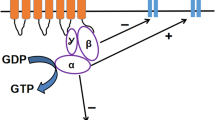
Abstract
Tramadol is an analgesic that is used worldwide for pain, but its mechanisms of action have not been fully elucidated. The majority of studies to date have focused on activation of the μ-opioid receptor (μOR) and inhibition of monoamine reuptake as mechanisms of tramadol. Although it has been speculated that tramadol acts primarily through activation of the μOR, no evidence has revealed whether tramadol directly activates the μOR. During the past decade, major advances have been made in our understanding of the physiology and pharmacology of ion channels and G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) signaling. Several studies have shown that GPCRs and ion channels are targets for tramadol. In particular, tramadol has been shown to affect GPCRs. Here, the effects of tramadol on GPCRs, monoamine transporters, and ion channels are presented with a discussion of recent research on the mechanisms of tramadol.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andurkar SV, Gendler L, Gulati A (2012) Tramadol antinociception is potentiated by clonidine through alpha(2)-adrenergic and I(2)-imidazoline but not by endothelin ET(A) receptors in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 683:109–115
Bamigbade TA, Davidson C, Langford RM, Stamford JA (1997) Actions of tramadol, its enantiomers and principal metabolite, O-desmethyltramadol, on serotonin (5-HT) efflux and uptake in the rat dorsal raphe nucleus. Br J Anaesth 79:352–356
Bannon AW, Decker MW, Curzon P, Buckley MJ, Kim DJ, Radek RJ, Lynch JK, Wasicak JT, Lin NH, Arnold WH, Holladay MW, Williams M, Arneric SP (1998a) ABT-594 [(R)-5-(2-azetidinylmethoxy)-2-chloropyridine]: a novel, orally effective antinociceptive agent acting via neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: II. In vivo characterization. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 285:787–794
Bannon AW, Decker MW, Kim DJ, Campbell JE, Arneric SP (1998b) ABT-594, a novel cholinergic channel modulator, is efficacious in nerve ligation and diabetic neuropathy models of neuropathic pain. Brain Res 801:158–163
Basbaum AI (1999) Distinct neurochemical features of acute and persistent pain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:7739–7743
Butcher JW, De Felipe C, Smith AJ, Hunt SP, Paton JF (1998) Comparison of cardiorespiratory reflexes in NK1 receptor knockout, heterozygous and wild-type mice in vivo. J Auton Nerv Syst 69:89–95
Cao T, Gerard NP, Brain SD (1999) Use of NK(1) knockout mice to analyze substance P-induced edema formation. Am J Physiol 277:R476–481
Caulfield MP, Birdsall NJ (1998) International Union of Pharmacology. XVII. Classification of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Pharmacol Rev 50:279–290
Dascal N (1987) The use of Xenopus oocytes for the study of ion channels. CRC Crit Rev Biochem 22:317–387
De Koninck Y, Henry JL (1991) Substance P-mediated slow excitatory postsynaptic potential elicited in dorsal horn neurons in vivo by noxious stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88:11344–11348
Desmeules JA, Piguet V, Collart L, Dayer P (1996) Contribution of monoaminergic modulation to the analgesic effect of tramadol. Br J Clin Pharmacol 41:7–12
Driessen B, Reimann W (1992) Interaction of the central analgesic, tramadol, with the uptake and release of 5-hydroxytryptamine in the rat brain in vitro. Br J Pharmacol 105:147–151
Driessen B, Reimann W, Giertz H (1993) Effects of the central analgesic tramadol on the uptake and release of noradrenaline and dopamine in vitro. Br J Pharmacol 108:806–811
Durieux ME (1996) Muscarinic signaling in the central nervous system. Recent developments and anesthetic implications. Anesthesiology 84:173–189
Frink EJ Jr, Malan TP, Atlas M, Dominguez LM, DiNardo JA, Brown BR Jr (1992) Clinical comparison of sevoflurane and isoflurane in healthy patients. Anesth Analg 74:241–245
Frink MC, Hennies HH, Englberger W, Haurand M, Wilffert B (1996) Influence of tramadol on neurotransmitter systems of the rat brain. Arzneimittelforschung 46:1029–1036
Gillen C, Haurand M, Kobelt DJ, Wnendt S (2000) Affinity, potency and efficacy of tramadol and its metabolites at the cloned human mu-opioid receptor. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 362:116–121
Grunfeld JA, Tiedemann GJ, Westerman RA (1991) Chronic nicotine exposure enhances cutaneous axon reflexes in the rat. Neuroreport 2:421–424
Gyermek L (1996) Pharmacology of serotonin as related to anesthesia. J Clin Anesth 8:402–425
Halfpenny DM, Callado LF, Hopwood SE, Bamigbade TA, Langford RM, Stamford JA (1999) Effects of tramadol stereoisomers on norepinephrine efflux and uptake in the rat locus coeruleus measured by real time voltammetry. Br J Anaesth 83:909–915
Hara K, Minami K, Sata T (2005) The effects of tramadol and its metabolite on glycine, gamma-aminobutyric acidA, and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Anesth Analg 100:1400–1405
Hennies HH, Friderichs E, Schneider J (1988) Receptor binding, analgesic and antitussive potency of tramadol and other selected opioids. Arzneimittelforschung 38:877–880
Heyer G, Hornstein OP, Handwerker HO (1991) Reactions to intradermally injected substance P and topically applied mustard oil in atopic dermatitis patients. Acta Derm Venereol 71:291–295
Horishita T, Minami K, Uezono Y, Shiraishi M, Ogata J, Okamoto T, Shigematsu A (2006) The tramadol metabolite, O-desmethyl tramadol, inhibits 5-hydroxytryptamine type 2C receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Pharmacology 77:93–99
Ide S, Minami M, Ishihara K, Uhl GR, Sora I, Ikeda K (2006) Mu opioid receptor-dependent and independent components in effects of tramadol. Neuropharmacology 51:651–8
Kroeze WK, Kristiansen K, Roth BL (2002) Molecular biology of serotonin receptors structure and function at the molecular level. Curr Top Med Chem 2:507–528
Lee CR, McTavish D, Sorkin EM (1993) Tramadol. A preliminary review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic potential in acute and chronic pain states. Drugs 46:313–340
Marincsak R, Toth BI, Czifra G, Szabo T, Kovacs L, Biro T (2008) The analgesic drug, tramadol, acts as an agonist of the transient receptor potential vanilloid-1. Anesth Analg 106:1890–1896
Mayer ML, Westbrook GL (1987) The physiology of excitatory amino acids in the vertebrate central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol 28:197–276
Minami K, Uezono Y (2006) Gq protein-coupled receptors as targets for anesthetics. Curr Pharm Des 12:1931–1937
Minami K, Minami M, Harris RA (1997a) Inhibition of 5-hydroxytryptamine type 2A receptor-induced currents by n-alcohols and anesthetics. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 281:1136–1143
Minami K, Vanderah TW, Minami M, Harris RA (1997b) Inhibitory effects of anesthetics and ethanol on muscarinic receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Eur J Pharmacol 339:237–244
Minami K, Gereau RW 4th, Minami M, Heinemann SF, Harris RA (1998) Effects of ethanol and anesthetics on type 1 and 5 metabotropic glutamate receptors expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Mol Pharmacol 53:148–156
Minami K, Shiraishi M, Uezono Y, Ueno S, Shigematsu A (2002) The inhibitory effects of anesthetics and ethanol on substance P receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Anesth Analg 94:79–83
Minami K, Ogata J, Horishita T, Shiraishi M, Okamoto T, Sata T, Shigematsu A (2004a) Intramuscular tramadol increases gastric pH during anesthesia. Can J Anaesth 51:545–548
Minami K, Uezono Y, Shiraishi M, Okamoto T, Ogata J, Horishita T, Taniyama K, Shigematsu A (2004b) Analysis of the effects of halothane on Gi-coupled muscarinic M2 receptor signaling in Xenopus oocytes using a chimeric G alpha protein. Pharmacology 72:205–212
Minami K, Uezono Y, Sakurai T, Horishita T, Shiraishi M, Ueta Y (2007a) Effects of anesthetics on the function of orexin-1 receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Pharmacology 79:236–242
Minami K, Uezono Y, Ueta Y (2007b) Pharmacological aspects of the effects of tramadol on G-protein coupled receptors. J Pharmacol Sci 103:253–260
Minami K, Sudo Y, Shiraishi S, Seo M, Uezono Y (2010) Analysis of the effects of anesthetics and ethanol on mu-opioid receptor. J Pharmacol Sci 112:424–431
Minami K, Sudo Y, Yokoyama T, Ogata J, Takeuchi M, Uezono Y (2011a) Sevoflurane inhibits the micro-opioid receptor function expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Pharmacology 88:127–132
Minami K, Yokoyama T, Ogata J, Uezono Y (2011b) The tramadol metabolite O-desmethyl tramadol inhibits substance P-receptor functions expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J Pharmacol Sci 115:421–424
Minami K, Sudo Y, Miyano K, Murphy RS, Uezono Y (2015) Micro-opioid receptor activation by tramadol and O-desmethyltramadol (M1). J Anesth 29:475–9
Miyano K, Minami K, Yokoyama T, Ohbuchi K, Yamaguchi T, Murakami S, Shiraishi S, Yamamoto M, Matoba M, Uezono Y (2015) Tramadol and its metabolite M1 selectively suppress the activity of the transient receptor potential ankyrin 1, but not that of the transient receptor potential vanilloid 1. Anesth Analg 120:790–8
Naguib M, Yaksh TL (1997) Characterization of muscarinic receptor subtypes that mediate antinociception in the rat spinal cord. Anesth Analg 85:847–853
Nakamura M, Minami K, Uezono Y, Horishita T, Ogata J, Shiraishi M, Okamoto T, Terada T, Sata T (2005) The effects of the tramadol metabolite O-desmethyl tramadol on muscarinic receptor-induced responses in Xenopus oocytes expressing cloned M1 or M3 receptors. Anesth Analg 101:180–186
Ogata J, Minami K, Uezono Y, Okamoto T, Shiraishi M, Shigematsu A, Ueta Y (2004) The inhibitory effects of tramadol on 5-hydroxytryptamine type 2C receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Anesth Analg 98:1401–1406
Okamoto T, Minami K, Uezono Y, Ogata J, Shiraishi M, Shigematsu A, Ueta Y (2003) The inhibitory effects of ketamine and pentobarbital on substance p receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Anesth Analg 97:104–110
Oliva P, Aurilio C, Massimo F, Grella A, Maione S, Grella E, Scafuro M, Rossi F, Berrino L (2002) The antinociceptive effect of tramadol in the formalin test is mediated by the serotonergic component. Eur J Pharmacol 445:179–185
Özdoğan UK, Lähdesmäki J, Scheinin M (2006) The analgesic efficacy of partial opioid agonists is increased in mice with targeted inactivation of the alpha2A-adrenoceptor gene. Eur J Pharmacol 529(1–3):105–13
Raffa RB, Friderichs E, Reimann W, Shank RP, Codd EE, Vaught JL (1992) Opioid and nonopioid components independently contribute to the mechanism of action of tramadol, an ‘atypical’ opioid analgesic. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 260:275–285
Raffa RB, Friderichs E, Reimann W, Shank RP, Codd EE, Vaught JL, Jacoby HI, Selve N (1993) Complementary and synergistic antinociceptive interaction between the enantiomers of tramadol. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 267:331–340
Reimann W, Hennies HH (1994) Inhibition of spinal noradrenaline uptake in rats by the centrally acting analgesic tramadol. Biochem Pharmacol 47:2289–2293
Roberts RG, Stevenson JE, Westerman RA, Pennefather J (1995) Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on capsaicin-sensitive nerves. Neuroreport 6:1578–1582
Sagata K, Minami K, Yanagihara N, Shiraishi M, Toyohira Y, Ueno S, Shigematsu A (2002) Tramadol inhibits norepinephrine transporter function at desipramine-binding sites in cultured bovine adrenal medullary cells. Anesth Analg 94:901–906
Sawynok J, Reid AR, Liu J (2013) Spinal and peripheral adenosine A(1) receptors contribute to antinociception by tramadol in the formalin test in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 714:373–378
Shiga Y, Minami K, Shiraishi M, Uezono Y, Murasaki O, Kaibara M, Shigematsu A (2002) The inhibitory effects of tramadol on muscarinic receptor-induced responses in Xenopus oocytes expressing cloned M(3) receptors. Anesth Analg 95:1269–1273
Shiraishi M, Minami K, Uezono Y, Yanagihara N, Shigematsu A (2001) Inhibition by tramadol of muscarinic receptor-induced responses in cultured adrenal medullary cells and in Xenopus laevis oocytes expressing cloned M1 receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 299:255–260
Shiraishi M, Minami K, Uezono Y, Yanagihara N, Shigematsu A, Shibuya I (2002) Inhibitory effects of tramadol on nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in adrenal chromaffin cells and in Xenopus oocytes expressing alpha 7 receptors. Br J Pharmacol 136:207–216
Steen KH, Reeh PW (1993) Actions of cholinergic agonists and antagonists on sensory nerve endings in rat skin, in vitro. J Neurophysiol 70:397–405
Wess J (1996) Molecular biology of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Crit Rev Neurobiol 10:69–99
Xu XJ, Dalsgaard CJ, Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z (1992) Spinal substance P and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors are coactivated in the induction of central sensitization of the nociceptive flexor reflex. Neuroscience 51:641–648
Zimmer A, Zimmer AM, Baffi J, Usdin T, Reynolds K, Konig M, Palkovits M, Mezey E (1998) Hypoalgesia in mice with a targeted deletion of the tachykinin 1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:2630–2635
Zoli M, Le Novere N, Hill JA Jr, Changeux JP (1995) Developmental regulation of nicotinic ACh receptor subunit mRNAs in the rat central and peripheral nervous systems. J Neuroscience 15:1912–1939
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Minami, K., Ogata, J. & Uezono, Y. What is the main mechanism of tramadol?. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 388, 999–1007 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-015-1167-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-015-1167-5