Abstract
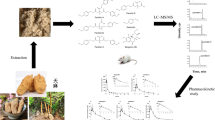
A new highly specific high-performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS) method coupled to microdialysis sampling was developed and validated for simultaneous determination of L-ephedrine, D-pseudoephedrine, L-methyl-ephedrine, cinnamic acid, liquiritin, amygdalin, and glycyrrhizic acid both in rat blood and brain after oral administration of Mahuang decoction in this paper. An Agilent Zorbax SB-C18 using the 0.1% formic acid water solution and acetonitrile as mobile phase with a gradient elution was applied to the chromatographic separation. The ion transitions were quantified in positive mode for D-pseudoephedrine, L-ephedrine, L-methylephedrine, and diphenhydramine (internal standard), while negative mode for liquiritin, glycyrrhizic acid, amygdalin, cinnamic acid, and prednisolone (internal standard). Several parameters of the method including linearity, accuracy, precision, stability, and matrix effect were within acceptable ranges. The results showed the LC–MS/MS method coupled to microdialysis sampling can be utilized for the pharmacokinetic studies of these seven ingredients in vivo. According to the pharmacokinetic results, the pharmacokinetic parameters of L-ephedrine, D-pseudoephedrine, L-methylephedrine, glycyrrhizic acid, cinnamic acid, liquiritin, and amygdalin were totally different in rat blood and brain, the bioavailability of ephedrine and amygdalin in the blood and brain was higher, while the MRT of ephedrine was the shortest. In the rat brain, the elimination rate of three Ephedra alkaloids was lower than that of the remaining four components. This research offered more basic pharmacokinetic information on the safety mechanisms of Mahuang decoction.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avois L, Robinson N, Saudan C, Baume N, Mangin P, Saugy M (2006) Central nervous system stimulants and sport practice. Br J Sports Med:i16–i20
Berman JA, Arathi S, Steiner MJ, Kaufman KR, Christine S (2006) Complicated hypertension related to the abuse of ephedrine and caffeine alkaloids. J Addict Dis 25:45–48
Cheng Y, Yang C, Zhao J, Tse HF, Rong J (2015) Proteomic identification of calcium-binding chaperone calreticulin as a potential mediator for the neuroprotective and neuritogenic activities of fruit-derived glycoside amygdalin. J Nutr Biochem 26:146–154
Fu YJ, Li ZY (2012) Advances in studies on neuroprotective effects of active components of Glycyrrhiza uralensis. J Int Neurol Neurosurg 39:298–298
He Y, Lou XH, Jin Z, Yu L, Deng L, Wan HT (2018) Mahuang decoction mitigates airway inflammation and regulates IL-21/STAT3 signaling pathway in rat asthma model. J Ethnopharmacol 224:373–380
He Y, ZhuY ZRP, Ge LJ, Wan HT (2014) Simultaneous quantification of nine major active components in traditional Chinese prescription Mahuang decoction and the influence of herbal compatibility on their contents. Pharmacogn Mag 10:S72–S79
Hou ML, Lu CM, Lin CH, Lin LC, Tsai TH (2016) Pharmacokinetics of maleic acid as a food adulterant determined by microdialysis in rat blood and kidney cortex. Molecules 21:367
Kockler DR, Mccarthy MW, Lawson CL (2012) Seizure activity and unresponsiveness after hydroxycut ingestion. Pharmacotherapy 21:647–651
Lange D, Boer D, Breimer DD (2000) Methodological issues in microdialysis sampling for pharmacokinetic studies. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 45:125–148
Li JL, Fang L, Zhang YQ, Wang X, Zhang QD (2012) Advances in research of chemical constituents and pharmacological activites of Ephedra. Modern Chin Med 14:21–27
Li XD, Gu LW, Ran QS, Zhou P, Zhan XL, Li CH, Jiang YL (2016) Protective effects of three phenylallyl compounds from Guizhi decoction ox-LDL-induced oxidative stress injury of human brain microvascular endothelial cells. China J Chin Mater Med 41:2315–2320
Liu P, Zhang LP (2012) Studies on chemical constituents in dried tender stem of Cinnamomi Cassia. Liaoning Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine 39:1926–1927
Nan F, Chen ZH, Xiang J, Yu Q, Qin YP, Liang MZ (2016) Simultaneous determination of ibuprofen, pseudoephedrine and chlorphenamine in plasma by HPLC-MS/MS with positive and negative ion switching. Chin J Clin Pharm Therap 21:173–177
Shekelle P, Hardy ML, Morton SC, Maglione M, Suttorp M, Roth E, Jungvig L, Mojica WA, Gagne J, Rhodes S, McKinnon E (2003) Ephedra and ephedrine for weight loss and athletic performance enhancement: clinical efficacy and side effects. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Summ):1–4
Song YG, Su D, Lu TL, Mao CQ, Ji D, Liu YL, Wei BB, Fan RH (2014) Differential pharmacokinetics and the brain distribution of morphine and ephedrine constitutional isomers in rats after oral administration with Keke capsule using rapid-resolution LC-MS/MS. J Sep Sci 37:352–359
Sun YX, Tang Y, Wu AL, Liu T, Dai XL, Zheng QS, Wang Z (2010) Neuroprotective effect of liquiritin against focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion in mice via its antioxidant and antiapoptosis properties. J Asian Nat Prod Res 12:1051–1060
Tang YH, Wan HT, Chen JZ, Zhou HF, Tian YF, He Y (2015) In vitro microdialysis recoveries of nine active ingredients in Mahuang decoction. China J Chin Mater Med 40:3667–3673
Tang YH, Wang YQ, Zhou HF, Jin J, He Y (2017) Effect of Mahuang decoction on the release of amino acid neurotransmitters in the hippocampus of rats by microdialysis. Chin Pharmacol Bull 33:426–432
Wang D, Guo TQ, Wang ZY, Lu JH, Liu DP, Meng QF, Xie J, Zhang XL, Liu Y, Teng LS (2014) ERKs and mitochondria-related pathways are essential for glycyrrhizic acid-mediated neuroprotection against glutamate-induced toxicity in differentiated PC12 cells. Braz J Med Biol Res 47:773–779
Wang L, Huang Y, Wu J, Lv G, Zhou L, Jia J (2013) Effect of Buyang Huanwu decoction on amino acid content in cerebrospinal fluid of rats during ischemic/reperfusion injury. J Pharmaceut Biomed 86:143–150
Wei JB, Qiao L, Shumyak SP, Xu LF, Zhang CX, Ling JJ, Yang Y (2015) An LC/MS quantitative and microdialysis method for cyclovirobuxine D pharmacokinetics in rat plasma and brain: the pharmacokinetic comparison of three different drug delivery routes. J Chromatogr B 1002:185–193
Wei P, Huo HL, Ma QH, Li HC, Xing XF, Tan XM, Luo JB (2014) Pharmacokinetic comparisons of five ephedrine alkaloids following oral administration of four different Mahuang-Guizhi herb-pair aqueous extracts ratios in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 155:642–648
Wu L, Zhang QL, Zhang XY, Lv C, Li J, Yuan Y, Yin FX (2012) Pharmacokinetics and blood-brain barrier penetration of (+)-catechin and (−)-epicatechin in rats by microdialysis sampling coupled to high-performance liquid chromatography with chemiluminescence detection. J Agric Food Chem 60:9377–9383
Yang M, Yang DS, Gu YW, Tang XM, Liu JY (2018) Pharmacokinetics of Tripterygium wilfordii Nanoemulsion based on simultaneous microdialysis of skin and blood. Chin Pharm J 53:894–899
Yang X, Peng WB, Yue XQ (2009) Syndrome differentiation and treatment of Taiyang disease in Shanghan Lun. J Chin Integr 7:171–174
Zhang XJ, Chen JH, Luo L, He W, Liu GH, Gong J, Zeng YF, Xie ZY, Liao QF (2018) Comparative brain pharmacokinetic study of Jiaotai pills in normal and insomnic rats using brain microdialysis combinated with LC–MS/MS. Chin Herb Med 10:206–214
Zhang YJ, Wu L, Zhang QL, Li J, Yin FX, Yuan Y (2011) Pharmacokinetics of phenolic compounds of Danshen extract in rat blood and brain by microdialysis sampling. J Ethnopharmacol 136:129–136
Zheng MK, Zhou HF, Wan HT, Chen YL, He Y (2015) Effects of herbal drugs in Mahuang decoction and their main components on intestinal transport characteristics of Ephedra alkaloids evaluated by a Caco-2 cell monolayer model. J Ethnopharmacol 164:22–29
Funding
This research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81573868, 81930111), Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No. LZ18H270001, LY16H280008), and Zhejiang Provincial Program for the Cultivation of High-level Innovative Health talents (No. 2014-108-24).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y He and HT Wan conceived and designed research. HY Wan, Y Wang, C Li, and L Yu performed all experiments. HY Wan, LJ Pan, and HF Zhou analyzed data. HY Wan, LJ Pan, and Y He wrote the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All animal experiments were performed in accordance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (NIH Publications, No.80–23, revised in 1996), and this research was approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University and performed according to its guidelines.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wan, H., Pan, L., Wang, Y. et al. Pharmacokinetics of seven major active components of Mahuang decoction in rat blood and brain by LC–MS/MS coupled to microdialysis sampling. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 393, 1559–1571 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-019-01786-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-019-01786-0