Abstract
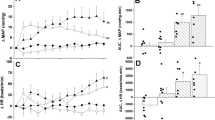
γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA), the principal brain inhibitory neurotransmitter, modulates inflammatory and neurodegenerative disease. Here, we tested the hypothesis that central GABAergic neurotransmission mediates the detrimental inflammatory, hemodynamic, and cardiac autonomic actions of endotoxemia. The effects of drugs that block GABA receptors or interfere with GABA uptake or degradation on blood pressure (BP), heart rate (HR), and HR variability (HRV) responses elicited by i.v. lipopolysaccharide (LPS) were assessed in conscious rats. The hypotensive effect of LPS (10 mg/kg) was blunted after intracisternal (i.c.) administration of bicuculline (GABAA receptor antagonist) or saclofen (GABAB receptor antagonist). By contrast, the concomitant LPS-evoked tachycardia and decreases in time domain and frequency domain indices of HRV (measures of cardiac autonomic control) were abolished upon treatment with bicuculline but not saclofen. Increases in serum tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) caused by LPS disappeared in the presence of bicuculline or saclofen, whereas LPS-evoked increases in serum nitric oxide metabolites (NOx) were counteracted by bicuculline only. None of the endotoxemia effects was altered in rats treated with i.c. tiagabine (GABA reuptake inhibitor) or vigabatrin (GABA transaminase inhibitor). These data suggest a major role for central GABAA receptors in the inflammatory and cardiovascular effects of endotoxemia.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BP:
-
Blood pressure
- DMV:
-
Dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus
- FFT:
-
Fast Fourier transform
- GABA:
-
γ-Aminobutyric acid
- HF:
-
High frequency
- HR:
-
Heart rate
- HRV:
-
Heart rate variability
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin-6
- iNOS:
-
Inducible nitric oxide synthase
- LF:
-
Low frequency
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- MAP:
-
Mean arterial pressure
- MAPKERK :
-
Extracellular signal-regulated mitogen-activated protein kinases
- NOx:
-
Nitric oxide metabolites
- rMSSD:
-
Root mean square of successive beat-to-beat differences in RR interval durations
- SDNN:
-
Standard deviation of beat-to-beat intervals
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
References
Balerio GN, Rubio MC (2002) Baclofen analgesia: involvement of the GABAergic system. Pharmacol Res 46:281–286
Bergeret M, Khrestchatisky M, Tremblay E, Bernard A, Gregoire A, Chany C (1998) GABA modulates cytotoxicity of immunocompetent cells expressing GABAA receptor subunits. Biomed Pharmacother 52:214–219 PMID: 9755818
Borovikova LV, Ivanova S, Zhang M, Yang H, Botchkina GI, Watkins LR, Wang H, Abumrad N, Eaton JW, Tracey KJ (2000) Vagus nerve stimulation attenuates the systemic inflammatory response to endotoxin. Nature 405:458–462
Carmans S, Hendriks JJ, Slaets H, Thewissen K, Stinissen P, Rigo JM, Hellings N (2013) Systemic treatment with the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid aggravates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by affecting proinflammatory immune responses. J Neuroimmunol 255:45–53. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2012.11.001
Catelli M, Feldman J, Bousquet P, Tibirica E (2003) Protective effects of centrally acting sympathomodulatory drugs on myocardial ischemia induced by sympathetic overactivity in rabbits. Braz J Med Biol Res 36:85–95
Cazareth J, Guyon A, Heurteaux C, Chabry J, Petit-Paitel A (2014) Molecular and cellular neuroinflammatory status of mouse brain after systemic lipopolysaccharide challenge: importance of CCR2/CCL2 signaling. J Neuroinflammation 11:132. doi:10.1186/1742-2094-11-132 PMID: 25065370
Chalmers J, Pilowsky P (1991) Brainstem and bulbospinal neurotransmitter systems in the control of blood pressure. J Hypertens 9:675–694
Chan SH, Wang LL, Chan JY (2003) Differential engagements of glutamate and GABA receptors in cardiovascular actions of endogenous nNOS or iNOS at rostral ventrolateral medulla of rats. Br J Pharmacol 138:584–593
Chaudhry H, Zhou J, Zhong Y, Ali MM, McGuire F, Nagarkatti PS, Nagarkatti M (2013) Role of cytokines as a double-edged sword in sepsis. In Vivo 27:669–684 PMID: 24292568
Dufour A, Tell F, Kessler JP, Baude A (2010) Mixed GABA-glycine synapses delineate a specific topography in the nucleus tractus solitarii of adult rat. J Physiol 588:1097–1115. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2009.184838
El-Mas MM, Abdel-Rahman AA (1995) Upregulation of imidazoline receptors in the medulla oblongata accounts for the enhanced hypotensive effect of clonidine in aortic barodenervated rats. Brain Res 691:195–204
El-Mas MM, Abdel-Rahman AA (2005) Longitudinal studies on the effect of hypertension on circadian hemodynamic and autonomic rhythms in telemetered rats. Life Sci 76:901–915
El-Mas MM, Abdel-Rahman AA (2007) Intermittent clonidine regimen abolishes tolerance to its antihypertensive effect: a spectral study. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 49:174–181 PMID: 17414230
El-Mas MM, Abdel-Galil AG, El-Gowelli HM, Daabees TT (1997) Short-term aortic barodenervation diminishes alpha 1-adrenoceptor reactivity in rat aortic smooth muscle. Eur J Pharmacol 322:201–210
El-Mas MM, Fan M, Abdel-Rahman AA (2008) Endotoxemia-mediated induction of cardiac inducible nitric-oxide synthase expression accounts for the hypotensive effect of ethanol in female rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 324:368–375
El-Mas MM, El-Gowelli HM, Ghazal AR, Harraz OF, Mohy El-Din MM (2009) Facilitation of central imidazoline I(1)-site/extracellular signal-regulated kinase/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling mediates the hypotensive effect of ethanol in rats with acute renal failure. Br J Pharmacol 158:1629–1640. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00444.x
El-Mas MM, El-gowilly SM, Fouda MA, Saad EI (2011a) Role of adenosine A2A receptor signaling in the nicotine-evoked attenuation of reflex cardiac sympathetic control. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 254:229–237. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2011.04.014
El-Mas MM, Fan M, Abdel-Rahman AA (2011b) Upregulation of cardiac NOS due to endotoxemia and vagal overactivity contributes to the hypotensive effect of chronic ethanol in female rats. Eur J Pharmacol 650:317–323. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2010.10.032
El-Mas MM, Omar AG, Helmy MM, Mohy El-Din MM (2012) Crosstalk between central pathways of nitric oxide and carbon monoxide in the hypertensive action of cyclosporine. Neuropharmacology 62:1890–1896. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.12.017
Fairchild KD, Saucerman JJ, Raynor LL, Sivak JA, Xiao Y, Lake DE, Moorman JR (2009) Endotoxin depresses heart rate variability in mice: cytokine and steroid effects. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 297:R1019–R1027. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00132.2009
Gao H, Smith BN (2010) Tonic GABAA receptor-mediated inhibition in the rat dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus. J Neurophysiol 103:904–914. doi:10.1152/jn.00511.2009
Gholami M, Mazaheri P, Mohamadi A, Dehpour T, Safari F, Hajizadeh S, Moore KP, Mani AR (2012) Endotoxemia is associated with partial uncoupling of cardiac pacemaker from cholinergic neural control in rats. Shock 37:219–227. doi:10.1097/SHK.0b013e318240b4be
Gong P, Hong H, Perkins EJ (2015) Ionotropic GABA receptor antagonism-induced adverse outcome pathways for potential neurotoxicity biomarkers. Biomark Med 9:1225–1239. doi:10.2217/bmm.15.58
Gonzalez-Clemente JM, Vilardell C, Broch M, Megia A, Caixas A, Gimenez-Palop O, Richart C, Simon I, Martinez-Riquelme A, Arroyo J, Mauricio D, Vendrell J (2007) Lower heart rate variability is associated with higher plasma concentrations of IL-6 in type 1 diabetes. Eur J Endocrinol 157:31–38
Hellstrom IC, Danik M, Luheshi GN, Williams S (2005) Chronic LPS exposure produces changes in intrinsic membrane properties and a sustained IL-beta-dependent increase in GABAergic inhibition in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. Hippocampus 15:656–664
Kadoi Y, Saito S (1996) An alteration in the gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor system in experimentally induced septic shock in rats. Crit Care Med 24:298–305
Lange M, Enkhbaatar P, Nakano Y, Traber DL (2009) Role of nitric oxide in shock: the large animal perspective. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 14:1979–1989
Li DP, Pan HL (2010) Role of GABA B receptors in autonomic control of systemic blood pressure. Adv Pharmacol 58:257–286
Malave HA, Taylor AA, Nattama J, Deswal A, Mann DL (2003) Circulating levels of tumor necrosis factor correlate with indexes of depressed heart rate variability: a study in patients with mild-to-moderate heart failure. Chest 123:716–724
Masuda N, Peng Q, Li Q, Jiang M, Liang Y, Wang X, Zhao M, Wang W, Ross CA, Duan W (2008) Tiagabine is neuroprotective in the N171-82Q and R6/2 mouse models of Huntington’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 30:293–302 PMID: 18395459
Mayyas F, Sakurai S, Ram R, Rennison JH, Hwang ES, Castel L, Lovano B, Brennan ML, Bibus D, Lands B, Barnard J, Chung MK, Van Wagoner DR (2011) Dietary ω3 fatty acids modulate the substrate for post-operative atrial fibrillation in a canine cardiac surgery model. Cardiovasc Res 89:852–861. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvq380
Mazloom R, Shirazi AH, Hajizadeh S, Dehpour AR, Mani AR (2014) The effect of endotoxin on the controllability of cardiac rhythm in rats. Physiol Meas 35:339–349
Meamar M, Dehpour T, Mazloom R, Sharifi F, Raoufy MR, Dehpour AR, Mani AR (2015) The effect of endotoxin on heart rate dynamics in diabetic rats. Auton Neurosci 2:222–227. doi:10.1016/j.autneu.2014.12.006
Mori M, Yamanashi Y, Kobayashi K, Sakamoto A (2010) Atrial natriuretic peptide alleviates cardiovascular and metabolic disorders in a rat endotoxemia model: a possible role for its anti-inflammatory properties. J Nippon Med Sch 77:296–305
Moshage H, Kok B, Huizenga JR, Jansen PL (1995) Nitrite and nitrate determinations in plasma: a critical evaluation. Clin Chem 41:892–896
Nagahama S, Dawson R, Oparil S (1985) Enhanced depressor effect of muscimol in the DOCA/NaCl hypertension rat: evidence for altered GABAergic activity in brain. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 180:277–283
Nikolov RP, Yakimova KS (2011) Effects of GABA-transaminase inhibitor vigabatrin on thermoregulation in rats. Amino Acids 40:1441–1445
Omar AG, El-Mas MM (2004) Time-domain evaluation of cyclosporine interaction with hemodynamic variability in rats. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 18:461–468
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, New York
Pellissier S, Dantzer C, Mondillon L, Trocme C, Gauchez AS, Ducros V, Mathieu N, Toussaint B, Fournier A, Canini F, Bonaz B (2014) Relationship between vagal tone, cortisol, TNF-alpha, epinephrine and negative affects in Crohn’s disease and irritable bowel syndrome. PLoS One 9:e105328. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0105328 PMID: 25207649
Rideau Batista Novais A, Crouzin N, Cavalier M, Boubal M, Guiramand J, Cohen-Solal C, de Jesus Ferreira MC, Cambonie G, Vignes M, Barbanel G (2014) Tiagabine improves hippocampal long-term depression in rat pups subjected to prenatal inflammation. PLoS One 9:e106302. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0106302
Rossi S, Muzio L, De Chiara V, Grasselli G, Musella A, Musumeci G, Mandolesi G, De Ceglia R, Maida S, Biffi E, Pedrocchi A, Menegon A, Bernardi G, Furlan R, Martino G, Centonze D (2011) Impaired striatal GABA transmission in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Brain Behav Immun 25:947–956. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2010.10.004
Rowan 3rd WH, Campen MJ, Wichers LB, Watkinson WP (2007) Heart rate variability in rodents: uses and caveats in toxicological studies. Cardiovasc Toxicol 7:28–51
Sapru HN (2013) Role of the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus in cardiovascular regulation. Auton Neurosci 175:38–50
Sayk F, Vietheer A, Schaaf B, Wellhoener P, Weitz G, Lehnert H, Dodt C (2008) Endotoxemia causes central downregulation of sympathetic vasomotor tone in healthy humans. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 295:R891–R898. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.90444.2008
Schmidt H, Saworski J, Werdan K, Muller-Werdan U (2007) Decreased beating rate variability of spontaneously contracting cardiomyocytes after co-incubation with endotoxin. J Endotoxin Res 13:339–342. doi:10.1177/0968051907086233
Serantes R, Arnalich F, Figueroa M, Salinas M, Andrés-Mateos E, Codoceo R, Renart J, Matute C, Cavada C, Cuadrado A (2006) Interleukin-1β enhances GABAA receptor cell-surface expression by a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway relevance to sepsis-associated encephalopathy. J Biol Chem 281:14632–14643
Sgoifo A, de Boer SF, Westenbroek C, Maes FW, Beldhuis H, Suzuki T, Koolhaas JM (1997) Incidence of arrhythmias and heart rate variability in wild-type rats exposed to social stress. Am J Physiol 273:H1754–H1760
Sill GJ, Butler E, Thompson GG, Brodie MJ (1999) Vigabatrin and tiagabine are pharmacologically different drugs. A pre-clinical study. Seizure Eur J Epilepsy 8:404–411
Song Q, Hu S, Wang H, Lv Y, Shi X, Sheng Z, Sheng W (2014) Electroacupuncturing at Zusanli point (ST36) attenuates pro-inflammatory cytokine release and organ dysfunction by activating cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway in rat with endotoxin challenge. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med 11:469–474
Stein PK, Bosner MS, Kleiger RE, Conger BM (1994) Heart rate variability: a measure of cardiac autonomic tone. Am Heart J 127:1376–1381
Sugiura S, Ishihara Y, Komatsu T, Hagiwara M, Tanigawa N, Kato Y, Mizutani H, Kawahara K, Maruyama I, Noguchi T, Matsushita K (2011) Valproic acid increases susceptibility to endotoxin shock through enhanced release of high-mobility group box 1. Shock 36:494–500. doi:10.1097/SHK.0b013e31822f7e58
Tateishi Y, Oda S, Nakamura M, Watanabe K, Kuwaki T, Moriguchi T, Hirasawa H (2007) Depressed heart rate variability is associated with high IL-6 blood level and decline in the blood pressure in septic patients. Shock 28:549–553
Theobaldo MC, Barbeiro HV, Barbeiro DF, Petroni R, Soriano FG (2012) Hypertonic saline solution reduces the inflammatory response in endotoxemic rats. Clinics 67:1463–1468 PMID: 23295602
Tian J, Dang H, Kaufman DL (2011) Combining antigen-based therapy with GABA treatment synergistically prolongs survival of transplanted ß-cells in diabetic NOD mice. PLoS One 6:e25337. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0025337
Travagli RA, Hermann GE, Browning KN, Rogers RC (2006) Brainstem circuits regulating gastric function. Annu Rev Physiol 68:279–305
Tunctan B, Korkmaz B, Sari AN, Kacan M, Unsal D, Serin MS, Buharalioglu CK, Sahan-Firat S, Cuez T, Schunck WH, Manthati VL, Falck JR, Malik KU (2013) Contribution of iNOS/sGC/PKG pathway, COX-2, CYP4A1, and gp91(phox) to the protective effect of 5,14-HEDGE, a 20-HETE mimetic, against vasodilation, hypotension, tachycardia, and inflammation in a rat model of septic shock. Nitric Oxide 33:18–41. doi:10.1016/j.niox.2013.05.001 PMID: 23684565
Vassalli P (1992) The pathophysiology of tumor necrosis factors. Annu Rev Immunol 10:411–452
Weil BR, Manukyan MC, Herrmann JL, Wang Y, Abarbanell AM, Poynter JA, Meldrum DR (2010) Mesenchymal stem cells attenuate myocardial functional depression and reduce systemic and myocardial inflammation during endotoxemia. Surgery 148:444–452. doi:10.1016/j.surg.2010.03.010
Wennstrom M, Janelidze S, Bay-Richter C, Minthon L, Brundin L (2014) Pro-inflammatory cytokines reduce the proliferation of NG2 cells and increase shedding of NG2 in vivo and in vitro. PLoS One 9:e109387. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0109387 PMID: 25285951
Zorn-Pauly K, Pelzmann B, Lang P, Machler H, Schmidt H, Ebelt H, Werdan K, Koidl B, Muller-Werdan U (2007) Endotoxin impairs the human pacemaker current if. Shock 28:655–661
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by the Science and Technology Development Fund, Egypt (STDF grant no. 14895).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sallam, M.Y., El-Gowilly, S.M., Abdel-Galil, AG.A. et al. Central GABAA receptors are involved in inflammatory and cardiovascular consequences of endotoxemia in conscious rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 389, 279–288 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-015-1201-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-015-1201-7