Abstract
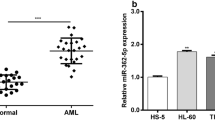
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a widely prevalent disease worldwide and poses a large threat to public health. Previous studies have shown that AML is associated with cytogenetic heterogeneity, complex subtypes, and different therapeutic approaches. In this study, we found that miR-486 was upregulated in AML using both The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database and patient tissues. After knockdown of miR-486 by short hairpin RNA (shRNA), we discovered that miR-486 was required for cell proliferation. Through miRNA profile analysis and a dual-luciferase reporter assay, suppressor of cytokine signaling 2 (SOCS2) was identified as a direct target of miR-486. Therefore, by silencing SOCS2, a negative regulator of the Janus kinase (JAK)–signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) pathway, miR-486 enhanced JAK-STAT3 activity and promoted cell proliferation. The miR-486-SOCS2-STAT3 proliferation axis is therefore involved in the pathogenesis of AML, providing a novel molecular mechanism and diagnostic and therapeutic clues for AML.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhter A, Farooq F, Elyamany G, Mughal MK, Rashid-Kolvear F, Shabani-Rad MT, Street L, Mansoor A (2018) Acute myeloid leukemia (AML): upregulation of BAALC/MN1/MLLT11/EVI1 gene cluster relate with poor overall survival and a possible linkage with coexpression of MYC/BCL2 proteins. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 26:483–488
Bai Z, Yao Q, Sun Z, Xu F, Zhou J (2019) Prognostic value of mRNA expression of MAP4K family in acute myeloid leukemia. Technol Cancer Res Treat 18:1533033819873927
Bournazou E, Bromberg J (2013) Targeting the tumor microenvironment: JAK-STAT3 signaling. Jak-stat 2:e23828
Chen P, Price C, Li Z, Li Y, Cao D, Wiley A, He C, Gurbuxani S, Kunjamma RB, Huang H, Jiang X, Arnovitz S, Xu M, Hong GM, Elkahloun AG, Neilly MB, Wunderlich M, Larson RA, Le Beau MM, Mulloy JC, Liu PP, Rowley JD, Chen J (2013) miR-9 is an essential oncogenic microRNA specifically overexpressed in mixed lineage leukemia-rearranged leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:11511–11516
Di Leva G, Garofalo M, Croce CM (2014) MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu Rev Pathol 9:287–314
Dohner H, Weisdorf DJ, Bloomfield CD (2015) Acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 373:1136–1152
Duan R, Zhang Z, Zheng F, Wang L, Guo J, Zhang T, Dai X, Zhang S, Yang D, Kuang R, Wang G, He C, Hakeem A, Shu C, Yin P, Lou X, Zeng F, Liang H, Xia F (2017) Combining protein and miRNA quantification for bladder cancer analysis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:23420–23427
Feng C, Sun P, Hu J, Feng H, Li M, Liu G, Pan Y, Feng Y, Xu Y, Feng K, Feng Y (2017) miRNA-556-3p promotes human bladder cancer proliferation, migration and invasion by negatively regulating DAB2IP expression. Int J Oncol 50:2101–2112
Gerloff D, Grundler R, Wurm AA, Brauer-Hartmann D, Katzerke C, Hartmann JU, Madan V, Muller-Tidow C, Duyster J, Tenen DG, Niederwieser D, Behre G (2015) NF-kappaB/STAT5/miR-155 network targets PU.1 in FLT3-ITD-driven acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 29:535–547
Ghamloush F, Ghayad SE, Rammal G, Fahs A, Ayoub AJ, Merabi Z, Harajly M, Zalzali H, Saab R (2019) The PAX3-FOXO1 oncogene alters exosome miRNA content and leads to paracrine effects mediated by exosomal miR-486. Sci Rep 9:14242
He M, Wang G, Jiang L, Qiu C, Li B, Wang J, Fu Y (2017) miR-486 suppresses the development of osteosarcoma by regulating PKC-delta pathway. Int J Oncol 50:1590–1600
Honda K, Yanai H, Negishi H, Asagiri M, Sato M, Mizutani T, Shimada N, Ohba Y, Takaoka A, Yoshida N, Taniguchi T (2005) IRF-7 is the master regulator of type-I interferon-dependent immune responses. Nature 434:772–777
Ivashkiv LB, Donlin LT (2014) Regulation of type I interferon responses. Nat Rev Immunol 14:36–49
Lange S, Banerjee I, Carrion K, Serrano R, Habich L, Kameny R, Lengenfelder L, Dalton N, Meili R, Borgeson E, Peterson K, Ricci M, Lincoln J, Ghassemian M, Fineman J, Del Alamo JC, Nigam V (2019) miR-486 is modulated by stretch and increases ventricular growth. JCI Insight 4
Li N, Sun ZH, Fang M, Xin JY, Wan CY (2017) Long non-coding RNA ZFAS1 sponges miR-486 to promote osteosarcoma cells progression and metastasis in vitro and vivo. Oncotarget 8:104160–104170
Lin L, Amin R, Gallicano GI, Glasgow E, Jogunoori W, Jessup JM, Zasloff M, Marshall JL, Shetty K, Johnson L, Mishra L, He AR (2009) The STAT3 inhibitor NSC 74859 is effective in hepatocellular cancers with disrupted TGF-beta signaling. Oncogene 28:961–972
Liu W, Rodgers GP (2016) Olfactomedin 4 expression and functions in innate immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 35:201–212
Liu Y, Zhang J, Xing C, Wei S, Guo N, Wang Y (2018) miR-486 inhibited osteosarcoma cells invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting PIM1. Cancer Biomark Sect A Dis Mark 23:269–277
Liu Y, Cheng Z, Pang Y, Cui L, Qian T, Quan L, Zhao H, Shi J, Ke X, Fu L (2019) Role of microRNAs, circRNAs and long noncoding RNAs in acute myeloid leukemia. J Hematol Oncol 12:51
Lonetti A, Pession A, Masetti R (2019) Targeted therapies for pediatric AML: gaps and perspective. Front Pediatr 7:463
Lujambio A, Lowe SW (2012) The microcosmos of cancer. Nature 482:347–355
Ma YY, Tao HQ (2012) Microribonucleic acids and gastric cancer. Cancer Sci 103:620–625
Morris R, Kershaw NJ, Babon JJ (2018) The molecular details of cytokine signaling via the JAK/STAT pathway. Protein Sci Publ Protein Soc 27:1984–2009
Nguyen CH, Gluxam T, Schlerka A, Bauer K, Grandits AM, Hackl H, Dovey O, Zochbauer-Muller S, Cooper JL, Vassiliou GS, Stoiber D, Wieser R, Heller G (2019) SOCS2 is part of a highly prognostic 4-gene signature in AML and promotes disease aggressiveness. Sci Rep 9:9139
Ojha R, Nandani R, Pandey RK, Mishra A, Prajapati VK (2019) Emerging role of circulating microRNA in the diagnosis of human infectious diseases. J Cell Physiol 234:1030–1043
Peng F, Li H, Xiao H, Li L, Li Y, Wu Y (2017) Identification of a three miRNA signature as a novel potential prognostic biomarker in patients with bladder cancer. Oncotarget 8:105553–105560
Schneider WM, Chevillotte MD, Rice CM (2014) Interferon-stimulated genes: a complex web of host defenses. Annu Rev Immunol 32:513–545
Schust J, Sperl B, Hollis A, Mayer TU, Berg T (2006) Stattic: a small-molecule inhibitor of STAT3 activation and dimerization. Chem Biol 13:1235–1242
Siddiquee K, Zhang S, Guida WC, Blaskovich MA, Greedy B, Lawrence HR, Yip ML, Jove R, McLaughlin MM, Lawrence NJ, Sebti SM, Turkson J (2007) Selective chemical probe inhibitor of Stat3, identified through structure-based virtual screening, induces antitumor activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:7391–7396
Sun H, Cui C, Xiao F, Wang H, Xu J, Shi X, Yang Y, Zhang Q, Zheng X, Yang X, Wu C, Wang L (2015) miR-486 regulates metastasis and chemosensitivity in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting CLDN10 and CITRON. Hepatol Res 45:1312–1322
Venugopal S, Bar-Natan M, Mascarenhas JO (2019) JAKs to STATs: a tantalizing therapeutic target in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Rev 100634
Vitali C, Bassani C, Chiodoni C, Fellini E, Guarnotta C, Miotti S, Sangaletti S, Fuligni F, De Cecco L, Piccaluga PP, Colombo MP, Tripodo C (2015) SOCS2 controls proliferation and stemness of hematopoietic cells under stress conditions and its deregulation marks unfavorable acute leukemias. Cancer Res 75:2387–2399
Wu SG, Li HT, Wang LL, Yan L (2019) Lidocaine promotes fibroblast proliferation after thermal injury via up-regulating the expression of miR-663 and miR-486. Kaohsiung J Med Sci
Xia L, Song M, Sun M, Chen W, Yang C (2019) miR-486 promotes Capan-2 pancreatic cancer cell proliferation by targeting phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN). Front Genet 10:541
Xu Y, Wang Y, Yao A, Xu Z, Dou H, Shen S, Hou Y, Wang T (2017) Low frequency magnetic fields induce autophagy-associated cell death in lung cancer through miR-486-mediated inhibition of Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Sci Rep 7:11776
Yang Q, Wang S, Huang J, Xia C, Jin H, Fan Y (2018) Serum miR-20a and miR-486 are potential biomarkers for discriminating colorectal neoplasia: a pilot study. J Cancer Res Ther 14:1572–1577
Zhang Z, Gong Q, Li M, Xu J, Zheng Y, Ge P, Chi G (2017) MicroRNA-124 inhibits the proliferation of C6 glioma cells by targeting Smad4. Int J Mol Med 40:1226–1234
Zhao X, Qi R, Sun C, Xie Y (2012) Silencing SOCS3 could inhibit TNF-alpha induced apoptosis in 3T3-L1 and mouse preadipocytes. Mol Biol Rep 39:8853–8860
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xu Guanghui designed the research and wrote the paper; Cao Sha, Zhao Jingjing, Gao Jia, and Hu Yapeng performed the research and analyzed the data. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclaimer
All data were generated in-house, and the authors did not use a paper mill.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical standards
Patients were diagnosed according to the criteria of the World Health Organization classification of hematological malignancies. Before the initiation of treatment, clinical features, including Mantle Cell Lymphoma International Prognostic Index (MIPI) score, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) content in serum, performance status (determined using Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status scores), and white blood cell (WBC) counts, were collected. All experimental protocols and procedures involved in the present study were approved by the Ethics Committee of the First People’s Hospital of Lianyungang. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants prior to publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sha, C., Jia, G., Jingjing, Z. et al. miR-486 is involved in the pathogenesis of acute myeloid leukemia by regulating JAK-STAT signaling. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 394, 177–187 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-020-01892-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-020-01892-4