Abstract
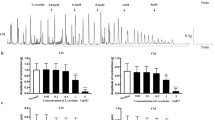
The effect of reactive oxygen species on contractions in β-escin permeabilized rat detrusor was investigated. Cumulative calcium contractions were inhibited by hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and hydroxyl (•OH) but not by superoxide (O2¯•). The sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium-ATPase inhibitor cyclopiazonic acid (CPA) and the mitochondrial blocker carbonyl cyanide p-trifluromethoxyphenylhydrazone (FCCP) decreased the calcium contractions, however in their presence, H2O2 and •OH did not have further effect. Carbachol contractions were inhibited by either H2O2/•OH/O2¯• or CPA/FCCP. In the presence of CPA, carbachol contractions were not affected by H2O2 and •OH but further decreased by O2¯•. On the other hand, only H2O2 and •OH elicited additional inhibition in carbachol responses in the presence of FCCP. Inositol triphosphate contraction was inhibited by •OH whereas none of the radicals affect carbachol induced calcium sensitization. These results show that H2O2 and •OH affects sarcoplasmic reticulum where O2¯• acts on mitochondria to change contractions in rat detrusor smooth muscle.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aikawa K, Leggett RE, Levin RM (2003) Effect of age on hydrogen peroxide mediated contraction damage in the male rat bladder. J Urol 170:2082–2085
An JY, Yun HS, Lee YP, Yang SJ, Shim JO, Jeong JH, Shin CY, Kim JH, Kim DS, Sohn UD (2002) The intracellular pathway of the acetylcholine-induced contraction in cat detrusor muscle cells. Br J Pharmacol 137(7):1001–1010
Andersson K-E (1993) Pharmacology of lower urinary tract smooth muscles and penile erectile tissues. Pharmacol Rev 45(3):253–308
Brooks SP, Storey KB (1992) Bound and determined: a computer program for making buffers of defined ion concentrations. Anal Biochem 201:119–126
Callahan LA, Nethery D, Stofan D, DiMarco A, Supinski G (2001) Free radical-induced contractile protein dysfunction in endotoxin-induced sepsis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 24(2):210–217
Chambers P, Neal DE, Gillespie JI (1999) Ryanodine receptors in human bladder smooth muscle. Exp Physiol 84(1):41–46
Darnley GM, Duke AM, Steele DS, MacFarlane NG (2001) Effects of reactive oxygen species on aspects of excitation-contraction coupling in chemically skinned rabbit diaphragm muscle fibers. Exp Physiol 86(2):161–168
de Jongh R, Haenen GR, van Koeveringe GA, Dambros M, De Mey JG, van Kerrebroeck PE (2007) Oxidative stress reduces the muscarinic receptor function in the urinary bladder. Neurourol Urodyn 26(2):302–308
Durlu-Kandilci NT, Brading AF (2006) Involvement of Rho kinase and protein kinase C in carbachol induced calcium sensitization in β-escin skinned rat and guinea pig bladders. Br J Pharmacol 148:376–384
Elmoselhi AB, Samson SE, Grover AK (1996) SR Ca2+ pump heterogeneity in coronary artery: free radicals and IP3-sensitive and insensitive pools. Am J Physiol 271:C1652–C1659
Endo MKT, Yagi S, Iino M, Kakuta Y (1977) Some properties of chemically skinned smooth muscle fibers. In: Casteels RGT, Rüegg JC (eds) Excitation-contraction coupling in smooth muscle. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 199–209
Endo M, Yagi S, Iino M (1982) Tension-pCa relation and sarcoplasmic reticulum responses in chemically skinned smooth muscle fibers. Federation Proc 41:2245–2250
Favero TG, Colter D, Hooper PF, Abramson JJ (1998) Hypochlorous acid inhibits Ca2+-ATPase from skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Applied Physiol 84:425–430
Grover AK, Samson SE, Fomin VP (1992) Peroxide inactivates calcium pumps in pig coronary artery. Am J Physiol 263(2 Pt 2):H537–H543
Iizuka K, Ikebe M, Somlyo AV, Somlyo AP (1994) Introduction of high molecular weight (IgG) proteins into receptor coupled, permeabilized smooth muscle. Cell Calcium 16:431–445
Kaneda T, Shimizu K, Nakajyo S, Urakawa N (1995) Effect of phorbol ester, 12-deoxyphorbol 13-isobutylate (DPB), on muscle tension and cytosolic Ca2+ in rat anococcygeus muscle. Jpn J Pharmacol 69(3):195–204
Kitazawa T, Kobayashi S, Horiuti K, Somlyo AV, Somlyo AP (1989) Receptor-coupled, permeabilized smooth muscle. Role of the phosphatidylinositol cascade, G-proteins, and modulation of the contractile response to Ca2+. J Biol Chem 264:5339–5342
Kobayashi S, Kitazawa T, Somlyo AV, Somlyo AP (1989) Cytosolic heparin inhibits muscarinic and α-adrenergic Ca2+ release in smooth muscle. J Biol Chem 264:17997–18004
Kuba M, Higure Y, Susaki H, Hayato R, Kuba K (2007) Bidirectional Ca2+ coupling of mitochondria with the endoplasmic reticulum and regulation of multimodal Ca2+ entries in rat brown adipocytes. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 292(2):C896–C908
Lin AT, Yang CH, Chen KK, Chang LS (2005) Detrusor mitochondrial lipid peroxidation and superoxide dismutase activity in partial bladder outlet obstruction of rabbits. Neurourol Urodyn 24(3):282–287
Lopes GS, Ferreira AT, Oshiro ME, Vladimirova I, Jurkiewicz NH, Jurkiewicz A, Smaili SS (2006) Aging-related changes of intracellular Ca2+ stores and contractile response of intestinal smooth muscle. Exp Gerontol 41(1):55–62
Masuda H, Kihara K, Saito K, Matsuoka Y, Yoshida S, Chancellor MB, de Groat WC, Yoshimura N (2008) Reactive oxygen species mediate detrusor overactivity via sensitization of afferent pathway in the bladder of anaesthetized rats. BJU Int 101(6):775–780
Nasu T (1989) Actions of some drugs on skinned smooth muscle preparations. Gen Pharmac 20(2):123–131
Parekh MH, Lobel R, O’Connor LJ, Leggett RE, Levin RM (2001) Protective effect of vitamin E on the response of the rabbit bladder to partial outlet obstruction. J Urol 166:341–346
Redondo PC, Salido GM, Pariente JA, Rosado JA (2004) Dual effect of hydrogen peroxide on store-mediated calcium entry in human platelets. Biochem Pharmacol 67:1065–1076
Schmidt T, Zaib F, Samsona SE, Kwan C-Y, Grover AK (2004) Peroxynitrite resistance of sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ pump in pig coronary artery endothelium and smooth muscle. Cell Calcium 36:77–82
Sen M, McMains E, Gleason E (2007) Local influence of mitochondrial calcium transport in retinal amacrine cells. Vis Neurosci 24(5):663–678
Somlyo AV (2002) New roads leading to Ca2+ sensitization. Circ Res 91:83–84
Somlyo AP, Himpens B (1989) Cell calcium and its regulation in smooth muscle. Faseb J 3:2266–2276
Somlyo AP, Somlyo AV (2003) Ca+2 sensitivity of smooth muscle and nonmuscle myosin II: modulated by G proteins, kinases, and myosin phosphatase. Physiol Rev 83(4):1325–1358
Takahashi R, Nishimura J, Hirano K, Seki N, Naito S, Kanaide H (2004) Ca2+ sensitization in contraction of human bladder smooth muscle. J Urol 172:748–752
Volpe P, Salviati G, Chu A (1986) Calcium-gated calcium channels in sarcoplasmic reticulum of rabbit skinned skeletal muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol 87(2):289–303
Wada S, Okabe E (1997) Susceptibility of caffeine- and Ins(1,4,5)P3-induced contractions to oxidants in permeabilized vascular smooth muscle. Eur J Pharm 320:51–59
Wibo M, Godfraind T (1994) Comparative localization of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and ryanodine receptors in intestinal smooth muscle: an analytical subfractionation study. Biochem J 297(Pt 2):415–423
Woodsome TP, Eto M, Everett A, Brautigan DL, Kitazawa T (2001) Expression of CPI-17 and myosin phosphatase correlates with Ca(2+) sensitivity of protein kinase C-induced contraction in rabbit smooth muscle. J Physiol 535:553–564
Yang SJ, An JY, Shim JO, Park CH, Huh IH, Sohn UD (2000) The mechanism of contraction by 2-chloroadenosine in cat detrusor muscle cells. J Urol 163(2):652–658
Acknowledgments
This study is supported by a project grant from NOVARTIS (Turkey).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Durlu-Kandilci, N.T., Sahin-Erdemli, I. The effects of reactive oxygen species on calcium- and carbachol- induced contractile responses in β-escin permeabilized rat bladder. Naunyn-Schmied Arch Pharmacol 378, 645–653 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-008-0326-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-008-0326-3