Abstract
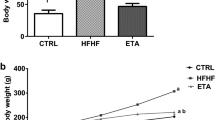
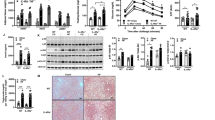
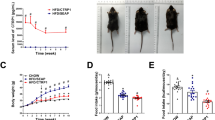
Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is a low-grade inflammation state that results from an interplay between genetic and environmental factors. The incidence of MetS among individuals with insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, elevated blood pressure, and obesity, which constitute the syndrome, is 40% in the Middle East. The absence of an approved therapeutic agent for MetS is one reason to investigate tocilizumab (TCZ), which might be effective in the treatment of MetS. Results have implicated interleukin 6 (IL-6) in the development of MetS, identifying inflammation as a critical factor in its etiology and offering hope for new therapeutic approaches development. Here, we evaluate whether tocilizumab can be used for metabolic syndrome treatment. We assigned rats to three groups, 8 rats each: a negative-control group, provided with standard rodent chow and water; a fructose-fed group, provided with standard rodent chow and 10% fructose in drinking water for 22 weeks; and a treatment group, fed as per the metabolic syndrome group but treated with tocilizumab (5 mg/kg/week, intraperitoneal) for the final 5 weeks. Treatment with TCZ successfully ameliorated the damaging effects of fructose by stabilizing body weight gain and through the normalization of serum biochemical parameters and histopathological examination. Significant differences in adipokine levels were perceived, resulting in a significant decline in serum leptin and interleukin 6 (IL-6) levels concurrent with adiponectin normalization. Tocilizumab might be an effective agent for the treatment of metabolic syndrome. However, further investigations on human subjects are needed before the clinical application of tocilizumab for this indication.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MetS:
-
Metabolic syndrome
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin 6
- TCZ:
-
Tocilizumab
- ALT:
-
Alanine aminotransaminase
- AST:
-
Aspartate aminotransaminase
- HDL:
-
High-density lipoprotein
- H&E:
-
Hematoxylin-eosin stain
- LDL:
-
Low-density lipoprotein
- i.p.:
-
Intraperitoneal
- HOMA-IR:
-
Hemostatic Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance
- GSH:
-
Reduced glutathione
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- MTC:
-
Masson’s trichrome
- SBP:
-
Systolic blood pressure
- IR:
-
Insulin receptor
- STAT3:
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3
References
Abate N, Chandalia M, Cabo-Chan AV Jr, Moe OW, Sakhaee K (2004) The metabolic syndrome and uric acid nephrolithiasis: novel features of renal manifestation of insulin resistance. Kidney Int 65(2):386–392
Abdelrahman AM, al Suleimani YM, Ashique M, Manoj P, Ali BH (2018) Effect of infliximab and tocilizumab on fructose-induced hyperinsulinemia and hypertension in rats. Biomed Pharmacother 105:182–186
Alberti KGM, Zimmet P, Shaw J (2005) The metabolic syndrome—a new worldwide definition. Lancet 366(9491):1059–1062
Ansarimoghaddam A et al. (2017) Prevalence of metabolic syndrome in middle-east countries: meta-analysis of cross-sectional studies. Diabetes Metab Syndr
Bataller R, Brenner DA (2005) Liver fibrosis. J Clin Invest 115(2):209–218
Beutler E (1963) Improved method for the determination of blood glutathione. J Lab Clin Med 61:882–888
Bowers LD (1980) Kinetic serum creatinine assays I. The role of various factors in determining specificity. Clin Chem 26(5):551–554
Bray GA, Nielsen SJ, Popkin BM (2004) Consumption of high-fructose corn syrup in beverages may play a role in the epidemic of obesity. Am J Clin Nutr 79(4):537–543
Bruun JM, Lihn AS, Verdich C, Pedersen SB, Toubro S, Astrup A, Richelsen B (2003) Regulation of adiponectin by adipose tissue-derived cytokines: in vivo and in vitro investigations in humans. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 285(3):E527–E533
Catena C et al (2003) Cellular mechanisms of insulin resistance in rats with fructose-induced hypertension. Am J Hypertens 16(11):973–978
Chen L, Chen R, Wang H, Liang F (2015) Mechanisms linking inflammation to insulin resistance. Int J Endocrinol 2015:1–9
Chrousos GP (2009) Stress and disorders of the stress system. Nat Rev Endocrinol 5(7):374–381
Conlon PJ, Lynn K, Winn MP, Quarles LD, Bembe ML, Pericak-Vance M, Speer M, Howell DN, on behalf of the International Collaborative Group for the Study of Familial Focal and Segmental Glomerulosclerosis (1999) Spectrum of disease in familial focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis. Kidney Int 56(5):1863–1871
Deen D (2004) Metabolic syndrome: time for action. Am Fam Physician. 69(12)
Di Luccia B et al (2015) Rescue of fructose-induced metabolic syndrome by antibiotics or faecal transplantation in a rat model of obesity. PLoS One 10(8):e0134893
Donath MY, Shoelson SE (2011) Type 2 diabetes as an inflammatory disease. Nat Rev Immunol 11(2):98–107
Eder K, Baffy N, Falus A, Fulop AK (2009) The major inflammatory mediator interleukin-6 and obesity. Inflamm Res 58(11):727–736
El-Abhar HS, Schaalan MF (2012) Topiramate-induced modulation of hepatic molecular mechanisms: an aspect for its anti-insulin resistant effect. PLoS One 7(5):e37757
Elliott SS, Keim NL, Stern JS, Teff K, Havel PJ (2002) Fructose, weight gain, and the insulin resistance syndrome. Am J Clin Nutr 76(5):911–922
Ellulu MS, Patimah I, Khaza'ai H, Rahmat A, Abed Y (2017) Obesity and inflammation: the linking mechanism and the complications. Arch Med Sci 13(4):851–863
Elmazar MM, el-Abhar HS, Schaalan MF, Farag NA (2013) Phytol/Phytanic acid and insulin resistance: potential role of phytanic acid proven by docking simulation and modulation of biochemical alterations. PLoS One 8(1):e45638
Fawcett J, Scott J (1960) A rapid and precise method for the determination of urea. J Clin Pathol 13(2):156–159
Fernandez-Real J-M, Vayreda M, Richart C, Gutierrez C, Broch M, Vendrell J, Ricart W (2001) Circulating interleukin 6 levels, blood pressure, and insulin sensitivity in apparently healthy men and women. J Clin Endocrinol Metabol 86(3):1154–1159
Forbes A, Correia MIT (2017) Current opinion in clinical nutrition & metabolic care, LWW
Furukawa S et al (2017) Increased oxidative stress in obesity and its impact on metabolic syndrome. J Clin Invest 114(12):1752–1761
Gaggini M, Morelli M, Buzzigoli E, DeFronzo R, Bugianesi E, Gastaldelli A (2013) Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and its connection with insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease. Nutrients 5(5):1544–1560
Galassetti P (2012) Inflammation and oxidative stress in obesity, metabolic syndrome, and diabetes. J Diabetes Res. 2012
Geidl-Flueck B, Gerber PA (2017) Insights into the hexose liver metabolism—glucose versus fructose. Nutrients 9(9):1026
Hançerli Y et al (2017) Efficacy of tocilizumab treatment in cerulein-induced experimental acute pancreatitis model in rats. Turk J Gastroenterol 28:485–491
Hashizume M, Mihara M (2011) IL-6 and lipid metabolism. Inflamm Regen 31(3):325–333
Hassan NF et al. (2019) Saroglitazar deactivates the hepatic LPS/TLR4 signaling pathway and ameliorates adipocyte dysfunction in rats with high-fat emulsion/LPS model-induced non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Inflammation: p. 1–15
Hersoug L-G, Møller P, Loft S (2018) Role of microbiota-derived lipopolysaccharide in adipose tissue inflammation, adipocyte size and pyroptosis during obesity. Nutr Res Rev, p. 1–11
Hirata H, Tetsumoto S, Kijima T, Kida H, Kumagai T, Takahashi R, Otani Y, Inoue K, Kuhara H, Shimada K, Nagatomo I, Takeda Y, Goya S, Yoshizaki K, Kawase I, Tachibana I, Kishimoto T, Kumanogoh A (2013) Favorable responses to tocilizumab in two patients with cancer-related cachexia. J Pain Symptom Manag 46(2):e9–e13
Jones G, Sebba A, Gu J, Lowenstein MB, Calvo A, Gomez-Reino JJ, Siri DA, Tomšič M, Alecock E, Woodworth T, Genovese MC (2010) Comparison of tocilizumab monotherapy versus methotrexate monotherapy in patients with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis: the AMBITION study. Ann Rheum Dis 69(01):88–96
Kadowaki T, Yamauchi T, Kubota N, Hara K, Ueki K, Tobe K (2006) Adiponectin and adiponectin receptors in insulin resistance, diabetes, and the metabolic syndrome. J Clin Invest 116(7):1784–1792
Kaur J (2014) A comprehensive review on metabolic syndrome. Cardiol Res Pract 2014:1–21
Kaya E, Sikka SC, Gur S (2015) A comprehensive review of metabolic syndrome affecting erectile dysfunction. J Sex Med 12(4):856–875
Kei S (1978) Serum lipid peroxide in cerebrovascular disorders determined by a new colorimetric method. Clin Chim Acta 90(1):37–43
Kielar ML, John R, Bennett M, Richardson JA, Shelton JM, Chen L, Jeyarajah DR, Zhou XJ, Zhou H, Chiquett B, Nagami GT, Lu CY (2005) Maladaptive role of IL-6 in ischemic acute renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol 16(11):3315–3325
Kleiner DE, Brunt EM, van Natta M, Behling C, Contos MJ, Cummings OW, Ferrell LD, Liu YC, Torbenson MS, Unalp-Arida A, Yeh M, McCullough AJ, Sanyal AJ, Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Clinical Research Network (2005) Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 41(6):1313–1321
Kotsis V, Stabouli S, Papakatsika S, Rizos Z, Parati G (2010) Mechanisms of obesity-induced hypertension. Hypertens Res 33(5):386–393
Liu Z, Liang S, Que S, Zhou L, Zheng S, Mardinoglu A (2018) Meta-analysis of adiponectin as a biomarker for the detection of metabolic syndrome. Front Physiol. 9
López-Mejías R et al. (2018) SAT0170 Anti-il-6 therapy modulates leptin in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, BMJ Publishing Group Ltd
Lutz TA (2016) The brain needs interleukin-6 (IL-6) to maintain a “healthy” energy balance. Focus on “IL-6 ameliorates defective leptin sensitivity in DIO ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus neurons”. Am J Phys Regul Integr Comp Phys 311(6):R989–R991
Mahmoud AA, Elshazly SM (2014) Ursodeoxycholic acid ameliorates fructose-induced metabolic syndrome in rats. PLoS One 9(9):e106993
Matthews D et al (1985) Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and β-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 28(7):412–419
Mihara M, Ohsugi Y, Kishimoto T (2011) Tocilizumab, a humanized anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody, for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Open Access Rheumatol 3:19
Morris PG, Hudis CA, Giri D, Morrow M, Falcone DJ, Zhou XK, du B, Brogi E, Crawford CB, Kopelovich L, Subbaramaiah K, Dannenberg AJ (2011) Inflammation and increased aromatase expression occur in the breast tissue of obese women with breast cancer. Cancer Prev Res 4(7):1021–1029
Nasr G et al (2010) Screening for diabetes and cardiovascular risk factors among Egyptian population. Clin Diabetes 9:127–135
Natsume M, Tsuji H, Harada A, Akiyama M, Yano T, Ishikura H, Nakanishi I, Matsushima K, Kaneko SI, Mukaida N (1999) Attenuated liver fibrosis and depressed serum albumin levels in carbon tetrachloride-treated IL-6-deficient mice. J Leukoc Biol 66(4):601–608
Nonogaki K, Fuller GM, Fuentes NL, Moser AH, Staprans I, Grunfeld C, Feingold KR (1995a) Interleukin-6 stimulates hepatic triglyceride secretion in rats. Endocrinology 136(5):2143–2149
Nonogaki K et al. (1995b) Interleukin-6 stimulates hepatic triglyceride secretion in rats. Vol. 136. 2143–9
Otero-Losada M, Gómez Llambí H, Ottaviano G, Cao G, Müller A, Azzato F, Ambrosio G, Milei J (2016) Cardiorenal involvement in metabolic syndrome induced by cola drinking in rats: proinflammatory cytokines and impaired antioxidative protection. Mediat Inflamm 2016:1–11
Patel VS, Chan ME, Pagnotti GM, Frechette DM, Rubin J, Rubin CT (2017) Incorporating refractory period in mechanical stimulation mitigates obesity-induced adipose tissue dysfunction in adult mice. Obesity 25(10):1745–1753
Prasad GR (2014) Metabolic syndrome and chronic kidney disease: current status and future directions. World J Nephrol 3(4):210–219
Reitman S, Frankel S (1957) A colorimetric method for the determination of serum glutamic oxalacetic and glutamic pyruvic transaminases. Am J Clin Pathol 28(1):56–63
Ricci G, Pirillo I, Tomassoni D, Sirignano A, Grappasonni I (2017) Metabolic syndrome, hypertension, and nervous system injury: epidemiological correlates. Clin Exp Hypertens 39(1):8–16
Rodrigues KF, Pietrani NT, Bosco AA, Campos FMF, Sandrim VC, Gomes KB (2017) IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-10 levels/polymorphisms and their association with type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity in Brazilian individuals. Arch Endocrinol Metab 61(5):438–446
Sánchez-Lozada LG, Tapia E, Jiménez A, Bautista P, Cristóbal M, Nepomuceno T, Soto V, Ávila-Casado C, Nakagawa T, Johnson RJ, Herrera-Acosta J, Franco M (2007) Fructose-induced metabolic syndrome is associated with glomerular hypertension and renal microvascular damage in rats. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 292(1):F423–F429
Schultz O, Oberhauser F, Saech J, Rubbert-Roth A, Hahn M, Krone W, Laudes M (2010) Effects of inhibition of interleukin-6 signalling on insulin sensitivity and lipoprotein (a) levels in human subjects with rheumatoid diseases. PLoS One 5(12):e14328
Schwarz J-M, Noworolski SM, Wen MJ, Dyachenko A, Prior JL, Weinberg ME, Herraiz LA, Tai VW, Bergeron N, Bersot TP, Rao MN, Schambelan M, Mulligan K (2015) Effect of a high-fructose weight-maintaining diet on lipogenesis and liver fat. J Clin Endocrinol Metabol 100(6):2434–2442
Stenlöf K, Wernstedt I, Fjällman T, Wallenius V, Wallenius K, Jansson JO (2003) Interleukin-6 levels in the central nervous system are negatively correlated with fat mass in overweight/obese subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metabol 88(9):4379–4383
Takashi K (2006) Adiponectin and adiponectin receptors in insulin resistance, diabetes, and the metabolic syndrome. J Clin Invest 116:1784–1792
Tappy L, Lê K-A (2010) Metabolic effects of fructose and the worldwide increase in obesity. Physiol Rev 90(1):23–46
Teixeira AA, Quinto BMR, Dalboni MA, Rodrigues CJO, Batista MC (2015) Association of IL-6 polymorphism-174G/C and metabolic syndrome in hypertensive patients. Biomed Res Int 2015:1–6
ter Horst KW, Serlie MJ (2017) Fructose consumption, lipogenesis, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Nutrients 9(9):981
Tilg H, Moschen AR (2008) Inflammatory mechanisms in the regulation of insulin resistance. Mol Med 14(3–4):222–231
Tournadre A, Pereira B, Dutheil F, Giraud C, Courteix D, Sapin V, Frayssac T, Mathieu S, Malochet-Guinamand S, Soubrier M (2017) Changes in body composition and metabolic profile during interleukin 6 inhibition in rheumatoid arthritis. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 8(4):639–646
Tran LT, Yuen VG, McNeill JH (2009) The fructose-fed rat: a review on the mechanisms of fructose-induced insulin resistance and hypertension. Mol Cell Biochem 332(1–2):145–159
Tsai J-P (2017) The association of serum leptin levels with metabolic diseases. Tzu-Chi Med J 29(4):192–196
Urushima H et al (2015) Tocilizumab increases serum adiponectin and reduces serum fatty acid binding protein 4 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Endocrinol Metab 4(5):143–147
Wellen KE, Hotamisligil GS (2005) Inflammation, stress, and diabetes. J Clin Invest 115(5):1111–1119
Wu D, Ren Z, Pae M, Guo W, Cui X, Merrill AH, Meydani SN (2007) Aging up-regulates expression of inflammatory mediators in mouse adipose tissue. J Immunol 179(7):4829–4839
Wynn TA, Ramalingam TR (2012) Mechanisms of fibrosis: therapeutic translation for fibrotic disease. Nat Med 18(7):1028–1040
Xue H, Yuan G, Guo X, Liu Q, Zhang J, Gao X, Guo X, Xu S, Li T, Shao Q, Yan S, Li G (2016) A novel tumor-promoting mechanism of IL6 and the therapeutic efficacy of tocilizumab: hypoxia-induced IL6 is a potent autophagy initiator in glioblastoma via the p-STAT3-MIR155-3p-CREBRF pathway. Autophagy 12(7):1129–1152
Yang Y –z et al (2019) Magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate ameliorates high fructose-induced liver fibrosis in rat by increasing miR-375-3p to suppress JAK2/STAT3 pathway and TGF-β1/Smad signaling. Acta Pharmacol Sin 40(7):879–894
Acknowledgments
This manuscript has been appreciatively scientifically edited, by nature research editing service.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HY: conceptualization, formal analysis, funding acquisition, conducted experiments, and writing—original draft. AH: investigation, conducted experiments, and review and editing. M.R.E: formal analysis, funding acquisition, and review and editing. M.Y.A: conceptualization, formal analysis, and writing—review and editing. M.F.E: conceptualization, writing—review and editing, and supervision. All authors read and approved the manuscript. All data were generated in-house and no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yahia, H., Hassan, A., El-Ansary, M.R. et al. IL-6/STAT3 and adipokine modulation using tocilizumab in rats with fructose-induced metabolic syndrome. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 393, 2279–2292 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-020-01940-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-020-01940-z