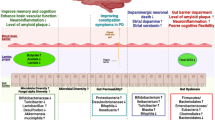
Abstract
Hyperhomocysteinemia is a well-known cause of cognitive impairment and neurodegeneration. Increased oxidative stress in the brain has a major possible role in hyperhomocysteinemia-induced pathogenesis. Edaravone is a potent free radical scavenger that has a neuroprotective effect against memory impairment in several experimental models. The current study investigated the possible protective effect of edaravone in L-methionine-induced vascular dementia in a rat model. L-methionine was given (1.7 mg/kg/day) through oral gavage, while edaravone was given (6 mg/kg/day) intraperitoneally. The administration of methionine and edaravone started concomitantly and continued for a total of 9 weeks. Spatial learning and memory were assessed using the radial arm water maze (RAWM). Changes in the oxidative stress-related biomarkers in the hippocampus were assessed using enzymatic assays. Chronic L-methionine administration resulted in short-term and long-term memory impairment, whereas edaravone prevented such effect. Furthermore, edaravone ameliorated L-methionine induced decrease in the activity of the antioxidant enzymes catalase and glutathione peroxidase as well as the ratio of reduced glutathione to oxidized glutathione (GSH/GSSG ratio). Edaravone also prevented increase in the oxidized glutathione (GSSG) secondary to chronic L-methionine administration. In conclusion, the current study suggests that memory impairment and oxidative stress secondary to chronic L-methionine administration can be prevented by edaravone, probably via enhancing antioxidant mechanisms in the hippocampus.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad A et al (2012) Edaravone ameliorates oxidative stress associated cholinergic dysfunction and limits apoptotic response following focal cerebral ischemia in rat. Mol Cell Biochem 367:215–225
Alzoubi KH, Khabour OF, Rashid BA, Damaj IM, Salah HA (2012) The neuroprotective effect of vitamin E on chronic sleep deprivation-induced memory impairment: the role of oxidative stress. Behav Brain Res 226:205–210
Alzoubi KH, Khabour OF, Tashtoush NH, Al-Azzam SI, Mhaidat NM (2013) Evaluation of the effect of pentoxifylline on sleep-deprivation induced memory impairment. Hippocampus 23:812–819. https://doi.org/10.1002/hipo.22135
Alzoubi H, Khabour F, Al-azzam SI, Tashtoush MH, Mhaidat NM (2014) Metformin eased cognitive impairment induced by chronic L-methionine administration: potential role of oxidative stress. Curr Neuropharmacol 12:186–192
Alzoubi KH, Mayyas FA, Khabour OF, Bani Salama FM, Alhashimi FH, Mhaidat NM (2016) Chronic Melatonin Treatment Prevents Memory Impairment Induced by Chronic Sleep Deprivation. Mol Neurobiol 53:3439–3447. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9286-z
Alzoubi KH, Khabour OF, Ahmed M (2018) Pentoxifylline prevents post-traumatic stress disorder induced memory impairment. Brain Res Bull 139:263–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2018.03.009
Alzoubi KH, Al Mosabih HS, Mahasneh AF (2019a) The protective effect of edaravone on memory impairment induced by chronic sleep deprivation. Psychiatry Res 281:112577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2019.112577
Alzoubi KH, Shatnawi A, Al-Qudah MA, Alfaqih MA (2019b) Edaravone prevents memory impairment in an animal model of post-traumatic distress. Behav Pharmacol 30:201–207. https://doi.org/10.1097/FBP.0000000000000479
Ansari R, Mahta A, Mallack E, Luo JJ (2014) Hyperhomocysteinemia and neurologic disorders: a review. J Clin Neurol 10:281–288. https://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2014.10.4.281
Banno M et al (2005) The radical scavenger edaravone prevents oxidative neurotoxicity induced by peroxynitrite and activated microglia. Neuropharmacology 48:283–290
Baydas G, Ozer M, Yasar A, Tuzcu M, Koz ST (2005) Melatonin improves learning and memory performances impaired by hyperhomocysteinemia in rats. Brain Res 1046:187–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2005.04.011
Cervellati C et al (2014) Oxidative balance, homocysteine, and uric acid levels in older patients with late onset Alzheimer's disease or vascular dementia. J Neurol Sci 337:156–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2013.11.041
Chen Z, Zhang J, Chen Q, Guo J, Zhu G, Feng H (2014) Neuroprotective effects of edaravone after intraventricular hemorrhage in rats. Neuroreport 25:635–640. https://doi.org/10.1097/wnr.0000000000000050
El-Dessouki AM, Galal MA, Awad AS, Zaki HF (2017) Neuroprotective Effects of Simvastatin and Cilostazol in L-Methionine-Induced Vascular Dementia in Rats. Mol Neurobiol 54:5074–5084. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0051-8
Garcia A, Zanibbi K (2004) Homocysteine and cognitive function in elderly people. Cmaj 171:897–904
Górska-Warsewicz H, Laskowski W, Kulykovets O, Kudlińska-Chylak A, Czeczotko M, Rejman K (2018) Food Products as Sources of Protein and Amino Acids-The Case of Poland. Nutrients 10:1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10121977
Hainsworth AH, Yeo NE, Weekman EM, Wilcock DM (2016) Homocysteine, hyperhomocysteinemia and vascular contributions to cognitive impairment and dementia (VCID). Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) - Mol Basis Dis 1862:1008–1017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2015.11.015
He F, Cao YP, Che FY, Yang LH, Xiao SH, Liu J (2014) Inhibitory effects of edaravone in beta-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity in rats. Biomed Res Int 2014:370368. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/370368
Hemanth Kumar B, Dinesh Kumar B, Diwan PV (2017) Hesperidin, a citrus flavonoid, protects against l-methionine-induced hyperhomocysteinemia by abrogation of oxidative stress, endothelial dysfunction and neurotoxicity in Wistar rats. Pharm Biol 55:146–155
Higashi Y (2009) Edaravone for the treatment of acute cerebral infarction: role of endothelium-derived nitric oxide and oxidative stress. Expert Opin Pharmacother 10:323–331. https://doi.org/10.1517/14656560802636888
Jiao SS et al (2015) Edaravone alleviates Alzheimer's disease-type pathologies and cognitive deficits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:5225–5230. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1422998112
Kikuchi K et al (2011) Potential of edaravone for neuroprotection in neurologic diseases that do not involve cerebral infarction. Exp Ther Med 2:771–775. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2011.281
Kikuchi K, Tancharoen S, Takeshige N, Yoshitomi M, Morioka M, Murai Y, Tanaka E (2013) The efficacy of edaravone (radicut), a free radical scavenger, for cardiovascular disease. Int J Mol Sci 14:13909–13930. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140713909
Koladiya RU, Jaggi AS, Singh N, Sharma BK (2008) Ameliorative role of Atorvastatin and Pitavastatin in L-Methionine induced vascular dementia in rats. BMC Pharmacol 8:14
Koladiya RU, Jaggi AS, Singh N, Sharma BK (2009) Beneficial effects of donepezil on vascular endothelial dysfunction-associated dementia induced by L-methionine in rats. J Health Sci 55:215–225
Lapchak PA (2010) A critical assessment of edaravone acute ischemic stroke efficacy trials: is edaravone an effective neuroprotective therapy? Expert Opin Pharmacother 11:1753–1763. https://doi.org/10.1517/14656566.2010.493558
Li X et al (2017) Edaravone injection reverses learning and memory deficits in a rat model of vascular dementia. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 49:83–89. https://doi.org/10.1093/abbs/gmw116
McVeigh C, Passmore P (2006) Vascular dementia: prevention and treatment. Clin Interv Aging 1:229–235
Miller AL (2003) The methionine-homocysteine cycle and its effects on cognitive diseases. Altern Med Rev 8:7–19
Moretti R, Caruso P (2019) The controversial role of Homocysteine in neurology: from labs to clinical practice Int J Mol Sci 20 doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20010231
Nagase M, Yamamoto Y, Miyazaki Y, Yoshino H (2016) Increased oxidative stress in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and the effect of edaravone administration. Redox Rep 21:104–112
Noor JI et al (2005) Short-term administration of a new free radical scavenger, edaravone, is more effective than its long-term administration for the treatment of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Stroke 36:2468–2474. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.0000185653.49740.c6
Obeid R, Herrmann W (2006) Mechanisms of homocysteine neurotoxicity in neurodegenerative diseases with special reference to dementia. FEBS Lett 580:2994–3005. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2006.04.088
Pandey P, Pradhan S (2010) Homocysteine: A possible modifiable risk factor in vascular dementia. Ann Neurosci 13:12–17
Price BR, Wilcock DM, Weekman EM (2018) Hyperhomocysteinemia as a Risk Factor for Vascular Contributions to Cognitive Impairment and Dementia. Front Aging Neurosci 10:350. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2018.00350
Saini AK, Hs AK, Sharma SS (2007) Preventive and curative effect of edaravone on nerve functions and oxidative stress in experimental diabetic neuropathy. Eur J Pharmacol 568:164–172
Tian A, Ma H, Zhang R, Cui Y, Wan C (2017) Edaravone improves spatial memory and modulates endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis after abdominal surgery in mice. Exp Ther Med 14:355–360. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2017.4489
Wang G-H et al (2011) Free-radical scavenger edaravone treatment confers neuroprotection against traumatic brain injury in rats. J Neurotrauma 28:2123–2134. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2011.1939
Watanabe K, Tanaka M, Yuki S, Hirai M, Yamamoto Y (2018) How is edaravone effective against acute ischemic stroke and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis? J Clin Biochem Nutr 62:20–38. https://doi.org/10.3164/jcbn.17-62
Zhang D, Xiao Y, Lv P, Teng Z, Dong Y, Qi Q, Liu Z (2018) Edaravone attenuates oxidative stress induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion injury: role of ERK/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Neurol Res 40:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1080/01616412.2017.1376457
Funding
Deanship of Research/Jordan University of Science and Technology, grant number 522/2018.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KA and FM conceived and designed research. ZA conducted experiments. KA and FM contributed new reagents, analytical tools, and in supervising the experimental procedure. KA and ZA analyzed data. KA, ZA, and FM participated in interpreting study results and wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. The experimental protocol was approved by the animal care and use committee (ACUC) of the Jordan University of Science and Technology (approval number: IACUC-522/2018, 25-11-2018).
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alzoubi, K.H., Aburashed, Z.O. & Mayyas, F. Edaravone protects from memory impairment induced by chronic L-methionine administration. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 393, 1221–1228 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-020-01827-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-020-01827-z