Abstract
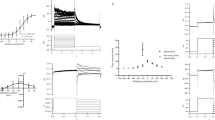
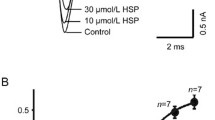
We studied the effects of isoquinoline alkaloid neferine (Nef) extracted from the seed embryo of Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn on Human ether-à-go-go-related gene (HERG) channels stably expressed in human embryonic kidney (HEK293) cells using whole-cell patch clamp technique, western blot analysis and immunofluorescence experiment. Nef induced a concentration-dependent decrease in current amplitude according to the voltage steps and tail currents of HERG with an IC50 of 7.419 μM (n H −0.5563). Nef shifted the activation curve in a significantly negative direction and accelerated recovery from inactivation and onset of inactivation, however, slowed deactivation. In addition, it had no significant influence on steady-state inactivation curve. Western blot and immunofluorescence results suggested Nef had no significant effect on the expression of HERG protein. In summary, Nef can block HERG K+ channels that functions by changing the channel activation and inactivation kinetics. Nef has no effect on the generation and trafficking of HERG protein. A blocked-off HERG channel was one mechanism of the anti-arrhythmic effects by Nef.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cai BZ, Gong DM, Pan ZW, Liu Y, Qian H, Zhang Y, Jiao JD, Lu YJ, Yang BF (2007) Large-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ currents blocked and impaired by homocysteine in human and rat mesenteric artery smooth muscle cells. Life Sci 80:2060–2066
Chapman H, Pasternack M (2007) The action of the novel gastrointestinal prokinetic prucalopride on the HERG K+ channel and the common T897 polymorph. Eur J Pharmacol 554:98–105
Danielsson BR, Lansdell K, Patmore L, Tomson T (2003) Phenytoin and phenobarbital inhibit human HERG potassium channels. Epilepsy Res 55:147–157
David F, Steele JE, David F (2007) Mechanisms of cardiac potassium channel trafficking. J Physiol 582:17–26
Ducroq J, Printemps R, Guilbot S, Gardette J, Salvetat C, Le GM (2007) Action potential experiments complete hERG assay and QT-interval measurements in cardiac preclinical studies. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 56:159–170
Eckhardt LL, Rajamani S, January CT (2005) Protein trafficking abnormalities: a new mechanism in drug-induced long QT syndrome. Br J Pharmacol 145:3–4
Ficker E, Kuryshev YA, Dennis AT, Obejero-Paz C, Wang L, Hawryluk P, Wible BA, Brown AM (2004) Mechanisms of arsenic-induced prolongation of cardiac repolarization. Mol Pharmacol 66:33–44
Gong Q, Anderson CL, January CT, Zhou Z (2002) Role of glycolsylation in cell surface expression and stability of HERG potassium channels. Am J Physiol 283:H77–H84
Guo ZB, Li Q, Cao HY, Xu Z (2002) Antiarrhythmic efficacy of neferine assessed by programmed electrical stimulation in a canine model of electropharmacology. J Chin Pharm Sci 11:35–42
Hancox JC, McPate MJ, EI Harchi A, Zhang YH (2008) The hERG potassium channel and hERG screening for drug-induced torsades de pointes. Pharmacol Ther 119:118–132
Li GR, Li XG, Qian JQ, Lue FH (1987) Effects of neferine on electrical and mechanical activity in isolated guinea pig myocardium. Chinese Journal of Pharmacology and Toxicology 1:268–271
Li GR, Lu FH, Qian JQ (1988) Effects of neferine on physiologic properties and the dose-effect response of isoprenaline and Ca2+ in guinea pig atria. Acta Pharm Sin 23:241–245
Li BX, Yang BF, Zhou J, Xu CQ, Li YR (2001) Inhibitory effects of berberine on I k1, I k and HERG channels of cardiac myocytes. Acta Pharmacologica Sin 22:125–131
Qian JQ (2002) Cardiovascular pharmacological effects of bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloid derivatives. Acta Pharmacol Sin 23:1086–1092
Rajamani S, Eckhardt LL, Valdivia CR, Klemens CA, Gillman BM, Anderson CL, Holzem KM, Delisle BP, Anson BD, Makielski JC, January CT (2006) Drug-induced long QT syndrome: HERG K+ channel block and disruption of protein trafficking by fluoxetine and norfluoxetine. Br J Pharmacol 149:481–489
Ravens U, Cerbai E (2008) Role of potassium in cardiac arrhythmias. Europace 10:1133–1137
Redfern WS, Carlsson L, Davis AS, Lynch WG, MacKenzie I, Palethorpe S, Siegl PKS, Strang I, Sullivan AT, Wallis R, Camm AJ, Hammond TG (2003) Cardiovasc Res 58:32–45
Sanguinetti MC, Tristani-Firouzi M (2006) hERG potassium channels and cardiac arrhythmia. Nature 440:463–469
Sanguinetti MC, Jiang C, Curran ME, Keating MT (1995) A mechanistic link between an inherited and an acquired cardiac arrhythmia: HERG encodes the I kr potassium channel. Cell 81:299–307
Shin WH, Kim KS, Kim EJ (2006) Electrophysiological effects of brompheniramine on cardiac ion channels and action potential. Pharmacol Res 54:414–420
Tang XQ, Cao JG (2004) Review on the pharmacological research of neferine. Chin Pharmacol Bull 20:8–10
Traebert M, Dumotier B, Meister L, Hoffmann P, Dominguez-Estevez M, Suter W (2004) Inhibition of HERG K+ currents by antimalarial drugs in stably transfected HEK293 cells. Eur J Pharmacol 484:41–48
Tsujimae K, Suzuki S, Yamada M, Kurachi Y (2004) Comparison of kinetic properties of quinidine and dofetilide block of HERG channels. Eur J Pharmacol 493:29–40
Wang JL, Zong XG, Yao WX, Jiang MX (1999) Effects of neferine on I Na, I Ca-L and steady-state outward K+ current of ventricular myocytes. Chin Pharmacol Bull 15:357–360
Webster G, Berul CI (2008) Congenital long-QT syndromes: a clinical and genetic update from infancy through adulthood. Trends Cardiovasc Med 18:216–224
Xia GJ, Liu YF, Lu FH (1986) Effects of methyl-liensinine on experimental arrhythmias. Acta Univ Med Tongji 3:200–202
Yabuuchi F, Beckmann R, Wettwer E, Hegele-hartung C, Heubach JF (2007) Reduction of HERG potassium currents by hyperosmolar solutions. Eur J Pharmacol 566:222–225
Yang Y, Shui QL, Zeng XR, Liu ZF, Zhou W, Li ML (2000) Effects of neferine on potassium channels in guinea pig ventricular cells and porcine coronary artery smooth muscle cells. Chinese Journal of Pharmacology and Toxicology 14:405–410
Yang BF, Lin HX, Xiao JN, Lu YJ, Luo XB, Li BX, Zhang Y, Xu CQ, Bai YL, Wang HZ, Chen GH, Wang ZG (2007) The muscle-specific microRNA miR-1 regulates cardiacarrhythmogenic potential by targeting GJA1 and KCNJ2. Nat Med 13:486–491
Yeung KS, Meanwell NA (2008) Inhibition of hERG trafficking: an under-explored mechanism for drug-induced QT prolongation. ChemMedChem 3:1501–1502
Zitron E, Kiesecker C, Scholz E, Luck S, Bloehs R, Kathofer S, Thomas D, Kiehn J, Kreye VA, Katus HA, Schoels W, Karle CA (2004) Inhibition of cardiac HERG potassium channels by the atypical antidepressant trazodone. Naumyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 370:146–156
Zünkler BJ (2006) Human ether-a-go-go-related (HERG) gene and ATP-sensitive potassium channels as targets for adverse drug effects. Pharmacol Ther 112:12–37
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 30572181), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 30672644), the National Grand Fundamental Research 973 Program of China (no. 2007CB512000, 2007CB512006), and the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (no. 20060226019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Dong-fang Gu and Xue-lian Li made equal contributions to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, Df., Li, Xl., Qi, Zp. et al. Blockade of HERG K+ channel by isoquinoline alkaloid neferine in the stable transfected HEK293 cells. Naunyn-Schmied Arch Pharmacol 380, 143–151 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-009-0419-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-009-0419-7