Abstract
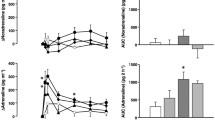
We investigated the effect of intermedin/adrenomedullin-2 (3 and 10 nmol/kg, i.v.), a member of the calcitonin gene-related peptide family, relative to the vehicle (0.9% NaCl) on mean circulatory filling pressure (index of venous tone) in conscious rats: intact (unblocked) or ganglionic blocked through treatment with mecamylamine (10 mg/kg, i.v.) and noradrenaline (4 μg/kg/min, i.v.). In intact rats, both doses of intermedin/adrenomedullin-2 reduced mean arterial pressure (−14±3, −30±3 mmHg), but did not alter mean circulatory filling pressure; the high dose also increased heart rate. In ganglionic-blocked rats, both doses decreased mean arterial pressure (−22±3, −46±5 mmHg) and the high dose also decreased mean circulatory filling pressure (−2.81±0.82 mmHg), but neither dose affected heart rate. The vehicle did not have any effects in any of the groups. In addition, intermedin/adrenomedullin-2 did not have any effect on blood volume in both intact and ganglion-blocked rats. The results show that intermedin/adrenomedullin-2 is a dilator of arterial resistance and capacitance vessels.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelrahman A, Pang CCY (1990) Differential venous effects of isoprenaline in conscious rats. Eur J Pharmacol 190:321–327
Abdelrahman A, Pang CCY (1992) Calcitonin gene-related peptide is a venous dilator in conscious rats. Eur J Pharmacol 217:185–189
Abdelrahman A, Pang CCY (2002) Effect of nociceptin/orphanin FQ on venous tone in conscious rats. Eur J Pharmacol 455:143–147
Abdelrahman A, Lim SL, Pang CCY (2005) Influence of urocortin and corticotrophin releasing factor on venous tone in conscious rats. Eur J Pharmacol 510:107–111
Cheng X, Cheng XS, Pang CCY (2003) Venous dilator effect of apelin, an endogenous peptide ligand for the orphan APJ receptor, in conscious rats. Eur J Pharmacol 470:171–175
D’Oyley HM, Tabrizchi R, Pang CCY (1989) Effects of vasodilator drugs on venous tone in conscious rats. Eur J Pharmacol 162:337–344
Fujisawa Y, Nagai Y, Miyatake A, Takei Y, Miura K, Shoukouji T, Nishiyama A, Kimura S, Abe Y (2004) Renal effects of a new member of adrenomedullin family, adrenomedullin2, in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 497:75–80
Guyton AC (1955) Determination of cardiac output by equating venous return curves with cardiac response curves. Physiol Rev 35:123–129
Juaneda C, Dumont Y, Quirion R (2000) The molecular pharmacology of CGRP and related peptide receptor subtypes. Trends Pharmacol Sci 21:432–438
Ng S, Pang CCY (1998) Zaprinast, a type V phosphodiesterase inhibitor, dilates capacitance vessels in anaesthetised rats. Eur J Pharmacol 351:323–328
Palacios B, Lim SL, Pang CCY (2002) Role of endothelin ETA-and ETB-receptors in hemodynamic compensation following haemorrhage in anaesthetized rats. Br J Pharmacol 135:876–882
Pang CCY (2000) Measurement of body venous tone. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 44:341–360
Pang CCY (2001) Autonomic control of the venous system in health and disease. Effects of drugs. Pharmacol Ther 90:179–230
Poon KS, Pang CCY (2002) Venodilator action of an organotransition-metal nitrosyl complex. Eur J Pharmacol 436:107–110
Poyner DR, Sexton PM, Marshall I, Smith DM, Quirion R, Born W, Muff R, Fisher JA, Foord SM (2002) International Union of Pharmacology. XXXII. The mammalian calcitonin gene-related peptides, adrenomedullin, amylin and calcitonin receptors. Pharmacol Rev 54:233–246
Roh J, Chang CL, Bhalla A, Klein C, Hsu SY (2004) Intermedin is a calcitonin/calcitonin gene-related peptide family peptide acting through the calcitonin receptor-like receptor/receptor activity-modifying protein receptor complexes. J Biol Chem 279:7264–7274
Sterling K, Gray SJ (1950) Determination of circulating red cell volume in man by radioactive chromium. J Clin Invest 29:1614–1619
Takei Y, Hyodo S, Katafuchi T, Minamino N (2004a) Novel fish-derived adrenomedullin in mammals: structure and possible function. Peptides 25:1643–1656
Takei Y, Inoue K, Ogoshi M, Kawahara T, Bannai H, Miyano S (2004b) Identification of novel adrenomedullin in mammals: a potent cardiovascular and renal regulator. FEBS Lett 556:53–58
Taylor MM, Bagley SL, Samson WK (2005) Intermedin/adrenomedullin-2 acts within central nervous system to elevate blood pressure and inhibit food and water intake. Am J Physiol 288:R919–R927
Waite RP, Pang CCY, Walker MJA (1988) Effects of calcium antagonists on mean circulatory filling pressure in the conscious rat. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 12:499–504
Waite RP, Lim SL, Pang CCY (1995) Effects of pinacidil on arterial and venous resistances and mean circulatory filling pressure in rats. Br J Pharmacol 116:2322–2326
Wang YX, Lim SL, Pang CC (1995) Increase by NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) of resistance to venous return in rats. Br J Pharmacol 114:1454–1458
Yang JH, Jia YX, Pan CS, Zhao J, Ouyang M, Yang J, Chang JK, Tang CS, Qi YF (2005a) Effects of intermedin (1–53) on cardiac function and ischemia/reperfusion injury in isolated rat hearts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 327:713–719
Yang JH, Qi YF, Jia YX, Pan CS, Zhao J, Yang J, Chang JK, Tang CS (2005b) Protective effects of intermedin/adrenomedullin2 on ischemia/reperfusion injury in isolated rat hearts. Peptides 26:501–507
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Heart & Stroke Foundation of B.C. and Yukon. The authors would like to thank Su Lin Lim for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdelrahman, A.M., Pang, C.C.Y. Effect of intermedin/adrenomedullin-2 on venous tone in conscious rats. Naunyn-Schmied Arch Pharmacol 373, 376–380 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-006-0076-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-006-0076-z