Abstract
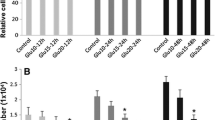
Apoptosis of endothelial cells may be an important risk factor contributing to the incidence of vascular complications in diabetes. In the present study, we tested the effect of 3,4,5,6-tetrahydroxyxanthone, a synthetic xanthone derivative, on apoptosis induced in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) by a high glucose concentration. Cell apoptosis was detected using DNA ladder formation and flow cytometric techniques. The expression of Bcl-2 protein was analysed using flow cytometric techniques. Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activity and malonyldialdehyde (MDA) content in the medium were measured. Cell viability was assayed by the 3-[4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) method. Exposure of HUVEC to a high glucose concentration (30 mM) for 48 h markedly increased LDH release and MDA content in the medium and induced apoptosis and Bcl-2 protein expression in HUVEC. Pretreatment with 3,4,5,6-tetrahydroxyxanthone (1, 3 or 10 μM) or probucol (10 μM) significantly decreased the level of LDH and MDA in the medium, reduced apoptosis and increased the expression of Bcl-2 protein in HUVEC. These results suggest that 3,4,5,6-tetrahydroxyxanthone inhibits high-glucose-induced endothelial cell apoptosis by increasing Bcl-2 protein expression in HUVEC.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JM, Cory S (1998) The Bcl-2 protein family: arbiters of cell survival. Science 281:1322–1326
Basnet P, Kadota S, Shimizu M, Takata Y, Kobayashi M, Namba T (1995) Bellidifolin stimulates glucose uptake in rat 1 fibroblasts and ameliorates hyperglycemia in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats. Planta Med 61:402–405
Chai W, Chen J, Wang H, Shen J, Ma L, Ma X (2000) The effects of glucose, insulin and oxidized low density lipoprotein on apoptosis in vascular endothelial cells. Chin Med J (Engl) 113:903–906
Chang CH, Lin CC, Hattori M, Namba T (1994) Effects on anti-lipid peroxidation of Cudrania cochinchinensis var. gerontogea. J Ethnopharmacol 44:79–85
Cohen RA (1993) Pathways controlling healthy and diseased arterial smooth muscle. Am J Cardiol 72:39C–46C
Cosentino F, Luscher TF (1997) Endothelial function in coronary artery disease. Cardiologia 42:1221–1227
Du XL, Sui GZ, Stockklauser-Farber K, Weiss J, Zink S, Schwippert B, Wu QX, Tschope D, Rosen P (1998) Introduction of apoptosis by high proinsulin and glucose in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells is mediated by reactive oxygen species. Diabetologia 41:249–256
Gonda R, Takeda T, Akiyama T (2000) Studies on the constituents of Anaxagorea luzonensis A. GRAY. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 48:1219–1222
Hildeman DA, Mitchell T, Aronow B, Wojciechowski S, Kappler J, Marrack P (2003) Control of Bcl-2 expression by reactive oxygen species. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:15035–15040
Jiang DJ, Tan GS, Zhou ZH, Xu KP, Ye F, Li YJ (2002a) Protective effects of demethylbellidifolin on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Planta Med 68:710–713
Jiang JL, Li NS, Li YJ, Deng HW (2002b) Probucol preserves endothelial function by reduction of the endogenous nitric oxide synthase inhibitor level. Br J Pharmacol 135:1175–1182
Jiang DJ, Hu GY, Jiang JL, Xiang HL, Deng HW, Li YJ (2003a) Relationship between protective effect of xanthone on endothelial cells and endogenous nitric oxide synthase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem 11:5171–5177
Jiang DJ, Jiang JL, Tan GS, Du YH, Xu KP, Li YJ (2003b) Protective effects of daviditin A against endothelial damage induced by lysophosphatidylcholine. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 367:600–606
Kunsch C, Medford RM (1999) Oxidative stress as a regulator of gene expression in the vasculature. Circ Res 85:753–766
Lorenzi M, Cagliero E (1991) Pathobiology of endothelial and other vascular cells in diabetes mellitus. Call for data. Diabetes 40:653–659
Mahabusarakam W, Proudfoot J, Taylor W, Croft K (2000) Inhibition of lipoprotein oxidation by prenylated xanthones derived from mangostin. Free Radic Res 33:643–659
Marshall HE, Merchant K, Stamler JS (2000) Nitrosation and oxidation in the regulation of gene expression. FASEB J 14:1889–1900
Minami H, Takahashi E, Fukuyama Y, Kodama M, Yoshizawa T, Nakagawa K (1995) Novel xanthones with superoxide scavenging activity from Garcinia subelliptica. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 43:347–349
Miura T, Ichiki H, Iwamoto N, Kato M, Kubo M, Sasaki H et al (2001) Antidiabetic activity of the rhizoma of Anemarrhena asphodeloides and active components, mangiferin and its glucoside. Biol Pharm Bull 24:1009–1011
Nathan DM (1993) Long-term complications of diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 328:1676–1685
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Ortiz A, Ziyadeh FN, Neilson EG (1997) Expression of apoptosis-regulatory genes in renal proximal tubular epithelial cells exposed to high ambient glucose and in diabetic kidneys. J Investig Med 45:50–56
Recchioni R, Marcheselli F, Moroni F, Pieri C (2002) Apoptosis in human aortic endothelial cells induced by hyperglycemic condition involves mitochondrial depolarization and is prevented by N-acetyl-l-cysteine. Metabolism 51:1384–1388
Tesfamariam B (1994) Free radicals in diabetic endothelial cell dysfunction. Free Radic Biol Med 16:383–391
Totzke G, Metzner C, Ulrich-Merzenich G, Ko Y, Sachinidis A, Vetter H (2001) Effect of vitamin E and vitamin C on the DNA synthesis of human umbilical arterial endothelial cells. Eur J Nutr 40:121–126
Vermes I, Haanen C, Steffens-Nakken H, Reutelingsperger C (1995) A novel assay for apoptosis. Flow cytometric detection of phosphatidylserine expression on early apoptotic cells using fluorescein labelled Annexin V. J Immunol Methods 184:39–51
Wu QD, Wang JH, Fennessy F, Redmond HP, Bouchier-Hayes D (1999) Taurine prevents high-glucose-induced human vascular endothelial cell apoptosis. Am J Physiol 277:C1229–C1238
Xiong Y, Li YJ, Deng HW (1994) Protection of l-arginine against oxygen free radicals-injured rabbit aortic endothelium. Acta Pharmacol Sin 15:119–123
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant from the Provincial Natural Science Foundation of Hunan, China, No. 02jjy2046.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, Z., Liao, DF., Jiang, DJ. et al. 3,4,5,6-Tetrahydroxyxanthone prevents vascular endothelial cell apoptosis induced by high glucose. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 370, 314–319 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-004-0973-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-004-0973-y