Abstract
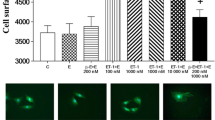
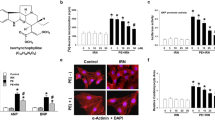
Trilinolein, isolated from the traditional Chinese herb Sanchi (Panax notoginseng), has been shown to have myocardial protective effects via its antioxidant ability. However, the cellular and molecular mechanisms of the protective effect of trilinolein in the heart remain to be elucidated. Oxidative mechanisms have been implicated in neonatal cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. We previously reported that ET-1 induces ROS generation via the ETA receptor and ROS modulates c-fos gene expression. We have therefore examined whether trilinolein attenuates ROS production and ET-1-induced c-fos gene expression in cardiomyocytes. Cultured neonatal rat cardiomyocytes were stimulated with ET-1 (10 nM), and c-fos gene expression was examined. Trilinolein (1 and 10 μM) inhibited ET-1-induced c-fos gene expression in cardiomyocytes. We also examined the effects of trilinolein on ET-1- increased NADPH oxidase activity and superoxide formation. Trilinolein inhibited ET-1-increased NADPH oxidase activity and superoxide formation in a concentration-dependent manner. This increase in superoxide production by ET-1 was significantly inhibited by trilinolein, diphenyleneiodonium, or N-acetylcysteine. Trilinolein also decreased ET-1- or H2O2-induced extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) phosphorylation, c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) phosphorylation, and activator protein-1 activation. These data indicate that trilinolein inhibits ET-1-induced ERK phosphorylation, JNK phosphorylation, and c-fos gene expression via attenuating superoxide production in cardiomyocytes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn NG, Weiel JE, Chan CP, Krebs EG (1990) Identification of multiple epidermal growth factor-stimulated protein serine/threonine kinases from Swiss 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem 265:11487–11494
Baas AS, Berk BC (1995) Differential activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases by H2O2 and O2- in vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ Res 77:29–36
Bhunia AK, Han H, Snowden A, Chatterjee S (1997) Redox-regulated signaling by lactosylceramide in the proliferation of human aortic smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem 272:15642–15649
Boulton TG, Gregory JS, Jong SM, Wang LH, Ellis L, Cobb MH (1990) Evidence for insulin-dependent activation of S6 and microtubule-associated protein-2 kinases via a human insulin receptor/v-ros hybrid. J Biol Chem 265:2713–2719
Cantley LC, Auger KR, Carpenter C, Duckworth B, Graziani A, Kapeller R, Soltoff S (1991) Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell 64:281–302
Chan P, Cheng JT, Tsao CW, Niu CS, Hong CY (1996) The in vitro antioxidant activity of trilinolein and other lipid-related natural substances as measured by enhanced chemiluminescence. Life Sci 59:2067–2073
Chan P, Niu CS, Tomlinson B, Hong CT, Chen JP, Hong CY, Tsai SK, Cheng JT (1997) Effect of trilinolein on superoxide dismutase activity and left ventricular pressure in isolated rat hearts subjected to hypoxia and normoxic perfusion. Pharmacology 55:252–258
Chan P, Thomas GN, Tomlinson B (2002) Protective effects of trilinolein extracted from Panax notoginseng against cardiovascular disease. Acta Pharmacol Sin 23:1157–1162
Cheng TH, Shih NL, Chen SY, Wang DL, Chen JJ (1999) Reactive oxygen species modulate endothelin-I-induced c-fos gene expression in cardiomyocytes. Cardiovasc Res 41:654–662
Cheng CM, Hong HJ, Liu JC, Shih NL, Juan SH, Loh SH, Chan P, Chen JJ, Cheng TH (2003) Crucial role of extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway in reactive oxygen species-mediated endothelin-1 gene expression induced by endothelin-1 in rat cardiac fibroblasts. Mol Pharmacol 63:1002–1011
Cheng TH, Shih NL, Chen CH, Lin H, Liu JC, Chao HH, Liou JY, Chen YL, Tsai HW, Chen YS, Cheng CF, Chen JJ (2005) Role of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in reactive oxygen species-mediated endothelin-1-induced (-myosin heavy chain gene expression and cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. J Biomed Sci 12:123–133
Choukroun G, Hajjar R, Kyriakis JM, Bonventre JV, Rosenzweig A, Force T (1998) Role of the stress-activated protein kinases in endothelin-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. J Clin Invest 102:1311–1320
De Keulenaer GW, Wang Y, Feng Y, Muangman S, Yamamoto K, Thompson JF, Turi TG, Landschutz K, Lee RT (2002) Identification of IEX-1 as a biomechanically controlled nuclear factor-kappaB target gene that inhibits cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Circ Res 90:690–696
Duerrschmidt N, Wippich N, Goettsch W, Broemme HJ, Morawietz H (2000) Endothelin-1 induces NAD(P)H oxidase in human endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 269:713–717
Force T, Haq S, Kilter H, Michael A (2002) Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase/nuclear factor-kappaB: a novel signaling pathway regulates cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Circulation 105:402–404
Higuchi Y, Otsu K, Nishida K, Hirotani S, Nakayama H, Yamaguchi O, Matsumura Y, Ueno H, Tada M, Hori M (2002) Involvement of reactive oxygen species-mediated NF-kappa B activation in TNF-alpha-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. J Mol Cell Cardiol 34:233–240
Hirotani S, Otsu K, Nishida K, Higuchi Y, Morita T, Nakayama H, Yamaguchi O, Mano T, Matsumura Y, Ueno H, Tada M, Hori M (2002) Involvement of nuclear factor-kappaB and apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 in G-protein-coupled receptor agonist-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Circulation 105:509–515
Hong CY, Lai LJ, Shiao MS, Chiang BN (1993) Effect of triacylglycerols on erythrocyte deformability in vitro. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 48:351–353
Juan SH, Chen JJ, Chen CH, Lin H, Cheng CF, Liu JC, Hsieh MH, Chen YL, Chao HH, Chen TH, Chan P, Cheng TH (2004) 17beta-estradiol inhibits cyclic strain-induced endothelin-1 gene expression within vascular endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 287:H1254–H1261
Li L, Fink GD, Watts SW, Northcott CA, Galligan JJ, Pagano PJ, Chen AF (2003) Endothelin-1 increases vascular superoxide via endothelin(A)-NADPH oxidase pathway in low-renin hypertension. Circulation 107:1053–1058
Liu JC, Chen JJ, Chan P, Cheng CF, Cheng TH (2003) Inhibition of cyclic strain-induced endothelin-1 gene expression by resveratrol. Hypertension 42:1198–1205
Liu JC, Chan P, Chen JJ, Lee HM, Lee WS, Shih NL, Chen YL, Hong HJ, Cheng TH (2004a) The inhibitory effect of trilinolein on norepinephrine-induced beta-myosin heavy chain promoter activity, reactive oxygen species generation, and extracellular signal-regulated kinase phosphorylation in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. J Biomed Sci 11:11–18
Liu JC, Cheng TH, Lee HM, Lee WS, Shih NL, Chen YL, Chen JJ, Chan P (2004b) Inhibitory effect of trilinolein on angiotensin II-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Eur J Pharmacol 484:1–8
Luo JD, Xie F, Zhang WW, Ma XD, Guan JX, Chen X (2001) Simvastatin inhibits noradrenaline-induced hypertrophy of cultured neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. Br J Pharmacol 132:159–164
Nelson MT, Herrera GM (2002) Molecular physiology: protecting the heart. Nature 416:273–274
Omura T, Yoshiyama M, Yoshida K, Nakamura Y, Kim S, Iwao H, Takeuchi K, Yoshikawa J (2002) Dominant negative mutant of c-Jun inhibits cardiomyocyte hypertrophy induced by endothelin 1 and phenylephrine. Hypertension 39:81–86
Purcell NH, Tang G, Yu C, Mercurio F, DiDonato JA, Lin A (2001) Activation of NF-kappa B is required for hypertrophic growth of primary rat neonatal ventricular cardiomyocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:6668–6673
Qin F, Rounds NK, Mao W, Kawai K, Liang CS (2001) Antioxidant vitamins prevent cardiomyocyte apoptosis produced by norepinephrine infusion in ferrets. Cardiovasc Res 51:736–748
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor
Shih NL, Cheng TH, Loh SH, Cheng PY, Wang DL, Chen YS, Liu SH, Liew CC, Chen JJ (2001) Reactive oxygen species modulate angiotensin II-induced beta-myosin heavy chain gene expression via Ras/Raf/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 283:143–148
Takemoto Y, Yoshiyama M, Takeuchi K, Omura T, Komatsu R, Izumi Y, Kim S, Yoshikawa J (1999) Increased JNK, AP-1 and NF-kappa B DNA binding activities in isoproterenol-induced cardiac remodeling. J Mol Cell Cardiol 31:2017–2030
Van Wamel AJ, Ruwhof C, van der Valk-Kokshoom LE, Schrier PI, van der Laarse A (2001) The role of angiotensin II, endothelin-1 and transforming growth factor-beta as autocrine/paracrine mediators of stretch-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Mol Cell Biochem 218:113–124
Wedgwood S, McMullan DM, Bekker JM, Fineman JR, Black SM (2001) Role for endothelin-1-induced superoxide and peroxynitrite production in rebound pulmonary hypertension associated with inhaled nitric oxide therapy. Circ Res 89:357–364
Weisz A, Rosales R (1990) Identification of an estrogen response element upstream of the human c-fos gene that binds the estrogen receptor and the AP-1 transcription factor. Nucleic Acids Res 18:5097–5106
Yamazaki T, Komuro I, Kudoh S, Zou Y, Shiojima I, Hiroi Y, Mizuno T, Maemura K, Kurihara H, Aikawa R, Takano H, Yazaki Y (1996) Endothelin-1 is involved in mechanical stress-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. J Biol Chem 271:3221–3228
Yue TL, Gu JL, Wang C, Reith AD, Lee JC, Mirabile RC, Kreutz R, Wang Y, Maleeff B, Parsons AA, Ohlstein EH (2000) Extracellular signal-regulated kinase plays an essential role in hypertrophic agonists, endothelin-1 and phenylephrine-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. J Biol Chem 275:37895–37901
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by Taipei Medical University Grant (TMU93-AE1-B-04), Taipei, Taiwan, Republic of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Hung-Yu Yang and Ju-Chi Liu equally contributed to this work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, HY., Liu, JC., Chen, YL. et al. Inhibitory effect of trilinolein on endothelin-1-induced c-fos gene expression in cultured neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. Naunyn Schmied Arch Pharmacol 372, 160–167 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-005-0003-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-005-0003-8