Abstract
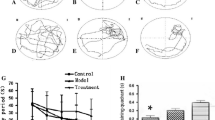
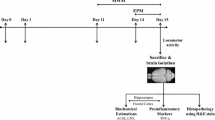
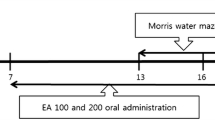
It is shown that l-3-n-butylphthalide (l-NBP), the isomer of dl-NBP (racemic 3-n-butylphthalide, a new anti-cerebral ischemic agent) significantly attenuated cerebral hypoperfusion-induced learning dysfunction and brain damage in rats. In the present study, l-NBP (10 and 30 mg/kg) long-term (3-month) treatment of aged rat (21-month-old) significantly improved the learning and memory capability measured by the Morris water maze test. Hematoxylin–eosin-stained slices showed that both l-NBP at 30 mg/kg, and memantine as control at 20 mg/kg, attenuated the neurodegenerative changes in aged rats. l-NBP treatment significantly increased the choline acetyltransferase activity and dose-dependently decreased the acetylcholinesterases activity in the hippocampus of aged rats. The immunohistological study demonstrated that expressions of β-secretase and hyperphosphorylated tau protein were significantly increased in the hippocampus CA1 subfield and parietal cortex in aged rats. However, they were decreased significantly by treatment of l-NBP and memantine for 3 months. Our results indicated that long-term treatment with l-NBP might prevent age-related neurodegenerative changes by modulation of cholinergic system, reduction of phosphorylated tau and maintain structure and morphology of neurons. Therefore, l-NBP might be a potential drug for treatment of senile dementia.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed MM, Hoshino H, Chikuma T, Yamada M, Kato T (2004) Effect of memantine on the levels of glial cells, neuropeptides, and peptide-degrading enzymes in rat brain regions of ibotenic acid-treated Alzheimer's disease model. Neuroscience 126:639–649
Anderton BH (1997) Changes in the ageing brain in health and disease. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 352:1781–1792
Aubert I, Rowe W, Meaney MJ, Gauthier S, Quirion R (1995) Cholinergic markers in aged cognitively impaired Long–Evans rats. Neuroscience 67:277–292
Bahr BA, Vicente JS (1998) Age-related phosphorylation and fragmentation events influence the distribution profiles of distinct tau isoforms in mouse brain. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 57:111–121
Beracochea D, Boucard A, Trocme-Thibierge C, Morain P (2008) Improvement of contextual memory by S 24795 in aged mice: comparison with memantine. Psychopharmacology 196:555–564
Blasko I, Beer R, Bigl M, Apelt J, Franz G, Rudzki D, Ransmayr G, Kampfl A, Schliebs R (2004) Experimental traumatic brain injury in rats stimulates the expression, production and activity of Alzheimer's disease beta-secretase (BACE-1). J Neural Transm 111:523–536
Bowen DM, Smith CB, White P, Davison AN (1976) Neurotransmitter-related enzymes and indices of hypoxia in senile dementia and other abiotrophies. Brain 99:459–496
Bresink I, Danysz W, Parsons CG, Tiedtke P, Mutschler E (1995) Chronic treatment with the uncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonist memantine influences the polyamine and glycine binding sites of the NMDA receptor complex in aged rats. J Neural Transm Park Dis Dement Sect 10:11–26
Chang Q, Wang XL (2003) Effects of chiral 3-n-butylphthalide on apoptosis induced by transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin 24:796–804
Chong ZZ, Feng YP (1997) Effects of dl-3-n-butylphthalide on production of TXB2 and 6-keto-PGF1 alpha in rat brain during focal cerebral ischemia and reperfusion. Acta Pharmacol Sin 18:505–508
Colombo PJ, Gallagher M (1998) Individual differences in spatial memory and striatal ChAT activity among young and aged rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem 70:314–327
Creeley C, Wozniak DF, Labruyere J, Taylor GT, Olney JW (2006) Low doses of memantine disrupt memory in adult rats. J Neurosci 26:3923–3932
Degerman Gunnarsson M, Kilander L, Basun H, Lannfelt L (2007) Reduction of phosphorylated tau during memantine treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 24:247–252
Dong GX, Feng YP (2002) Effects of NBP on ATPase and anti-oxidant enzymes activities and lipid peroxidation in transient focal cerebral ischemic rats. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao 24:93–97
Enz A, Gentsch C (2004) Co-administration of memantine has no effect on the in vitro or ex vivo determined acetylcholinesterase inhibition of rivastigmine in the rat brain. Neuropharmacology 47:408–413
Gallagher M, Burwell R, Burchinal M (1993) Severity of spatial learning impairment in aging: development of a learning index for performance in the Morris water maze. Behav Neurosci 107:618–626
Gallo P, Bracco F, Morara S, Battistin L, Tavolato B (1985) The cerebrospinal fluid transferrin/tau proteins. A study by two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (2D) and agarose isoelectrofocusing (IEF) followed by double-antibody peroxidase labeling and avidin–biotin amplification. J Neurol Sci 70:81–92
Hof PR, Morrison JH (2004) The aging brain: morphomolecular senescence of cortical circuits. Trends Neurosci 27:607–613
Johnson JW, Kotermanski SE (2006) Mechanism of action of memantine. Curr Opin Pharmacol 6:61–67
Jolitha AB, Subramanyam MV, Asha Devi S (2006) Modification by vitamin E and exercise of oxidative stress in regions of aging rat brain: studies on superoxide dismutase isoenzymes and protein oxidation status. Exp Gerontol 41:753–763
Lang UE, Mühlbacher M, Hesselink MB, Zajaczkowski W, Danysz W, Danker-Hopfe H, Hellweg R (2004) No nerve growth factor response to treatment with memantine in adult rats. J Neural Transm 111:181–190
Li L, Sengupta A, Haque N, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K (2004) Memantine inhibits and reverses the Alzheimer type abnormal hyperphosphorylation of tau and associated neurodegeneration. FEBS Lett 566:261–269
Michalek H, Fortuna S, Pintor A (1989) Age-related differences in brain choline acetyltransferase, cholinesterases and muscarinic receptor sites in two strains of rats. Neurobiol Aging 10:143–148
Miguel-Hidalgo JJ, Alvarez XA, Cacabelos R, Quack G (2002) Neuroprotection by memantine against neurodegeneration induced by beta-amyloid (1–40). Brain Res 958:210–221
Misztal M, Frankiewicz T, Parsons CG, Danysz W (1996) Learning deficits induced by chronic intraventricular infusion of quinolinic acid-protection by MK-801 and memantine. Eur J Pharmacol 296:1–8
Nabeshima T, Noda Y, Kamei H (2002) Anti-dementia drugs for Alzheimer disease in present and future. Nippon Yakurigaku Zasshi 120:24P–29P
Niewiadomska G, Baksalerska-Pazera M, Lenarcik I, Riedel G (2006) Compartmental protein expression of Tau, GSK-3beta and TrkA in cholinergic neurons of aged rats. J Neural Transm 113:1733–1746
Olshansky SJ, Hayflick L, Carnes BA (2002) No truth to the fountain of youth. Sci Amer 286:92–95
Peng Y, Xu S, Chen G, Wang L, Feng Y, Wang X (2007) L-3-n-butylphthalide improves cognitive impairment induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 321:902–910
Peng Y, Zeng X, Feng Y, Wang X (2004) Antiplatelet and antithrombotic activity of L-3-n-butylphthalide in rats. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 43:876–881
Petersen RC, Smith G, Kokmen E, Ivnik RJ, Tangalos EG (1992) Memory function in normal aging. Neurology 42:396–401
Pomara N, Ott BR, Peskind E, Resnick EM (2007) Memantine treatment of cognitive symptoms in mild to moderate Alzheimer disease: secondary analyses from a placebo-controlled randomized trial. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 21:60–64
Sergeant N, David JP, Goedert M, Jakes R, Vermersch P, Buée L, Lefranc D, Wattez A, Delacourte A (1997) Two-dimensional characterization of paired helical filament-tau from Alzheimer's disease: demonstration of an additional 74-kDa component and age-related biochemical modifications. J Neurochem 69:834–844
Sirvio J, Pitkanen A, Paakkonen A, Partanen J, Riekkinen PJ (1989) Brain cholinergic enzymes and cortical EEG activity in young and old rats. Comp Biochem Physiol C 94:277–283
Small SA (2001) Age-related memory decline: current concepts and future directions. Arch Neurol 58:360–364
Stemmelin J, Cassel JC, Will B, Kelche C (1999) Sensitivity to cholinergic drug treatments of aged rats with variable degrees of spatial memory impairment. Behav Brain Res 98:53–66
Sun X, He G, Qing H, Zhou W, Dobie F, Cai F, Staufenbiel M, Huang LE, Song W (2005) Hypoxia facilitates Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis by up-regulating BACE1 gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:18727–18732
Taylor L, Griffith WH (1993) Age-related decline in cholinergic synaptic transmission in hippocampus. Neurobiol Aging 14:509–515
Tong Y, Zhou W, Fung V, Christensen MA, Qing H, Sun X, Song W (2005) Oxidative stress potentiates BACE1 gene expression and A beta generation. J Neural Transm 112:455–469
Xu HL, Feng YP (2000) Inhibitory effects of chiral 3-n-butylphthalide on inflammation following focal ischemic brain injury in rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin 21:433–438
Yan CH, Feng YP, Zhang JT (1998) Effects of dl-3-n-butylphthalide on regional cerebral blood flow in right middle cerebral artery occlusion rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin 19:117–120
Yan XX, Xiong K, Luo XG, Struble RG, Clough RW (2007) Beta-secretase expression in normal and functionally deprived rat olfactory bulbs: inverse correlation with oxidative metabolic activity. J Comp Neurol 501:52–69
Youngjohn JR, Crook TH 3rd (1993) Learning, forgetting, and retrieval of everyday material across the adult life span. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 15:447–460
Acknowledgements
We appreciate Dr. Song Wu for the supply of memantine. We thank Mrs. Li Zhang and Xiping Chen for their technical help.
This work was supported by the National 973 Fundamental Project of China (no. 2004CB518906); National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 30640096); Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (no. IRT0514); and Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substances and Resources Utilization of Chinese Herbal Medicine, Ministry of Education.
Statement of conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, S., Xu, S., Liu, B. et al. Long-term treatment of l-3-n-butylphthalide attenuated neurodegenerative changes in aged rats. Naunyn-Schmied Arch Pharmacol 379, 565–574 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-009-0398-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-009-0398-8