Abstract
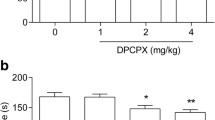
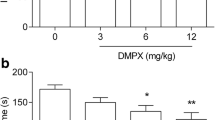
Considering the involvement of GABAergic system in the action of the fast-acting antidepressant ketamine, and that agmatine may exert an antidepressant-like effect through mechanisms similar to ketamine, the purpose of the present study was to evaluate the involvement of GABAA and GABAB receptors in the antidepressant-like effect of agmatine. The administration of muscimol (0.1 mg/kg, i.p., GABAA receptor agonist) or diazepam (0.05 mg/kg, p.o., GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator) at doses that caused no effect in the tail suspension test (TST) combined with a subeffective dose of agmatine (0.0001 mg/kg, p.o.) produced a synergistic antidepressant-like effect in the TST. In another set of experiments, the administration of baclofen (1 mg/kg, i.p., GABAB receptor agonist) abolished the reduction of immobility time in the TST elicited by agmatine (0.1 mg/kg, p.o., active dose). In another cohort of animals, treatment with NMDA (0.1 pmol/site, i.c.v.) prevented the antidepressant-like effect of the combined administration of agmatine and muscimol as well as ketamine and muscimol in the TST. Results suggest that the effect of agmatine in the TST may involve an activation of GABAA receptors dependent on NMDA receptor inhibition, similar to ketamine, as well as modulation of GABAB receptors.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdallah CG, Salas R, Jackowski A, Baldwin P, Sato JR, Mathew SJ (2015) Hippocampal volume and the rapid antidepressant effect of ketamine. J Psychopharmacol 29:591–595
Andrade C (2017) Ketamine for depression, 5: potential pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic drug interactions. J Clin Psychiatry 78:858–861
Arranz B, Cowburn R, Eriksson A, Vestling M, Marcusson J (1992) Gamma-aminobutyric acid-B (GABAB) binding sites in postmortem suicide brains. Neuropsychobiology 26:33–36
Autry AE, Adachi M, Nosyreva E, Na ES, Los MF, Cheng PF, Kavalali ET, Monteggia LM (2011) NMDA receptor blockade at rest triggers rapid behavioural antidepressant responses. Nature 475:91–95
Banasr M, Lepack A, Fee C et al (2017) Characterization of GABAergic marker expression in the chronic unpredictable stress model of depression. Chronic Stress (Thousand Oaks) 1:30
Bergfeld IO, Mantione M, Figee M, Schuurman PR, Lok A, Denys D (2018) Treatment-resistant depression and suicidality. J Affect Disord 235:362–367
Berman RM, Cappiello A, Anand A, Oren DA, Heninger GR, Charney DS, Krystal JH (2000) Antidepressant effects of ketamine in depressed patients. Biol Psychiatry 47:351–354
Bettio LE, Cunha MP, Budni J et al (2012) Guanosine produces an antidepressant-like effect through the modulation of NMDA receptors, nitric oxide-cGMP and PI3K/mTOR pathways. Behav Brain Res 234:137–148
Bhagwagar Z, Wylezinska M, Jezzard P, Evans J, Boorman E, M Matthews P, J Cowen P (2008) Low GABA concentrations in occipital cortex and anterior cingulate cortex in medication-free, recovered depressed patients. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 11:255–260
Biggio G, Concas A, Corda MG, Giorgi O, Sanna E, Serra M (1990) GABAergic and dopaminergic transmission in the rat cerebral cortex: effect of stress, anxiolytic and anxiogenic drugs. Pharmacol Ther 48:121–142
Celada P, Puig M, Amargos-Bosch M et al (2004) The therapeutic role of 5-HT1A and 5-HT2A receptors in depression. J Psychiatry Neurosci 29:252–265
Choudary PV, Molnar M, Evans SJ et al (2005) Altered cortical glutamatergic and GABAergic signal transmission with glial involvement in depression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:15653–15658
Clevenger SS, Malhotra D, Dang J, Vanle B, IsHak WW (2018) The role of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in preventing relapse of major depressive disorder. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol 8:49–58
Cross JA, Cheetham SC, Crompton MR, Katona CLE, Horton RW (1988) Brain GABAB binding sites in depressed suicide victims. Psychiatry Res 26:119–129
Cunha MP, Pazini FL, Ludka FK, Rosa JM, Oliveira Á, Budni J, Ramos-Hryb AB, Lieberknecht V, Bettio LEB, Martín-de-Saavedra MD, López MG, Tasca CI, Rodrigues ALS (2015) The modulation of NMDA receptors and L-arginine/nitric oxide pathway is implicated in the anti-immobility effect of creatine in the tail suspension test. Amino Acids 47:795–811
Dixit MP, Thakre PP, Pannase AS, Aglawe MM, Taksande BG, Kotagale NR (2014) Imidazoline binding sites mediates anticompulsive-like effect of agmatine in marble-burying behavior in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 732:26–31
Farzin D, Mansouri N (2006) Antidepressant-like effect of harmane and other beta-carbolines in the mouse forced swim test. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 6:324–328
Freitas AE, Bettio LE, Neis VB et al (2014) Agmatine abolishes restraint stress-induced depressive-like behavior and hippocampal antioxidant imbalance in mice. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 50:143–150
Gao Y, Zhou JJ, Zhu Y, Wang L, Kosten TA, Zhang X, Li DP (2017) Neuroadaptations of presynaptic and postsynaptic GABAB receptor function in the paraventricular nucleus in response to chronic unpredictable stress. Br J Pharmacol 174:2929–2940
Gawali NB, Bulani VD, Chowdhury AA, Deshpande PS, Nagmoti DM, Juvekar AR (2016) Agmatine ameliorates lipopolysaccharide induced depressive-like behaviour in mice by targeting the underlying inflammatory and oxido-nitrosative mediators. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 149:1–8
Gawali NB, Bulani VD, Gursahani MS, Deshpande PS, Kothavade PS, Juvekar AR (2017) Agmatine attenuates chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced anxiety, depression-like behaviours and cognitive impairment by modulating nitrergic signalling pathway. Brain Res 1663:66–77
Glennon RA, Dukat M, Grella B, Hong SS, Costantino L, Teitler M, Smith C, Egan C, Davis K, Mattson MV (2000) Binding of beta-carbolines and related agents at serotonin (5-HT(2) and 5-HT(1A)), dopamine (D(2)) and benzodiazepine receptors. Drug Alcohol Depend 60:121–132
Gomez AF, Barthel AL, Hofmann SG (2018) Comparing the efficacy of benzodiazepines and serotonergic anti-depressants for adults with generalized anxiety disorder: a meta-analytic review. Expert Opin Pharmacother 19:883–894
Gray JA, Green AR (1987) Increased GABAB receptor function in mouse frontal cortex after repeated administration of antidepressant drugs or electroconvulsive shocks. Br J Pharmacol 92:357–362
Hardeveld F, Spijker J, De Graaf R et al (2013) Recurrence of major depressive disorder and its predictors in the general population: results from the Netherlands Mental Health Survey and Incidence Study (NEMESIS). Psychol Med 43:39–48
Heinzel A, Steinke R, Poeppel TD, Grosser O, Bogerts B, Otto H, Northoff G (2008) S-ketamine and GABA-A-receptor interaction in humans: an exploratory study with I-123-iomazenil SPECT. Hum Psychopharmacol 23:549–554
Hill DR (1985) GABAB receptor modulation of adenylate cyclase activity in rat brain slices. Br J Pharmacol 84:249–257
Kaster MP, Gadotti VM, Calixto JB, Santos ARS, Rodrigues ALS (2012) Depressive-like behavior induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha in mice. Neuropharmacology 62:419–426
Korf J, Venema K (1983) Desmethylimipramine enhances the release of endogenous GABA and other neurotransmitter amino acids from the rat thalamus. J Neurochem 40:946–950
Krystal JH, Perry EB Jr, Gueorguieva R et al (2005) Comparative and interactive human psychopharmacologic effects of ketamine and amphetamine: implications for glutamatergic and dopaminergic model psychoses and cognitive function. Arch Gen Psychiatry 62:985–994
Song C, Leonard BE (2005) The olfactory bulbectomised rat as a model of depression. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 29:627–647
Li NX, Lee B, Liu RJ, Banasr M, Dwyer JM, Iwata M, Li XY, Aghajanian G, Duman RS (2010) mTOR-dependent synapse formation underlies the rapid antidepressant effects of NMDA antagonists. Science 329:959–964
Li N, Liu RJ, Dwyer JM, Banasr M, Lee B, Son H, Li XY, Aghajanian G, Duman RS (2011) Glutamate N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists rapidly reverse behavioral and synaptic deficits caused by chronic stress exposure. Biol Psychiatry 69:754–761
Luscher B, Fuchs T (2015) GABAergic control of depression-related brain states. Adv Pharmacol 73:97–144
Luscher B, Shen Q, Sahir N (2011) The GABAergic deficit hypothesis of major depressive disorder. Mol Psychiatry 16:383–406
Magni G, Garreau M, Orofiamma B et al (1989) Fengabine, a new GABAmimetic agent in the treatment of depressive disorders: an overview of six double-blind studies versus tricyclics. Neuropsychobiology 20:126–131
Mathew SJ, Charney DS (2009) Publication bias and the efficacy of antidepressants. Am J Psychiatry 166:140–145
McCarson KE, Duric V, Reisman SA et al (2006) GABA(B) receptor function and subunit expression in the rat spinal cord as indicators of stress and the antinociceptive response to antidepressants. Brain Res 1068:109–117
Meylan EM, Breuillaud L, Seredenina T et al (2016) Involvement of the agmatinergic system in the depressive-like phenotype of the Crtc1 knockout mouse model of depression. Transl Psychiatry 6:1–11
Mohler H (2012) The GABA system in anxiety and depression and its therapeutic potential. Neuropharmacology 62:42–53
Moretti M, Neis VB, Matheus FC, Cunha MP, Rosa PB, Ribeiro CM, Rodrigues ALS, Prediger RD (2015) Effects of agmatine on depressive-like behavior induced by intracerebroventricular administration of 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP(+)). Neurotox Res 28:222–231
Muir JK, Lobner D, Monyer H, Choi DW (1996) GABAA receptor activation attenuates excitotoxicity but exacerbates oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced neuronal injury in vitro. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 16:1211–1218
Neis VB, Manosso LM, Moretti M, Freitas AE, Daufenbach J, Rodrigues ALS (2014) Depressive-like behavior induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha is abolished by agmatine administration. Behav Brain Res 261:336–344
Neis VB, Bettio LEB, Moretti M, Rosa PB, Ribeiro CM, Freitas AE, Gonçalves FM, Leal RB, Rodrigues ALS (2016a) Acute agmatine administration, similar to ketamine, reverses depressive-like behavior induced by chronic unpredictable stress in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 150-151:108–114
Neis VB, Moretti M, Bettio LE et al (2016b) Agmatine produces antidepressant-like effects by activating AMPA receptors and mTOR signaling. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 26:959–971
Neis VB, Rosa PB, Olescowicz G, Rodrigues ALS (2017) Therapeutic potential of agmatine for CNS disorders. Neurochem Int 108:318–331
Neis VB, Bettio LB, Moretti M, Rosa PB, Olescowicz G, Fraga DB, Gonçalves FM, Freitas AE, Heinrich IA, Lopes MW, Leal RB, Rodrigues ALS (2018) Single administration of agmatine reverses the depressive-like behavior induced by corticosterone in mice: comparison with ketamine and fluoxetine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 173:44–50
O’Leary OF, Felice D, Galimberti S et al (2014) GABAB(1) receptor subunit isoforms differentially regulate stress resilience. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:15232–15237
Oh DH, Son H, Hwang S, Kim SH (2012) Neuropathological abnormalities of astrocytes, GABAergic neurons, and pyramidal neurons in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortices of patients with major depressive disorder. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 22:330–338
Parker GB, Graham RK (2015) Determinants of treatment-resistant depression: the salience of benzodiazepines. J Nerv Ment Dis 203:659–663
Patel MRBR, Kardile DP, Naik RA (2011) Agmatine inhibit the tolerance to the anxiolytic effect of diazepam in rats. Int J Pharm Appl Sci:44–51
Paxinos G, Franklin KBJ (2004) The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Elsevier Academic Press, Amsterdam
Petty F, Fulton M, Kramer GL, Kram M, Davis LL, Rush AJ (1999) Evidence for the segregation of a major gene for human plasma GABA levels. Mol Psychiatry 4:587–589
Pigott HE, Leventhal AM, Alter GS, Boren JJ (2010) Efficacy and effectiveness of antidepressants: current status of research. Psychother Psychosom 79:267–279
Piletz JE, Aricioglu F, Cheng JT, Fairbanks CA, Gilad VH, Haenisch B, Halaris A, Hong S, Lee JE, Li J, Liu P, Molderings GJ, Rodrigues ALS, Satriano J, Seong GJ, Wilcox G, Wu N, Gilad GM (2013) Agmatine: clinical applications after 100 years in translation. Drug Discov Today 18:880–893
Post RM, Ketter TA, Joffe RT, Kramlinger KL (1991) Lack of beneficial effects of l-baclofen in affective disorder. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 6:197–207
Price RB, Shungu DC, Mao X, Nestadt P, Kelly C, Collins KA, Murrough JW, Charney DS, Mathew SJ (2009) Amino acid neurotransmitters assessed by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy: relationship to treatment resistance in major depressive disorder. Biol Psychiatry 65:792–800
Ren Z, Pribiag H, Jefferson SJ, Shorey M, Fuchs T, Stellwagen D, Luscher B (2016) Bidirectional homeostatic regulation of a depression-related brain state by gamma-aminobutyric acidergic deficits and ketamine treatment. Biol Psychiatry 80:457–468
Rodrigues AL, Rocha JB, Mello CF, Souza DO (1996) Effect of perinatal lead exposure on rat behaviour in open-field and two-way avoidance tasks. Pharmacol Toxicol 79:150–156
Rosa PB, Neis VB, Ribeiro CM, Moretti M, Rodrigues ALS (2016) Antidepressant-like effects of ascorbic acid and ketamine involve modulation of GABAA and GABAB receptors. Pharmacol Rep 68:996–1001
Sapkota K, Mao Z, Synowicki P, Lieber D, Liu M, Ikezu T, Gautam V, Monaghan DT (2016) GluN2D N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor subunit contribution to the stimulation of brain activity and gamma oscillations by ketamine: implications for schizophrenia. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 356:702–711
Sigel E, Ernst M (2018) The benzodiazepine binding sites of GABAA receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci 39:659–671
Spijker J, van Straten A, Bockting CL et al (2013) Psychotherapy, antidepressants, and their combination for chronic major depressive disorder: a systematic review. Can J Psychiatr 58:386–392
Steru L, Chermat R, Thierry B, Simon P (1985) The tail suspension test: a new method for screening antidepressants in mice. Psychopharmacology 85:367–370
Taksande BG, Kotagale NR, Patel MR, Shelkar GP, Ugale RR, Chopde CT (2010) Agmatine, an endogenous imidazoline receptor ligand modulates ethanol anxiolysis and withdrawal anxiety in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 637:89–101
Taksande BG, Sharma O, Aglawe MM, Kale MB, Gawande DY, Umekar MJ, Kotagale NR (2017) Acute orexigenic effect of agmatine involves interaction between central alpha2-adrenergic and GABAergic receptors. Biomed Pharmacother 93:939–947
Tavares MK, Dos Reis S, Platt N et al (2018) Agmatine potentiates neuroprotective effects of subthreshold concentrations of ketamine via mTOR/S6 kinase signaling pathway. Neurochem Int 118:275–285
Vasavada MM, Leaver AM, Espinoza RT, Joshi SH, Njau SN, Woods RP, Narr KL (2016) Structural connectivity and response to ketamine therapy in major depression: a preliminary study. J Affect Disord 190:836–841
Wang HY, Kuo ZC, Fu YS, Chen RF, Min MY, Yang HW (2015) GABAB receptor-mediated tonic inhibition regulates the spontaneous firing of locus coeruleus neurons in developing rats and in citalopram-treated rats. J Physiol 593:161–180
Wang DS, Penna A, Orser BA (2017) Ketamine increases the function of gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptors in hippocampal and cortical neurons. Anesthesiology 126:666–677
Widman AJ, McMahon LL (2018) Disinhibition of CA1 pyramidal cells by low-dose ketamine and other antagonists with rapid antidepressant efficacy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115:3007–3016
Workman ER, Niere F, Raab-Graham KF (2013) mTORC1-dependent protein synthesis underlying rapid antidepressant effect requires GABABR signaling. Neuropharmacology 73:192–203
Yamamoto T, Nakayama T, Yamaguchi J, Matsuzawa M, Mishina M, Ikeda K, Yamamoto H (2016) Role of the NMDA receptor GluN2D subunit in the expression of ketamine-induced behavioral sensitization and region-specific activation of neuronal nitric oxide synthase. Neurosci Lett 610:48–53
Zarate CA, Singh JB, Carlson PJ, Brutsche NE, Ameli R, Luckenbaugh DA, Charney DS, Manji HK (2006) A randomized trial of an N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist in treatment-resistant major depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 63:856–864
Zhang T, Du Y, Liu X et al (2019) Study on antidepressant-like effect of protoilludane sesquiterpenoid aromatic esters from Armillaria Mellea. Nat Prod Res:1–4
Zheng W, Xiao-Hong L, Xiao-Min Z et al (2019) Adjunctive ketamine and electroconvulsive therapy for major depressive disorder: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Affec Dis 250:123–131
Zomkowski ADE, Hammes L, Lin J, Calixto JB, Santos ARS, Rodrigues ALS (2002) Agmatine produces antidepressant-like effects in two models of depression in mice. Neuroreport 13:387–391
Zomkowski ADE, Rosa AO, Lin J et al (2004) Evidence for serotonin receptor subtypes involvement in agmatine antidepressant like-effect in the mouse forced swimming test. Brain Res 1023:253–263
Funding
This study was supported by grants from Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) # 449436/2014-4, # 310113/2017-2 and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES). ALSR is a CNPq Research Fellow. V.B.N. acknowledges postdoctoral funding from the CNPq (158126/2018-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
VBN, GO, and ALSR designed the study and wrote the protocol. VBN, MM, PBR, NP, and AFR conducted experiments. VBN, AFR, and PBR analyzed data. MM and PBR provided essential critical analysis of the manuscript. VBN and ALSR wrote the manuscript and managed the literature searches. All authors contributed to the design, acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of data. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Animals were used according to the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, and the protocol and experiments were approved by the Ethical Committee of Animal Research of Federal University of Santa Catarina.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neis, V.B., Rosado, A.F., Olescowicz, G. et al. The involvement of GABAergic system in the antidepressant-like effect of agmatine. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 393, 1931–1939 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-020-01910-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-020-01910-5