Abstract
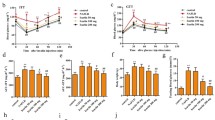
The prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is much higher in diabetic and obese individuals. Combined exposure of high-fat diet (HFD) and single low-dose streptozotocin (STZ) was used to induce type II diabetes–associated NAFLD, as it better replicates the human pathology of fatty liver. Glibenclamide (GLB) is a potent NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitor and possesses anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant properties. So it was pertinent to investigate its hepatoprotective potential against NAFLD in rat. HFD was provided to rat for 17 consecutive weeks and glibenclamide (GLB; 0.5 and 2.5 mg/kg/day, orally) was administered for the last 12 consecutive weeks. Establishment of NAFLD was clearly indicated by significant increase in liver weight, glucose, triglyceride, cholesterol, % glycosylated haemoglobin and insulin levels, and GLB intervention reduced the same. GLB restored HFD-induced significant increase in ROS, MDA and decrease in GSH. Histopathological studies revealed the macro- and micro-vascular steatosis and mild degree of inflammation in HFD-fed rat compared with control, and GLB intervention reduced the same. HFD exposure significantly increased the DNA damage and apoptosis compared with control, and GLB intervention reduced the same. Immunohistochemical and immunoblotting findings showed that GLB improved the hepatic expressions of inflammatory markers (NLRP3, ASC, caspase-1, IL-1β, NF-κB), anti-oxidant markers (SOD, catalase) and insulin signalling markers (p-AKT, p-GSK-3β, p-IRS). Hepatoprotective effects of GLB was mediated by decreasing the levels of glucose, triglycerides, cholesterol, DNA damage, apoptosis and inflammatory markers, and by improving the anti-oxidant status and insulin signalling pathway in HFD fed rat.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdallah DM, Nassar NN, Abd-El-Salam RM (2011) Glibenclamide ameliorates ischemia-reperfusion injury via modulating oxidative stress and inflammatory mediators in the rat hippocampus. Brain Res 1385:257–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2011.02.007
Ahren B, Schersten B (1984) Effect of sulfonylurea on glucose, insulin and C-peptide responses to a meal stimulus in a patient with type 2 diabetes and liver disease. Acta Med Scand 215:487–491. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0954-6820.1984.tb17683.x
Akazawa Y, Nakao K (2018) To die or not to die: death signaling in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Gastroenterol 53:893–906. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-018-1451-5
Alba LM, Lindor K (2003) Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 17:977–986. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2036.2003.01493.x
Blasiak J, Arabski M, Krupa R, Wozniak K, Zadrozny M, Kasznicki J, Zurawska M, Drzewoski J (2004) DNA damage and repair in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Mutat Res 554:297–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2004.05.011
Buzzetti E, Pinzani M, Tsochatzis EA (2016) The multiple-hit pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Metabolism 65:1038–1048. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2015.12.012
Carlsen H, Haugen F, Zadelaar S, Kleemann R, Kooistra T, Drevon CA, Blomhoff R (2009) Diet-induced obesity increases NF-kappaB signaling in reporter mice. Genes Nutr 4:215–222. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12263-009-0133-6
Chen Z, Yu R, Xiong Y, du F, Zhu S (2017) A vicious circle between insulin resistance and inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Lipids Health Dis 16:203. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12944-017-0572-9
Choubey P, Kwatra M, Pandey SN, Kumar D, Dwivedi DK, Rajput P, Mishra A, Lahkar M, Jangra A (2018) Ameliorative effect of fisetin against lipopolysaccharide and restraint stress-induced behavioral deficits via modulation of NF-kappaB and IDO-1. Psychopharmacology 236:741–752. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-018-5105-3
D’Adamo E, Cali AMG, Weiss R et al (2010) Central role of fatty liver in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance in obese adolescents. Diabetes Care 33:1817–1822. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc10-0284
Dixon LJ, Flask CA, Papouchado BG, Feldstein AE, Nagy LE (2013) Caspase-1 as a central regulator of high fat diet-induced non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. PLoS One 8:e56100. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0056100
Dwivedi D, Jena GB (2019) THU-074-anti-fibrotic effect of dimethyl fumarate on rat liver fibrosis induced by thioacetamide: role of NF-kappa B, NLRP3, Nrf2 and autophagy. J Hepatol 70:e191–e192. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0618-8278(19)30355-X
Dwivedi DK, Jena GB (2018) Glibenclamide protects against thioacetamide-induced hepatic damage in Wistar rat: investigation on NLRP3, MMP-2, and stellate cell activation. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-018-1540-2
Dwivedi DK, Kumar D, Kwatra M, Pandey SN, Choubey P, Lahkar M, Jangra A (2018) Voluntary alcohol consumption exacerbated high fat diet-induced cognitive deficits by NF-κB-calpain dependent apoptotic cell death in rat hippocampus: ameliorative effect of melatonin. Biomed Pharmacother 108:1393–1403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.09.173
Fink SL, Cookson BT (2005) Apoptosis, pyroptosis, and necrosis: mechanistic description of dead and dying eukaryotic cells. Infect Immun 73:1907–1916. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.73.4.1907-1916.2005
Hao Y-R, Tang F-J, Zhang X, Wang H (2018) Suppression of NF-kappaB activation by PDLIM2 restrains hepatic lipogenesis and inflammation in high fat diet induced mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 503:564–571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.05.187
He K, Zhu X, Liu Y et al (2017) Inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome by thioredoxin-interacting protein in mouse Kupffer cells as a regulatory mechanism for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease development. Oncotarget 8:37657–37672. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.17489
Hirshman MF, Horton ES (1990) Glyburide increases insulin sensitivity and responsiveness in peripheral tissues of the rat as determined by the glucose clamp technique. Endocrinology 126:2407–2412. https://doi.org/10.1210/endo-126-5-2407
Hu C, Ding H, Li Y et al (2015) NLRP3 deficiency protects from type 1 diabetes through the regulation of chemotaxis into the pancreatic islets. Proc Natl Acad Sci 112:11318 LP–11311323. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1513509112
Ito M, Suzuki J, Tsujioka S, Sasaki M, Gomori A, Shirakura T, Hirose H, Ito M, Ishihara A, Iwaasa H, Kanatani A (2007) Longitudinal analysis of murine steatohepatitis model induced by chronic exposure to high-fat diet. Hepatol Res 37:50–57. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1872-034X.2007.00008.x
Jangra A, Kwatra M, Singh T, Pant R, Kushwah P, Ahmed S, Dwivedi D, Saroha B, Lahkar M (2016) Edaravone alleviates cisplatin-induced neurobehavioral deficits via modulation of oxidative stress and inflammatory mediators in the rat hippocampus. Eur J Pharmacol 791:51–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.08.003
Kewcharoenwong C, Rinchai D, Utispan K, Suwannasaen D, Bancroft GJ, Ato M, Lertmemongkolchai G (2013) Glibenclamide reduces pro-inflammatory cytokine production by neutrophils of diabetes patients in response to bacterial infection. Sci Rep 3:3363. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep03363
Koh GCKW, Weehuizen TA, Breitbach K et al (2013) Glyburide reduces bacterial dissemination in a mouse model of melioidosis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 7:e2500. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0002500
Kumar D, Kumar Dwivedi D, Lahkar M, Jangra A (2019) Hepatoprotective potential of 7,8-Dihydroxyflavone against alcohol and high-fat diet induced liver toxicity via attenuation of oxido-nitrosative stress and NF-ҡB activation. Pharmacol Reports. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2019.07.002
Lamkanfi M, Mueller JL, Vitari AC, Misaghi S, Fedorova A, Deshayes K, Lee WP, Hoffman HM, Dixit VM (2009) Glyburide inhibits the Cryopyrin/Nalp3 inflammasome. J Cell Biol 187:61–70. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200903124
Lee H-M, Kim J-J, Kim HJ, Shong M, Ku BJ, Jo EK (2013) Upregulated NLRP3 inflammasome activation in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 62:194–204. https://doi.org/10.2337/db12-0420
Liang W, Menke AL, Driessen A, Koek GH, Lindeman JH, Stoop R, Havekes LM, Kleemann R, van den Hoek A (2014) Establishment of a general NAFLD scoring system for rodent models and comparison to human liver pathology. PLoS One 9:e115922. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0115922
Loria P, Lonardo A, Anania F (2013) Liver and diabetes. A vicious circle. Hepatol Res 43:51–64. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1872-034X.2012.01031.x
Mehal WZ (2014) The inflammasome in liver injury and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig Dis 32:507–515
Mridha AR, Wree A, Robertson AAB, Yeh MM, Johnson CD, van Rooyen D, Haczeyni F, Teoh NC, Savard C, Ioannou GN, Masters SL, Schroder K, Cooper MA, Feldstein AE, Farrell GC (2017) NLRP3 inflammasome blockade reduces liver inflammation and fibrosis in experimental NASH in mice. J Hepatol 66:1037–1046. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2017.01.022
Mughal MA, Maheri WM, Aamir K, Jan M, Ali M (1999) The effects of glibenclamide on serum lipids and lipoproteins in type II non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. J Pak Med Assoc 49:89–92
Mullard A (2019) NLRP3 inhibitors stoke anti-inflammatory ambitions. Nat Rev Drug Discov 18:405–407
Nazaroglu NK, Sepici-Dincel A, Altan N (2009) The effects of sulfonylurea glyburide on superoxide dismutase, catalase, and glutathione peroxidase activities in the brain tissue of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat. J Diabetes Complicat 23:209–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2007.09.001
Perry RJ, Samuel VT, Petersen KF, Shulman GI (2014) The role of hepatic lipids in hepatic insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature 510:84–91. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13478
Saleh J (2015) Glycated hemoglobin and its spinoffs: cardiovascular disease markers or risk factors? World J Cardiol 7:449–453. https://doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v7.i8.449
Schmid D, Svoboda M, Sorgner A et al (2011) Glibenclamide reduces proinflammatory cytokines in an ex vivo model of human endotoxinaemia under hypoxaemic conditions. Life Sci 89:725–734
Sestili P, Martinelli C, Stocchi V (2006) The fast halo assay: an improved method to quantify genomic DNA strand breakage at the single-cell level. Mutat Res Toxicol Environ Mutagen 607:205–214
Srinivasan K, Viswanad B, Asrat L, Kaul CL, Ramarao P (2005) Combination of high-fat diet-fed and low-dose streptozotocin-treated rat: a model for type 2 diabetes and pharmacological screening. Pharmacol Res 52:313–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2005.05.004
Takahashi Y, Soejima Y, Fukusato T (2012) Animal models of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. World J Gastroenterol 18:2300–2308
Van Herck MA, Vonghia L, Francque SM (2017) Animal models of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-a starter’s guide. Nutrients 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9101072
Vornoli A, Pozzo L, Della Croce CM et al (2014) Drug metabolism enzymes in a steatotic model of rat treated with a high fat diet and a low dose of streptozotocin. Food Chem Toxicol 70:54–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2014.04.042
Wan X, Xu C, Yu C, Li Y (2016) Role of NLRP3 inflammasome in the progression of NAFLD to NASH. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016
Xu F, Shen G, Su Z, He Z, Yuan L (2019) Glibenclamide ameliorates the disrupted blood–brain barrier in experimental intracerebral hemorrhage by inhibiting the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome. Brain Behav 9:e01254. https://doi.org/10.1002/brb3.1254
Yang G, Lee HE, Lee JY (2016) A pharmacological inhibitor of NLRP3 inflammasome prevents non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in a mouse model induced by high fat diet. Sci Rep 6:24399
Younossi ZM (2019) Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease – A global public health perspective. J Hepatol 70:531–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2018.10.033
Zhang G, Lin X, Zhang S, Xiu H, Pan C, Cui W (2017a) A protective role of glibenclamide in inflammation-associated injury. Mediat Inflamm 2017:3578702. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3578702
Zhang X, Dai J, Li L, Chen H, Chai Y (2017b) NLRP3 inflammasome expression and signaling in human diabetic wounds and in high glucose induced macrophages. J Diabetes Res 2017:5281358. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5281358
Authors’ contribution statement
DKD conceived the idea, carried out the experiments, analysed the data and wrote the manuscript. GBJ conceived the idea, reviewed the manuscript and supervised the project. Both the authors have read and approved the present manuscript.
Funding
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial assistance received from National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research (NIPER), S.A.S. Nagar, India, for carrying out the present experiment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The animal protocol was approved by the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee (IAEC) against approval number IAEC/16/54.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 43.1 MB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dwivedi, D.K., Jena, G.B. NLRP3 inhibitor glibenclamide attenuates high-fat diet and streptozotocin-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rat: studies on oxidative stress, inflammation, DNA damage and insulin signalling pathway. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 393, 705–716 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-019-01773-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-019-01773-5