Abstract
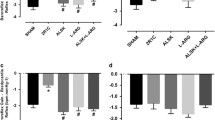
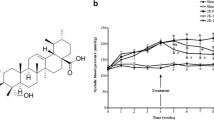
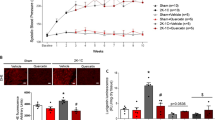
The vascular remodeling associated with hypertension involves oxidative stress and enhanced matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) expression/activity, especially MMP-2. While previous work showed that lercanidipine, a third-generation dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker (CCB), attenuated the oxidative stress and increased MMP-2 expression/activity in two-kidney, one-clip (2K1C) hypertension, no previous study has examined whether first- or second-generation dihydropyridines produce similar effects. We compared the effects of nifedipine, nimodipine, and amlodipine on 2K1C hypertension-induced changes in systolic blood pressure (SBP), vascular remodeling, oxidative stress, and MMPs levels/activity. Sham-operated and 2K1C rats were treated with water, nifedipine 10 mg/kg/day, nimodipine 15 mg/kg/day, or amlodipine 10 mg/kg/day by gavage, starting 3 weeks after hypertension was induced. SBP was monitored weekly. After 6 weeks of treatment, quantitative morphometry of structural changes in the aortic wall was studied in hematoxylin/eosin-stained sections. Aortic and systemic reactive oxygen species levels were measured by using dihydroethidine and thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances (TBARs), respectively. Aortic MMP-2 levels and activity were determined by gelatin zymography, in situ zymography, and immunofluorescence. Nifedipine, nimodipine, or amlodipine attenuated the increases in SBP in hypertensive rats by approximately 17% (P < 0.05) and prevented vascular hypertrophy (P < 0.05). These CCBs blunted 2K1C-induced increases in vascular oxidative stress and plasma TBARs concentrations (P < 0.05). All dihydropyridines attenuated the increases in aortic MMP-2 levels and activity associated with 2K1C hypertension. These findings suggest lack of superiority of one particular dihydropyridine, at least with respect to antioxidant effects, MMPs downregulation, and inhibition of vascular remodeling in hypertension.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed SH, Clark LL, Pennington WR, Webb CS, Bonnema DD, Leonardi AH, McClure CD, Spinale FG, Zile MR (2006) Matrix metalloproteinases/tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases: relationship between changes in proteolytic determinants of matrix composition and structural, functional, and clinical manifestations of hypertensive heart disease. Circulation 113(17):2089–2096
Arribas SM, Hinek A, Gonzalez MC (2006) Elastic fibres and vascular structure in hypertension. Pharmacol Ther 111(3):771–791
Asanuma K, Magid R, Johnson C, Nerem RM, Galis ZS, O’Callaghan CJ, Williams B (2003) Uniaxial strain upregulates matrix-degrading enzymes produced by human vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 284(5):H1778–H1784
Bouvet C, Gilbert LA, Girardot D, deBlois D, Moreau P (2005) Different involvement of extracellular matrix components in small and large arteries during chronic no synthase inhibition. Hypertension 45(3):432–437
Castier Y, Brandes RP, Leseche G, Tedgui A, Lehoux S (2005) P47phox-dependent NADPH oxidase regulates flow-induced vascular remodeling. Circ Res 97:533–540
Castro MM, Rizzi E, Rascado RR, Nagassaki S, Bendhack LM, Tanus-Santos JE (2004) Atorvastatin enhances sildenafil-induced vasodilation through nitric oxide-mediated mechanisms. Eur J Pharmacol 498(1–3):189–194
Castro MM, Rizzi E, Figueiredo-Lopes L, Fernandes K, Bendhack LM, Pitol DL, Gerlach RF, Tanus-Santos JE (2008) Metalloproteinase inhibition ameliorates hypertension and prevents vascular dysfunction and remodeling in renovascular hypertensive rats. Atherosclerosis 198(2):320–331
Castro MM, Rizzi E, Rodrigues GJ, Ceron CS, Bendhack LM, Gerlach RF, Tanus-Santos JE (2009) Antioxidant treatment reduces matrix metalloproteinase-2-induced vascular changes in renovascular hypertension. Free Radic Biol Med 46(9):1298–1307
Castro MM, Rizzi E, Prado CM, Rossi MA, Tanus-Santos JE, Gerlach RF (2010) Imbalance between matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases in hypertensive vascular remodeling. Matrix Biol 29(3):194–201
Ceron CS, Castro MM, Rizzi E, Montenegro MF, Fontana V, Salgado MC, Gerlach RF, Tanus-Santos JE (2010) Spironolactone and hydrochlorothiazide exert antioxidant effects and reduce vascular matrix metalloproteinase-2 activity and expression in a model of renovascular hypertension. Br J Pharmacol 160(1):77–87
Chesler NC, Ku DN, Galis ZS (1999) Transmural pressure induces matrix-degrading activity in porcine arteries ex vivo. Am J Physiol 277(5 Pt 2):H2002–H2009
Cohuet G, Struijker-Boudier H (2006) Mechanisms of target organ damage caused by hypertension: therapeutic potential. Pharmacol Ther 111(1):81–98
Dias-Junior CA, Montenegro MF, Florencio BC, Tanus-Santos JE (2008) Sildenafil improves the beneficial haemodynamic effects of intravenous nitrite infusion during acute pulmonary embolism. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 103(4):374–379
Flamant M, Placier S, Dubroca C, Esposito B, Lopes I, Chatziantoniou C, Tedgui A, Dussaule JC, Lehoux S (2007) Role of matrix metalloproteinases in early hypertensive vascular remodeling. Hypertension 50(1):212–218
Galis ZS, Khatri JJ (2002) Matrix metalloproteinases in vascular remodeling and atherogenesis: the good, the bad, and the ugly. Circ Res 90(3):251–262
Godfraind T (2005) Antioxidant effects and the therapeutic mode of action of calcium channel blockers in hypertension and atherosclerosis. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 360(1464):2259–2272
Griendling KK, FitzGerald GA (2003) Oxidative stress and cardiovascular injury: part II: animal and human studies. Circulation 108(17):2034–2040
Grote K, Flach I, Luchtefeld M, Akin E, Holland SM, Drexler H, Schieffer B (2003) Mechanical stretch enhances mRNA expression and proenzyme release of matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) via NAD(P)H oxidase-derived reactive oxygen species. Circ Res 92(11):e80–e86
Lehoux S, Lemarie CA, Esposito B, Lijnen HR, Tedgui A (2004) Pressure-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9 contributes to early hypertensive remodeling. Circulation 109(8):1041–1047
Luchtefeld M, Grote K, Grothusen C, Bley S, Bandlow N, Selle T, Struber M, Haverich A, Bavendiek U, Drexler H, Schieffer B (2005) Angiotensin II induces MMP-2 in a p47phox-dependent manner. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 328:183–188
Martinez ML, Lopes LF, Coelho EB, Nobre F, Rocha JB, Gerlach RF, Tanus-Santos JE (2006) Lercanidipine reduces matrix metalloproteinase-9 activity in patients with hypertension. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 47(1):117–122
Martinez ML, Castro MM, Rizzi E, Fernandes K, Demacq C, Bendhack LM, Gerlach RF, Tanus-Santos JE (2008a) Lercanidipine reduces matrix metalloproteinase-2 activity and reverses vascular dysfunction in renovascular hypertensive rats. Eur J Pharmacol 591(1–3):224–230
Martinez ML, Rizzi E, Castro MM, Fernandes K, Bendhack LM, Gerlach RF, Tanus-Santos JE (2008b) Lercanidipine decreases vascular matrix metalloproteinase-2 activity and protects against vascular dysfunction in diabetic rats. Eur J Pharmacol 599(1–3):110–116
Mason RP, Marche P, Hintze TH (2003) Novel vascular biology of third-generation L-type calcium channel antagonists: ancillary actions of amlodipine. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 23(12):2155–2163
Matrisian LM (1994) Matrix metalloproteinase gene expression. Ann NY Acad Sci 732:42–50
Montenegro MF, Neto-Neves EM, Dias-Junior CA, Ceron CS, Castro MM, Gomes VA, Kanashiro A, Tanus-Santos JE (2010) Quercetin restores plasma nitrite and nitroso species levels in renovascular hypertension. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 382(4):293–301
Murphy G, Willenbrock F, Crabbe T, O’Shea M, Ward R, Atkinson S, O’Connell J, Docherty A (1994) Regulation of matrix metalloproteinase activity. Ann NY Acad Sci 732:31–41
Nelson KK, Melendez JA (2004) Mitochondrial redox control of matrix metalloproteinases. Free Radic Biol Med 37(6):768–784
Newby AC (2006) Matrix metalloproteinases regulate migration, proliferation, and death of vascular smooth muscle cells by degrading matrix and non-matrix substrates. Cardiovasc Res 69(3):614–624
Okamoto T, Akaike T, Sawa T, Miyamoto Y, van der Vliet A, Maeda H (2001) Activation of matrix metalloproteinases by peroxynitrite-induced protein S-glutathiolation via disulfide S-oxide formation. J Biol Chem 276(31):29596–29602
Ra HJ, Parks WC (2007) Control of matrix metalloproteinase catalytic activity. Matrix Biol 26(8):587–596
Raffetto JD, Khalil RA (2008) Matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in vascular remodeling and vascular disease. Biochem Pharmacol 75(2):346–359
Rajagopalan S, Meng XP, Ramasamy S, Harrison DG, Galis ZS (1996) Reactive oxygen species produced by macrophage-derived foam cells regulate the activity of vascular matrix metalloproteinases in vitro. Implications for atherosclerotic plaque stability. J Clin Invest 98:2572–2579
Sica DA (2006) Pharmacotherapy review: calcium channel blockers. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich) 8(1):53–56
Sluijter JP, de Kleijn DP, Pasterkamp G (2006) Vascular remodeling and protease inhibition—bench to bedside. Cardiovasc Res 69(3):595–603
Taddei S, Virdis A, Ghiadoni L, Magagna A, Pasini AF, Garbin U, Cominacini L, Salvetti A (2001) Effect of calcium antagonist or beta blockade treatment on nitric oxide-dependent vasodilation and oxidative stress in essential hypertensive patients. J Hypertens 19(8):1379–1386
Tomassoni D, Sabbatini M, Amenta F (2003) Effect of different dihydropyridine-type Ca2+ antagonists on left ventricle hypertrophy and coronary changes in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 41(4):544–552
Van Wart HE, Birkedal-Hansen H (1990) The cysteine switch: a principle of regulation of metalloproteinase activity with potential applicability to the entire matrix metalloproteinase gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:5578–5582
Viappiani S, Nicolescu AC, Holt A, Sawicki G, Crawford BD, Leon H, van Mulligen T, Schulz R (2009) Activation and modulation of 72 kDa matrix metalloproteinase-2 by peroxynitrite and glutathione. Biochem Pharmacol 77(5):826–834
Watts SW, Rondelli C, Thakali K, Li X, Uhal B, Pervaiz MH, Watson RE, Fink GD (2007) Morphological and biochemical characterization of remodeling in aorta and vena cava of DOCA-salt hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 292(5):H2438–H2448
Yasmin McEniery CM, Wallace S, Dakham Z, Pulsalkar P, Maki-Petaja K, Ashby MJ, Cockcroft JR, Wilkinson IB (2005) Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), MMP-2, and serum elastase activity are associated with systolic hypertension and arterial stiffness. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25(2):372
Yue H, Uzui H, Shimizu H, Nakano A, Mitsuke Y, Ueda T, Lee JD (2004) Different effects of calcium channel blockers on matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression in cultured rat cardiac fibroblasts. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 44(2):223–230
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by Fundação de Amparo a Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP-Brazil) and Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq-Brazil).
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marçal, D.M.O., Rizzi, E., Martins-Oliveira, A. et al. Comparative study on antioxidant effects and vascular matrix metalloproteinase-2 downregulation by dihydropyridines in renovascular hypertension. Naunyn-Schmied Arch Pharmacol 383, 35–44 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-010-0573-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-010-0573-y