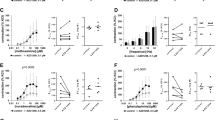
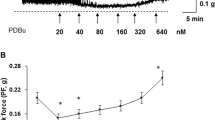
Abstract
Mixed lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) (voiding symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia plus storage symptoms, which can be caused by overactive bladder) are common in men. Unwanted contraction of prostate and/or bladder smooth muscle has been implied in the pathophysiology of male LUTS. Here, we examined effects of the serine/threonine kinase 16 (STK16) inhibitor STK16-IN-1 on contraction of human tissues from the prostate and male detrusor. Tissues were obtained from radical prostatectomy and radical cystectomy. Contractions were studied in an organ bath and STK16 expressions by Western blot analyses and fluorescence staining. In prostate tissues, STK16-IN-1 (1 μM) inhibited contractions induced by endothelin-1 and the thromboxane A2 analog U46619. Contractions of prostate tissues induced by noradrenaline, the α1-agonists phenylephrine and methoxamine, or electric field stimulation (EFS) were not changed by STK16-IN-1. In male detrusor tissues, STK16-IN-1 inhibited contractions induced by the cholinergic agonists carbachol and metacholine, and contractions induced by U46619. EFS-induced contractions of detrusor tissues were not changed by STK16-IN-1. Western blot analyses of prostate and detrusor tissues revealed bands matching the molecular weight of STK16. Fluorescence staining of prostate tissues using STK16 antibodies resulted in immunoreactivity in smooth muscle cells. STK16-IN-1 selectively inhibits non-adrenergic/non-neurogenic smooth muscle contractions in the male prostate and to limited extent in the bladder. Because non-adrenergic contractions in the male LUTS may account for limited efficacy of α1-blockers and for α1-blocker-resistant symptoms, studies assessing add-on of STK16-IN-1 to α1-blockers in mixed LUTS appear feasible.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akino H et al (2008) Spontaneous contractions of the pig urinary bladder: the effect of ATP-sensitive potassium channels and the role of the mucosa. BJU Int 102:1168–1174. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2008.07782.x
Alcaraz A, Hammerer P, Tubaro A, Schroder FH, Castro R (2009) Is there evidence of a relationship between benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer? Findings of a literature review. Eur Urol 55:864–873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2008.11.011
Andersson KE (2011) Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in the urinary tract. Handb Exp Pharmacol:319–344. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-16499-6_16
Andersson KE, Arner A (2004) Urinary bladder contraction and relaxation: physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol Rev 84:935–986. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00038.200384/3/935
Cindolo L et al (2015a) Drug adherence and clinical outcomes for patients under pharmacological therapy for lower urinary tract symptoms related to benign prostatic hyperplasia: population-based cohort study. Eur Urol 68:418–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2014.11.006
Cindolo L, Pirozzi L, Sountoulides P, Fanizza C, Romero M, Castellan P, Antonelli A, Simeone C, Tubaro A, de Nunzio C, Schips L (2015b) Patient's adherence on pharmacological therapy for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)-associated lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) is different: is combination therapy better than monotherapy? BMC Urol 15:96. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12894-015-0090-x
Drake MJ et al (2017) Incidence of urinary retention during treatment with single tablet combinations of solifenacin+tamsulosin OCAS for up to 1 year in adult men with both storage and voiding LUTS: a subanalysis of the NEPTUNE/NEPTUNE II randomized controlled studies. PLoS One 12:e0170726. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0170726
Eswaran J et al (2008) Structure of the human protein kinase MPSK1 reveals an atypical activation loop architecture. Structure 16:115–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2007.10.026
Fullhase C et al (2013) Systematic review of combination drug therapy for non-neurogenic male lower urinary tract symptoms. Eur Urol 64:228–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2013.01.018
Guinea B et al (2006) Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of STK16 (PKL12), a Golgi-resident serine/threonine kinase involved in VEGF expression regulation. Exp Cell Res 312:135–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2005.10.010
Hennenberg M et al (2013) The receptor antagonist picotamide inhibits adrenergic and thromboxane-induced contraction of hyperplastic human prostate smooth muscle. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 305:F1383–F1390. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00380.2013
Hennenberg M, Stief CG, Gratzke C (2014) Prostatic alpha1-adrenoceptors: new concepts of function, regulation, and intracellular signaling. Neurourol Urodyn 33:1074–1085. https://doi.org/10.1002/nau.22467
Hennenberg M et al (2017) Non-adrenergic, tamsulosin-insensitive smooth muscle contraction is sufficient to replace alpha1-adrenergic tension in the human prostate. Prostate 77:697–707. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.23293
Hennenberg M, Kuppermann P, Yu Q, Herlemann A, Tamalunas A, Wang Y, Rutz B, Ciotkowska A, Strittmatter F, Stief CG, Gratzke C (2018) Inhibition of prostate smooth muscle contraction by inhibitors of Polo-like kinases. Front Physiol 9:734. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.00734
In JG, Striz AC, Bernad A, Tuma PL (2014) Serine/threonine kinase 16 and MAL2 regulate constitutive secretion of soluble cargo in hepatic cells. Biochem J 463:201–213. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20140468
Irwin DE, Kopp ZS, Agatep B, Milsom I, Abrams P (2011) Worldwide prevalence estimates of lower urinary tract symptoms, overactive bladder, urinary incontinence and bladder outlet obstruction. BJU Int 108:1132–1138. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2010.09993.x
Kurioka K, Nakagawa K, Denda K, Miyazawa K, Kitamura N (1998) Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel protein serine/threonine kinase highly expressed in mouse embryo. Biochim Biophys Acta 1443:275–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0167-4781(98)00224-3
Kushida N, Fry CH (2015) On the origin of spontaneous activity in the bladder. BJU Int. https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.13240
Levitt JM, Slawin KM (2007) Prostate-specific antigen and prostate-specific antigen derivatives as predictors of benign prostatic hyperplasia progression. Curr Urol Rep 8:269–274
Li J, Wang Y, Meng X, Liang H (2018) Modulation of transcriptional activity in brain lower grade glioma by alternative splicing. PeerJ 6:e4686. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.4686
Ligos JM et al (2002) Functional interaction between the Ser/Thr kinase PKL12 and N-acetylglucosamine kinase, a prominent enzyme implicated in the salvage pathway for GlcNAc recycling. J Biol Chem 277:6333–6343. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M105766200
Liu F et al (2016) Discovery of a highly selective STK16 kinase inhibitor. ACS Chem Biol 11:1537–1543. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.6b00250
Liu J et al (2017) STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle. Sci Rep 7:44607. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep44607
Long Y, Song G, Yan J, He X, Li Q, Cui Z (2013) Transcriptomic characterization of cold acclimation in larval zebrafish. BMC Genomics 14:612. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-14-612
Lopez-Coral A, Striz AC, Tuma PL (2018) A serine/threonine kinase 16-based phospho-proteomics screen identifies WD repeat protein-1 as a regulator of constitutive secretion. Sci Rep 8:13049. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-31426-1
Motulsky HJ (2014) Common misconceptions about data analysis and statistics Naunyn Schmiedebergs. Arch Pharmacol 387:1017–1023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-014-1037-6
Nambiar AK et al (2018) EAU guidelines on assessment and nonsurgical management of urinary incontinence. Eur Urol 73:596–609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2017.12.031
Oelke M et al (2013) EAU guidelines on the treatment and follow-up of non-neurogenic male lower urinary tract symptoms including benign prostatic obstruction. Eur Urol 64:118–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2013.03.004
Ohta S, Takeuchi M, Deguchi M, Tsuji T, Gahara Y, Nagata K (2000) A novel transcriptional factor with Ser/Thr kinase activity involved in the transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta signalling pathway. Biochem J 350(Pt 2):395–404
Orsted DD, Bojesen SE (2013) The link between benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer. Nat Rev Urol 10:49–54. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrurol.2012.192
Pradidarcheep W, Wallner C, Dabhoiwala NF, Lamers WH (2011) Anatomy and histology of the lower urinary tract. Handb Exp Pharmacol:117–148. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-16499-6_7
Sexton CC, Notte SM, Maroulis C, Dmochowski RR, Cardozo L, Subramanian D, Coyne KS (2011) Persistence and adherence in the treatment of overactive bladder syndrome with anticholinergic therapy: a systematic review of the literature. Int J Clin Pract 65:567–585. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-1241.2010.02626.x
Shaikhibrahim Z, Lindstrot A, Ellinger J, Rogenhofer S, Buettner R, Perner S, Wernert N (2012) The peripheral zone of the prostate is more prone to tumor development than the transitional zone: is the ETS family the key? Mol Med Rep 5:313–316. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2011.647
Somlyo AP, Somlyo AV (2000) Signal transduction by G-proteins, rho-kinase and protein phosphatase to smooth muscle and non-muscle myosin II. J Physiol 522(Pt 2):177–185
Somlyo AP, Somlyo AV (2003) Ca2+ sensitivity of smooth muscle and nonmuscle myosin II: modulated by G proteins, kinases, and myosin phosphatase. Physiol Rev 83:1325–1358. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00023.2003
Stairs DB, Perry Gardner H, Ha SI, Copeland NG, Gilbert DJ, Jenkins NA, Chodosh LA (1998) Cloning and characterization of Krct, a member of a novel subfamily of serine/threonine kinases. Hum Mol Genet 7:2157–2166. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/7.13.2157
Stairs DB, Notarfrancesco KL, Chodosh LA (2005) The serine/threonine kinase, Krct, affects endbud morphogenesis during murine mammary gland development. Transgenic Res 14:919–940. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-005-1806-6
Strand DW, Costa DN, Francis F, Ricke WA, Roehrborn CG (2017) Targeting phenotypic heterogeneity in benign prostatic hyperplasia. Differentiation 96:49–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diff.2017.07.005
Uhlen M et al (2015) Proteomics. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science 347:1260419. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1260419
Wang Y et al (2016) Smooth muscle contraction and growth of stromal cells in the human prostate are both inhibited by the Src family kinase inhibitors, AZM475271 and PP2. Br J Pharmacol 173:3342–3358. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.13623
Wang J, Ji X, Liu J, Zhang X (2019a) Serine/threonine protein kinase STK16. Int J Mol Sci 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20071760
Wang J, Liu J, Ji X, Zhang X (2019b) Tyr198 is the essential autophosphorylation site for STK16 localization and kinase activity. Int J Mol Sci 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194852
Yu Q et al (2018) Inhibition of human prostate smooth muscle contraction by the LIM kinase inhibitors, SR7826 and LIMKi3. Br J Pharmacol 175:2077–2096. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.14201
Yu Q et al (2019a) A NAV2729-sensitive mechanism promotes adrenergic smooth muscle contraction and growth of stromal cells in the human prostate. J Biol Chem 294:12231–12249. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA119.007958
Yu Q et al (2019b) New strategies for inhibition of non-adrenergic prostate smooth muscle contraction by pharmacologic intervention. Prostate 79:746–756. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.23780
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. Dr. E. Noessner and her coworkers (Institute of Molecular Immunology, Helmholtz Center, Munich) for their support with immunofluorescence microscopy and Prof. Dr. T. Kirchner (Institute of Pathology, Ludwig-Maximilians University, Munich) and his coworkers for the asservation of tissue samples from prostates.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (grant HE 5825/8-1) and the Chinese Scholarship Council (CSC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MH conceived and designed the study. BL, XW, BR, RW, AT, FS, RW, CGS, and MH performed research. MH and BL analyzed data. BL and MH wrote the paper. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, B., Wang, X., Rutz, B. et al. The STK16 inhibitor STK16-IN-1 inhibits non-adrenergic and non-neurogenic smooth muscle contractions in the human prostate and the human male detrusor. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 393, 829–842 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-019-01797-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-019-01797-x