Abstract
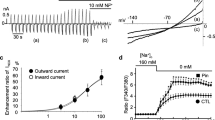
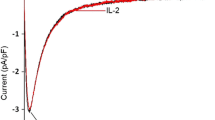
Fluorine-containing pinacidil-derivative flocalin is an effective adenosine triphosphate-sensitive potassium (KATP)-channel opener with pronounced vasodilatory, cardioprotective effects and low general toxicity. By activating cardiac KATP channels, flocalin hyperpolarizes cardiac myocytes, decreases their excitability, reduces Ca2+ entry, and inhibits Ca2+-dependent signalling processes. Since our previous studies indicated that the drug also influences the rate of rise and amplitude of the cardiomyocyte’s action potential, here we have investigated its possible actions on depolarizing inward currents through voltage-gated sodium (VGSC) and L-type calcium (VGCC) channels. Experiments were conducted on cultured cardiac myocytes prepared from the whole hearts of neonatal rats and maintained in culture for 1–3 days using whole-cell patch-clamp technique with no distinction of myocyte’s type. Flocalin concentration dependently inhibited the Na+ inward current through VGSCs with IC50 = 17.4 μM and a maximal extent of 0.54, slowed down its inactivation kinetics, and hyperpolarized steady-state inactivation by 5.6 mV. The drug also inhibited calcium current through L-type VGCCs with IC50 = 24.1 μM and a maximal block of 0.38, without affecting its inactivation but producing 5.3-mV hyperpolarization shifting of steady-state activation. Inhibition of both depolarizing currents by flocalin in addition to its ability to open KATP channels enhances the suppressive action of the drug on cardiac excitability and broadens its pharmacological effects. Since, according to our previous data, cardiac KATP-channel opening by flocalin occurs with ЕC50 = 8 μM, the possibility of partial blockade of VGSC and L-type VGCCs should be considered when determining the therapeutic concentrations of the compound during its use as a cardioprotector.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Begue JP, Bonnet-Delpon D (2008) Effects of fluorine substitution on biological properties. In: Begue JP, Bonnet-Delpon D (eds) Bioorganic and medicinal chemistry of fluorine. Wiley, Hoboken, pp 72–98
Charnock JS (1999) Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and ventricular fibrillation: the possible involvement of eicosanoids. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fat Acids 61:243–247
Grover GJ, Garlid KD (2000) ATP-sensitive potassium channels: a review of their cardioprotective pharmacology. J Mol Cell Cardiol 32:677–695
Harvey RD, Jurevicius JA, Hume JR (1991) Intracellular Na+ modulates the cAMP-dependent regulation of ion channels in the heart. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:6946–6950
Hughes AD (1995) Calcium channels in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Vasc Res 32:353–370
Irvine LA, Jafri MS, Winslow RL (1999) Cardiac sodium channel Markov model with temperature dependence and recovery from inactivation. Biophys J 76:1868–1885
Moibenko AA, Strutynskyi RB, Yagupolskii LM, Mohort NA (2009) Organization of industrial production of flocalin—new myotropic spasmolytic and cardioprotector. Sci Innov 1:80–84, Ukrainian
Movafagh S, Cleemann L, Morad M (2011) Regulation of cardiac Ca2+ channel by extracellular Na+. Cell Calcium 49:162–173
Rogers TB, Gaa ST, Allen IS (1986) Identification and characterization of functional angiotensin II receptors on cultured heart myocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 236:438–444
Strutyns’kyi RB (2010) The vasodilation effects of flokalin, a fluorine-containing K(ATP) channel opener. Fiziol Zh 56:59–65, Ukrainian
Strutyns’kyi RB, Pyvovar SM, Tumanovs’ka LV, Moibenko OO (2008) Cardioprotective effects of flokalin: relative role of activation of sarcolemmal and mitochondrial adenosine triphosphate-dependent potassium channels. Fiziol Zh 54:15–23, Ukrainian
Strutyns’kyi RB, Neshcheret OP, Tumanovs’ka LV, Rovenets’ RA, Moĭbenko OO (2009) Cardioprotective effects of flokalin in experiments in vivo: influence on hemodynamic and myocardial lesions in ischemia–reperfusion. Fiziol Zh 55:9–16, Ukrainian
Strutyns’kyi RB, Kotsiuruba AV, Neshcheret OP, Rovenets’ RA, Moĭbenko OO (2012) The changes of metabolism in myocardium at ischemia–reperfusion and activating of the ATP-sensitive potassium channels. Fiziol Zh 58:13–26, Ukrainian
Voitychuk OI, Strutynskyi RB, Yagupolskii LM, Tinker A, Moibenko OO, Shuba YM (2011) Sarcolemmal cardiac KATP channels as a target for the cardioprotective effects of the fluorine-containing pinacidil analogue, flocalin. Br J Pharmacol 162:701–711
Wakili R, Voigt N, Kääb S, Dobrev D, Nattel S (2011) Recent advances in the molecular pathophysiology of atrial fibrillation. J Clin Invest 121:2955–2968
Yagupolskii LM, Maletina II, Petko KI, Fedyuk DV, Handrock R, Shavaran SS, Klebanov BM, Herzig S (2001) New fluorine-containing hypotensive preparations. J Fluor Chem 109:87–94
Yanchii RI, Dzhuran BV, Filippov IB, Vladimirova IA (2005) Suppressive effect of an activator of ATP-dependent potassium channels, flocalin, on electrical and contractile activities of smooth muscles of the guinea-pig ureter. Neurophysiology/Neurofiziologiya (Kiev) 37:353–358
Zingman LV, Alekseev AE, Hodgson-Zingman DM, Terzic A (2007) ATP-sensitive potassium channels: metabolic sensing and cardioprotection. J Appl Physiol 103:1888–1893
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine and by the State Fund for Fundamental Research, Ukraine (F46.2/001 grant).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Voitychuk, O.I., Strutynskyi, R.B., Moibenko, O.O. et al. Effects of fluorine-containing opener of ATP-sensitive potassium channels, pinacidil-derivative flocalin, on cardiac voltage-gated sodium and calcium channels. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 385, 1095–1102 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-012-0792-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-012-0792-5