spectrum of lung adenocarcinoma’ Seminars in Ultrasound CT and MRI Elsevier pp 255–264 3 https://doi.org/10.1053/j.sult.2018.11.009
Jiménez B, Grande MAC, Anaya J, Torres P, Grande M (2000) Coumarins from Ferulago capillaris and F. brachyloba. Phytochemistry 53 8 1025–1031 https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9422(99)00524-5
Karakaya S, Koca M, Kılıc CS, Coskun M (2018) Antioxidant and anticholinesterase activities of Ferulago syriaca Boiss and F isaurica Peșmen growing in Turkey. Medicinal Chemistry Research 27(7):1843–1850. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-018-2196-7
Karakaya S, Göger G, Bostanlik FD, Demirci B, Duman H, Kilic CS (2019) Comparison of the essential oils of Ferula orientalis L Ferulago sandrasica Peşmen and Quézel and Hippomarathrum microcarpum Petrov and their antimicrobial activity Turkish. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 16(1):69. https://doi.org/10.4274/tjps.77200
Karakaya S, Koca M, Sytar O, Dursunoglu B, Ozbek H, Duman H et al (2019c) Antioxidant and anticholinesterase potential of Ferulago cassia with farther bio-guided isolation of active coumarin constituents. S Afr J Bot 121:536–542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2019.01.020
Karakaya S, Bi̇ngöl Z, Gülçi̇n İ, Deli̇mustafaoğlu F, Duman H, Kilic CS (2021) Carbonic anhydrase isoenzymes I and II inhibition potentials of Leiotulus dasyanthus (K. Koch) Pimenov&Ostr. and Ferulago pauciradiata Boiss. &Heldr.(Apiaceae). Bezmialem Science, 9(2) 153–157 https://doi.org/10.14235/bas.galenos.2020.4127
Karakaya S, Ozbek H, Gözcü S, Güvenalp Z, Yuca H, Duman H et al. (2018c) α-Amylase and α-glucosidase inhibitory activities of the extracts and constituents of Ferulago blancheana F pachyloba and F trachycarpa roots Bangladesh Journal of Pharmacology 13 1 35–40 https://doi.org/10.1080/13880209.2017.1414857
Karakaya S, Koca M, Simsek D, Bostanlik FD, Özbek H, Kiliç CS et al (2018b) Antioxidant antimicrobial and anticholinesterase activities of Ferulago pauciradiata Boiss & Heldr growing in Turkey. Journal of Biologically Active Products from Nature 8 6 364–375 https://doi.org/10.1080/22311866.2018.1503562
Karakaya S, Delimustafaoğlu Bostanlik F, Göğer G, Demirci B, Kılıç CS (2019a). Comparison of essential oils and antimicrobial activities of Ferulago mughlae Pesmen (Apiaceae) growing in Turkey. https://doi.org/10.12991/jrp.2018.111
Karakaya S, Oral DY, Serap G, Duman H, Kilic CS (2019d) Effect of extracts of the aerial parts and roots from four Ferulago species on erectile dysfunction in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Turkish Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 16(3):317–325. https://doi.org/10.4274/tjps.galenos.2018.26879
Karakaya S, Şimşek D, Özbek H, Güvenalp Z, Altanlar N, Kazaz C et al. (2019e) Antimicrobial activities of extracts and isolated coumarins from the roots of four Ferulago species growing in Turkey. Iranian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research: IJPR 18(3):1516–1529. https://doi.org/10.22037/ijpr.2019.1100718
Kutlu Z, Celik M, Bilen A, Halıcı Z, Yıldırım S, Karabulut S et al. (2020) Effects of umbelliferone isolated from the Ferulago pauciradiata Boiss. & Heldr. Plant on cecal ligation and puncture-induced sepsis model in rats. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 127, 110206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110206
Li K, Li Y, Shelton JM, Richardson JA, Spencer E, Chen ZJ et al (2000) Cytochrome c deficiency causes embryonic lethality and attenuates stress-induced apoptosis. Cell 101(4):389–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80849-1
Liu J-J, Lin M, Yu J-Y, Liu B, Bao J-K (2011) Targeting apoptotic and autophagic pathways for cancer therapeutics. Cancer Lett 300(2):105–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2010.10.001
Lu Z, Xiao Y, Liu X, Zhang Z, Xiao F, Bi Y (2017) Matrine reduces the proliferation of A549 cells via the p53/p21/PCNA/eIF4E signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep 15(5):2415–2422. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.6331
Mohan CD, Rangappa S, Preetham HD, Nayaka SC, Gupta VK, Basappa S et al. (2020) Targeting STAT3 signaling pathway in cancer by agents derived from Mother Nature Seminars in cancer biology Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.03.016
Namwan N, Senawong G, Phaosiri C, Kumboonma P, Somsakeesit L-O, Samankul A et al (2022) HDAC inhibitory and anti-cancer activities of curcumin and curcumin derivative CU17 against human lung cancer A549 cells. Molecules 27(13):4014. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27134014
Papadimitrakopoulou V, Adjei AA (2006) The Akt/mTOR and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in lung cancer therapy. J Thorac Oncol 1(7):749–751. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1556-0864(15)30399-3
Park HJ, Jeon YK, You DH, Nam MJ (2013) Daidzein causes cytochrome c-mediated apoptosis via the Bcl-2 family in human hepatic cancer cells. Food Chem Toxicol 60:542–549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2013.08.022
Riedl SJ, Shi Y (2004) Molecular mechanisms of caspase regulation during apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5(11):897–907. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm1496
Roberts PJ, Der CJ (2007) Targeting the Raf-MEK-ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade for the treatment of cancer. Oncogene 26(22):3291–3310. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210422
Rosselli S, Maggio AM, Faraone N, Spadaro V, Morris-Natschke SL, Bastow KF et al. (2009). The cytotoxic properties of natural coumarins isolated from roots of Ferulago campestris (Apiaceae) and of synthetic ester derivatives of aegelinol. Natural Product Communications 4 12. 1934578X0900401219
Roy S, Sil A, Chakraborty T (2019) Potentiating apoptosis and modulation of p53, Bcl2, and Bax by a novel chrysin ruthenium complex for effective chemotherapeutic efficacy against breast cancer. J Cell Physiol 234(4):4888–4909. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27287
Salem AA, El Haty IA, Abdou IM, Mu Y (2015) Interaction of human telomeric G-quadruplex DNA with thymoquinone: a possible mechanism for thymoquinone anticancer effect. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-General Subjects 1850(2), 329–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2014.10.018
Samarghandian S, Azimi-Nezhad M, Farkhondeh T (2019) Thymoquinone-induced antitumor and apoptosis in human lung adenocarcinoma cells. J Cell Physiol 234(7):10421–10431. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27710
Sardeli C, Zarogoulidis P, Kosmidis C, Amaniti A, Katsaounis A, Giannakidis D et al. (2019) Inhaled chemotherapy adverse effects: mechanisms and protection methods. Lung Cancer Management 8(4), LMT19 https://doi.org/10.2217/lmt-2019-0007
Sgarra R, Pegoraro S, Ros G, Penzo C, Chiefari E, Foti D et al. (2018) High mobility group A (HMGA) proteins: molecular instigators of breast cancer onset and progression. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Reviews on Cancer 1869(2) 216–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2018.03.001
Shen M, Zhao X, Zhao L, Shi L, An S, Huang G et al (2018) Met is involved in TIGAR-regulated metastasis of non-small-cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer 17(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0839-4
Stinchcombe TE, Johnson GL (2014) MEK inhibition in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 86(2):121–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2014.09.005
Tao M-H (2019) Epidemiology of lung cancer. Lung Cancer and Imaging
Tavakoli S, Delnavazi M-R, Hadjiaghaee R, Jafari-Nodooshan S, Khalighi-Sigaroodi F, Akhbari M et al. (2018) Bioactive coumarins from the roots and fruits of Ferulago trifida Boiss an endemic species to Iran. Natural Product Research 32(22), 2724–2728 https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2017.1375915
Wattanathamsan O, Hayakawa Y, Pongrakhananon V (2019) Molecular mechanisms of natural compounds in cell death induction and sensitization to chemotherapeutic drugs in lung cancer. Phytother Res 33(10):2531–2547. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.6422
Wong RS (2011) Apoptosis in cancer: from pathogenesis to treatment. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 30(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-9966-30-87
Yip C, Tacelli N, Remy-Jardin M, Scherpereel A, Cortot A, Lafitte J-J et al (2015) Imaging tumor response and tumoral heterogeneity in non–small cell lung cancer treated with antiangiogenic therapy. J Thorac Imaging 30(5):300–307. https://doi.org/10.1097/RTI.0000000000000164
Zhang H, Feng QQ, Gong JH, Ma JP (2018) Anticancer effects of isofraxidin against A549 human lung cancer cells via the EGFR signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep 18(1):407–414. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2018.8950
Zhou J, Zhang X, Ashoori F, McConkey DJ, Knowles MA, Dong L et al (2009) Early RB94-produced cytotoxicity in cancer cells is independent of caspase activation or 50 kb DNA fragmentation. Cancer Gene Ther 16(1):13–19. https://doi.org/10.1038/cgt.2008.54
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our gratitude to the technicians, students, and professors of the laboratory of the Department of Cell and Molecular Biology and Pharmacognosy for their help in offering us the resources in running the project.
Funding
This study is funded by the Department of Cell & Molecular Biology, School of Biology, College of Science, University of Tehran, Tehran, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the project has been done by Fatemeh Zomorodi Anbaji and the manuscript has been written by her; grandivittin extraction has been done by Dr. Saeed Tavakoli; and Dr. Seyed Jalal Zargar managed the proposal and the project.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This declaration is not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Anbaji, F.Z., Zargar, S.J. & Tavakoli, S. Effect of isolated grandivittin from Ferulago trifida Boiss. (Apiaceae) on the proliferation and apoptosis of human lung cancer A549 cells. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 396, 1525–1533 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02419-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02419-3