Abstract
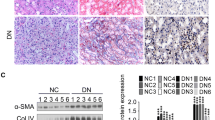
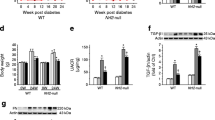
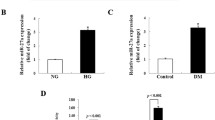
Deregulated activity of protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin complex-1 (Akt/mTORC1) incites crucial pathological characteristics of diabetic nephropathy. The acyclic monoterpene geraniol has been recently reported to possess antidiabetic effects; however, its potential renoprotective effect in diabetes has not yet been elucidated. This study aimed to assess the possible modulatory effect of geraniol on the Akt/mTORC1 pathway in diabetes-induced nephropathy in rats compared to the standard antidiabetic drug gliclazide. Geraniol and gliclazide was administered daily to diabetic rats for 6 weeks starting on the 3rd-day post diabetes induction by streptozotocin (STZ). Geraniol amended the deteriorated renal function (serum creatinine; blood urea nitrogen). It exerted a remarkable antihyperglycemic effect that is comparable to that of gliclazide and suppressed the fibrotic marker, transforming growth factor-β. Geraniol restored redox balance and inhibited lipid peroxidation by reducing nicotine amide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase and enhancing the antioxidant enzyme, superoxide dismutase. These beneficial effects were associated with a robust downregulation of miRNA-21 and consequently, reversion of tumor suppressor protein phosphatase and tension homolog (PTEN)/Akt/mTORC1 cue and its downstream proteins required for mesangial cell proliferation and matrix protein synthesis. The current study indicates that geraniol interfered with miRNA-21/ PTEN/AKT/mTORC1 pathway signaling that contributes largely to the progression of mesangial expansion and extracellular matrix deposition in diabetic nephropathy.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afanas’ev I (2010) Signaling of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in diabetes mellitus. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 3:361–373
Afkarian M, Sachs MC, Kestenbaum B, Hirsch IB, Tuttle KR, Himmelfarb J, De Boer IH (2013) Kidney disease and increased mortality risk in type 2 diabetes. J Am Soc Nephrol 24:302–308
Ahmad ST, Arjumand W, Seth A, Nafees S, Rashid S, Ali N, Sultana S (2011) Preclinical renal cancer chemopreventive efficacy of geraniol by modulation of multiple molecular pathways. Toxicology 290:69–81
Babukumar S, Vinothkumar V, Sankaranarayanan C, Srinivasan S (2017) Geraniol, a natural monoterpene, ameliorates hyperglycemia by attenuating the key enzymes of carbohydrate metabolism in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Pharm Biol 55:1442–1449
Baltrusch S, Schmitt H, Brix A, Langer S, Lenzen S (2012) Additive activation of glucokinase by the bifunctional enzyme 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2, 6-bisphosphatase and the chemical activator LY2121260. Biochem Pharmacol 83:1300–1306
Bera A, Das F, Ghosh-Choudhury N, Mariappan MM, Kasinath BS, Choudhury GG (2017) Reciprocal expression of mir-214 and PTEN by high glucose regulates glomerular mesangial and proximal tubular epithelial cell hypertrophy and matrix expansion. Am J Phys Cell Phys 313:C430–C447
Boukhris M, Bouaziz M, Feki I, Jemai H, El Feki A, Sayadi S (2012) Hypoglycemic and antioxidant effects of leaf essential oil of Pelargonium graveolens L'Hér. in alloxan induced diabetic rats. Lipids Health Dis 11:81
Chau BN, Xin C, Hartner J, Ren S, Castano AP, Linn G, Li J, Tran PT, Kaimal V, Huang X (2012) MicroRNA-21 promotes fibrosis of the kidney by silencing metabolic pathways. Sci Transl Med 4:121ra18
Dey N, Ghosh-Choudhury N, Kasinath BS, Choudhury GG (2012) TGFb-stimulated microRNA-21 utilizes PTEN to orchestrate AKT/mTORC1 signaling for mesangial cell hypertrophy and matrix expansion. PLoS One 7:e42316
Dronavalli S, Duka I, Bakris GL (2008) The pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Nat Rev Endocrinol 4:444–452
El Sayed MES, Eid N, Kamel ASED (2014) Beneficial effects of certain phosphodiesterase inhibitors on diabetes mellitus in rats. Bull Fac Pharm Cairo Univ 52:179–189
Forbes JM, Coughlan MT, Cooper ME (2008) Oxidative stress as a major culprit in kidney disease in diabetes. Diabetes 57:1446–1454
Gödel M, Hartleben B, Herbach N, Liu S, Zschiedrich S, Lu S, Debreczeni-Mór A, Lindenmeyer MT, Rastaldi MP, Hartleben G (2011) Role of mTOR in podocyte function and diabetic nephropathy in humans and mice. J Clin Invest 121:2197–2209
Goldfarb S, Ziyadeh FN (2001) TGF-beta: a crucial component of the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc 112:27
Gomide M, Lemos F, Reis D, José G, Lopes M, Machado MA, Alves T, Coelho CM (2016) Identification of dysregulated microRNA expression and their potential role in the antiproliferative effect of the essential oils from four different Lippia species against the CT26. WT colon tumor cell line. Rev Bras Farmacogn 26:627–633
Górriz J, Nieto J, Navarro-González J, Molina P, Martínez-Castelao A, Pallardó L (2015) Nephroprotection by hypoglycemic agents: do we have supporting data? J Clin Med 4:1866–1889
He L, Hannon GJ (2004) MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet 5:522–531
Ibrahim SM, El-Denshary ES, Abdallah DM (2015) Geraniol, alone and in combination with pioglitazone, ameliorates fructose-induced metabolic syndrome in rats via the modulation of both inflammatory and oxidative stress status. PLoS One 10:e0117516
Jain D, Saha S (2017) Antioxidant and antihyperglycaemic effects of naringenin arrest the progression of diabetic nephropathy in diabetic rats. Egypt Pharm J 16:144
Jha JC, Banal C, Chow BS, Cooper ME, Jandeleit-Dahm K (2016) Diabetes and kidney disease: role of oxidative stress. Antioxid Redox Signal 25:657–684
Jin J, Hu K, Ye M, Wu D, He Q (2018) Rapamycin reduces podocyte apoptosis and is involved in autophagy and mTOR/P70S6K/4EBP1 signaling. Cell Physiol Biochem 48:765–772
Kamble SP, Ghadyale VA, Patil RS, Haldavnekar VS, Arvindekar AU (2019) Inhibition of GLUT2 transporter by geraniol from Cymbopogon martinii: a novel treatment for diabetes mellitus in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Pharm Pharmacol 72:294–304
Kim SH, Park EJ, Lee CR, Chun JN, Cho NH, Kim IG, Lee S, Kim TW, Park HH, So I (2012) Geraniol induces cooperative interaction of apoptosis and autophagy to elicit cell death in PC-3 prostate cancer cells. Int J Oncol 40:1683–1690
Lieberthal W, Levine JS (2009) The role of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) in renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 20:2493–2502
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408
Loboda A, Sobczak M, Jozkowicz A, Dulak J (2016) TGF-β1/Smads and miR-21 in renal fibrosis and inflammation. Mediat Inflamm 2016:8319283–8319294
Lopez-Parra V, Mallavia B, Egido J, Gomez-Guerrero C (2012) Immunoinflammation in diabetic nephropathy: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic options. In: Chan J (ed) Diabetic nephropathy. University of Montreal, Montreal, pp 127–146
Mahimainathan L, Das F, Venkatesan B, Choudhury GG (2006) Mesangial cell hypertrophy by high glucose is mediated by downregulation of the tumor suppressor PTEN. Diabetes 55:2115
Malini P, Kanchana G, Rajadurai MURU (2011) Antibiabetic efficacy of ellagic acid in streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus in albino wistar rats. Asian J Pharm Clin Res 4:124–128
Mestry SN, Dhodi JB, Kumbhar SB, Juvekar AR (2017) Attenuation of diabetic nephropathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats by Punica granatum Linn. leaves extract. J Tradit Complement Med 7:273–280
Moreno JA, Gomez-Guerrero C, Mas S, Sanz AB, Lorenzo O, Ruiz-Ortega M, Opazo L, Mezzano S, Egido J (2018) Targeting inflammation in diabetic nephropathy: a tale of hope. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 27:917–930
Nagai K, Matsubara T, Mima A, Sumi E, Kanamori H, Iehara N, Fukatsu A, Yanagita M, Nakano T, Ishimoto Y (2005) Gas6 induces Akt/mTOR-mediated mesangial hypertrophy in diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int 68:552–561
Onozato ML, Tojo A, Goto A, Fujita T (2004) Radical scavenging effect of gliclazide in diabetic rats fed with a high cholesterol diet. Kidney Int 65:951–960
Packham DK, Alves TP, Dwyer JP, Atkins R, de Zeeuw D, Cooper M, Shahinfar S, Lewis JB, Heerspink HJL (2012) Relative incidence of ESRD versus cardiovascular mortality in proteinuric type 2 diabetes and nephropathy: results from the DIAMETRIC (Diabetes Mellitus Treatment for Renal Insufficiency Consortium) database. Am J Kidney Dis 59:75–83
Prasad SN (2014) Protective effects of geraniol (a monoterpene) in a diabetic neuropathy rat model: attenuation of behavioral impairments and biochemical perturbations. J Neurosci Res 92:1205–1216
Prasad S, Muralidhara M (2017) Analysis of the antioxidant activity of geraniol employing various in-vitro models: relevance to neurodegeneration in diabetic neuropathy. Asian J Pharm Clin Res 10:101
Selvaraja W, William NA (2011) Antidiabetic activity of crude stem extracts of coscinium fenestratum on streptozotocin-induced type-2 diabetic rats. Asian J Pharm Clin Res 4:47–51
Singh DK, Winocour P, Farrington K (2011) Oxidative stress in early diabetic nephropathy: fueling the fire. Nat Rev Endocrinol 7:176–184
Stanton RC (2012) Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, NADPH, and cell survival. IUBMB Life 64:362–369
Tojo A, Asaba K, Onozato ML (2007) Suppressing renal NADPH oxidase to treat diabetic nephropathy. Expert Opin Ther Targets 11:1011–1018
Wadie W, El-Tanbouly DM (2017) Vinpocetine mitigates proteinuria and podocytes injury in a rat model of diabetic nephropathy. Eur J Pharmacol 814:187–195
Wu W, Hu W, Han WB, Liu YL, Tu Y, Yang HM, Fang QJ, Zhou MY, Wan ZY, Tang RM, Tang HT, Wan YG (2018) Inhibition of Akt/mTOR/p70S6K signaling activity with huangkui capsule alleviates the early glomerular pathological changes in diabetic nephropathy. Front Pharmacol 9:443
Zhang YW, Wang X, Ren X, Zhang M (2018) Involvement of glucose-regulated protein 78 and spliced X-box binding protein 1 in the protective effect of gliclazide in diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 146:41–47
Zhang C, Ma P, Zhao Z, Jiang N, Lian D, Huo P, Yang H (2019) miRNA-mRNA regulatory network analysis of mesenchymal stem cell treatment in cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury identifies roles for miR-210/Serpine1 and miR-378/Fos in regulating inflammation. Mol Med Rep 20:1509–1522
Zhong X, Chung AC, Chen HY, Meng XM, Lan HY (2011) Smad3-mediated upregulation of miR-21 promotes renal fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 22:668–1681
Ziyadeh FN, Wolf G (2008) Pathogenesis of the podocytopathy and proteinuria in diabetic glomerulopathy. Curr Diabetes Rev 4:39–45
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Assoc. Prof. Mohamed A. Salaheldin, Department of Cytology and Histology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Cairo University, for his efforts in performing and explaining the histopathological examinations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yasmin A. Mohamed, Nada A. Sallam, Afaf A. Ain-Shoka, and Hekma A. Abdel-Latif conceived and designed the original idea of the research. Yasmin A. Mohamed conducted the experiments, carried out the statistical analyses, and wrote the manuscript. Yasmin A. Mohamed and Nada A. Sallam modified the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript. All data were generated in-house and no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
Animal use and care procedures were approved by the Ethical Committee for Animal Experimentation at Faculty of Pharmacy, Cairo University and concur with the US National Institutes of Health guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.The ariticle doesn't include human participants.This part is presented in the animals section in the mateial and methods section.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Said, Y.A.M., Sallam, N.A.A., Ain-Shoka, A.AM. et al. Geraniol ameliorates diabetic nephropathy via interference with miRNA-21/PTEN/Akt/mTORC1 pathway in rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 393, 2325–2337 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-020-01944-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-020-01944-9