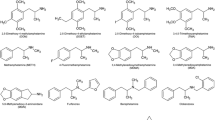
Abstract
3,4-Methylenedioximethamphetamine (MDMA; “ecstasy”) is a psychotropic drug with well-known neurotoxic effects mediated by hitherto not fully understood mechanisms. The Na+- and K+-activated adenosine 5′-triphosphatase (Na+/K+ ATPase), by maintaining the ion gradient across the cell membrane, regulates neuronal excitability. Thus, a perturbation of its function strongly impacts cell homeostasis, ultimately leading to neuronal dysfunction and death. Nevertheless, whether MDMA affects the Na+/K+ ATPase remains unknown. In this study, we used synaptosomes obtained from whole mouse brain to test the effects of MDMA, three of its major metabolites [α-methyldopamine, N-methyl-α-methyldopamine and 5-(glutathion-S-yl)-α-methyldopamine], serotonin (5-HT), dopamine, 3,4-dihydroxy-l-phenylalanine (l-Dopa) and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC) on the Na+/K+ ATPase function. A concentration-dependent increase of Na+/K+ ATPase activity was observed in synaptosomes exposed to the tested compounds (concentrations ranging from 0.0625 to 200 µM). These effects were independent of protein kinases A and C activities. Nevertheless, a rescue of the compounds’ effects was observed in synaptosomes pre-incubated with the antioxidant N-acetylcysteine (1 mM), suggesting a role for reactive species-regulated pathways on the Na+/K+ ATPase effects. In agreement with this hypothesis, a similar increase in the pump activity was found in synaptosomes exposed to the chemical generator of superoxide radicals, phenazine methosulfate (1–250 µM). This study demonstrates the ability of MDMA metabolites, monoamine neurotransmitters, l-Dopa and DOPAC to alter the Na+/K+ ATPase function. This could represent a yet unknown mechanism of action of MDMA and its metabolites in the brain.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 5-(GSH)-α-MeDA:
-
5-(Glutathion-S-yl)-α-methyldopamine
- 5-HT:
-
Serotonin/5-hydroxytryptamine
- ATP:
-
Adenosine 5′-triphosphate
- DOPAC:
-
3,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetic acid
- HEPES:
-
4-(2-Hydroxyethyl)piperazine-1-ethanesulfonic acid
- l-Dopa:
-
3,4-Dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine
- MDMA:
-
3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine/“ecstasy”
- α-MeDA:
-
α-Methyldopamine
- Na+/K+ ATPase:
-
Na+- and K+-activated adenosine 5′-triphosphatase
- NAC:
-
N-Acetylcysteine
- NADH:
-
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide reduced form
- N-Me-α-MeDA:
-
N-Methyl-α-methyldopamine
- PKA:
-
Cyclic adenosine 5′-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase A
- PKC:
-
Protein kinase C
- PMS:
-
Phenazine methosulfate
References
Alves E, Summavielle T, Alves CJ, Gomes-da-Silva J, Barata JC, Fernandes E, Bastos ML, Tavares MA, Carvalho F (2007) Monoamine oxidase-B mediates ecstasy-induced neurotoxic effects to adolescent rat brain mitochondria. J Neurosci 27:10203–10210. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2645-07.2007
Alves E, Summavielle T, Alves CJ, Custódio JB, Fernandes E, Lourdes Bastos M, Tavares MA, Carvalho F (2009) Ecstasy-induced oxidative stress to adolescent rat brain mitochondria in vivo: influence of monoamine oxidase type A. Addict Biol 14:185–193. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1369-1600.2008.00143.x
Bai F, Lau SS, Monks TJ (1999) Glutathione and N-acetylcysteine conjugates of α-methyldopamine produce serotonergic neurotoxicity: possible role in methylenedioxyamphetamine-mediated neurotoxicity. Chem Res Toxicol 12:1150–1157. https://doi.org/10.1021/tx990084t
Barbosa DJ, Capela JP, Oliveira JMA, Silva R, Ferreira LM, Siopa F, Branco PS, Fernandes E, Duarte JA, de Lourdes Bastos M, Carvalho F (2012) Pro-oxidant effects of Ecstasy and its metabolites in mouse brain synaptosomes. Br J Pharmacol 165:1017–1033. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01453.x
Barbosa DJ, Capela JP, Silva R, Ferreira LM, Branco PS, Fernandes E, Bastos ML, Carvalho F (2014) “Ecstasy”-induced toxicity in SH-SY5Y differentiated cells: role of hyperthermia and metabolites. Arch Toxicol 88:515–531. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-013-1147-9
Baumann MH, Clark RD, Budzynski AG, Partilla JS, Blough BE, Rothman RB (2004) N-Substituted piperazinesa abused by humans mimic the molecular mechanism of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, or Ecstasy). Neuropsychopharmacol 30:550–560. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1300585
Benarroch EE (2011) Na+, K+-ATPase: functions in the nervous system and involvement in neurologic disease. Neurology 76:287–289. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182074c2f
Bersier MG, Peña C, de Lores R, Arnaiz G (2011) Changes in Na+, K+-ATPase activity and alpha 3 subunit expression in CNS after administration of Na+, K+-ATPase inhibitors. Neurochem Res 36:297–303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-010-0317-x
Capela JP, Meisel A, Abreu AR, Branco PS, Ferreira LM, Lobo AM, Remião F, Bastos ML, Carvalho F (2006) Neurotoxicity of ecstasy metabolites in rat cortical neurons, and influence of hyperthermia. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 316:53–61. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.105.092577
Capela JP, Macedo C, Branco PS, Ferreira LM, Lobo AM, Fernandes E, Remião F, Bastos ML, Dirnagl U, Meisel A, Carvalho F (2007) Neurotoxicity mechanisms of thioether ecstasy metabolites. Neuroscience 146:1743–1757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.03.028
Capela JP, Carmo H, Remião F, Bastos ML, Meisel A, Carvalho F (2009) Molecular and cellular mechanisms of ecstasy-induced neurotoxicity: an overview. Mol Neurobiol 39:210–271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-009-8064-1
Carranza ML, Rousselot M, Chibalin AV, Bertorello AM, Favre H, Féraille E (1998) Protein kinase A induces recruitment of active Na+, K+-ATPase units to the plasma membrane of rat proximal convoluted tubule cells. J Physiol 511:235–243. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.235bi.x
Ciudad-Roberts A, Camarasa J, Pubill D, Escubedo E (2013) Heteromeric nicotinic receptors are involved in the sensitization and addictive properties of MDMA in mice. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 44:201–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2013.02.013
Costa G, Gołembiowska K (2022) Neurotoxicity of MDMA: main effects and mechanisms. Exp Neurol 347:113894. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2021.113894
Costa TGF, Oliveira MM, Toledo MM, Santos HB, Thome RG, Cortes VF, Santos HL, Quintas LEM, Sousa L, Fontes CFL, Barbosa LA (2022) Effect of Fe3+ on Na, K-ATPase: unexpected activation of ATP hydrolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 1864:183868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2022.183868
Doltchinkova V, Mouleshkova N, Vitkova V (2021) Surface properties of synaptosomes in the presence of L-glutamic and kainic acids: in vitro alteration of the ATPase and acetylcholinesterase activities. Membranes. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11120987
Erecinska M, Nelson D, Silver IA (1996) Metabolic and energetic properties of isolated nerve ending particles (synaptosomes). Biochim Biophys Acta 1277:13–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0005-2728(96)00103-X
Erives GV, Lau SS, Monks TJ (2008) Accumulation of neurotoxic thioether metabolites of 3,4-(±)-methylenedioxymethamphetamine in rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 324:284–291. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.107.128785
Esteban B, O’Shea E, Camarero J, Sanchez V, Green AR, Colado MI (2001) 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine induces monoamine release, but not toxicity, when administered centrally at a concentration occurring following a peripherally injected neurotoxic dose. Psychopharmacology 154:251–260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130000645
Ferreira PS, Nogueira TB, Costa VM, Branco PS, Ferreira LM, Fernandes E, Bastos ML, Meisel A, Carvalho F, Capela JP (2013) Neurotoxicity of “ecstasy” and its metabolites in human dopaminergic differentiated SH-SY5Y cells. Toxicol Lett 216:159–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2012.11.015
Foley TD, Montovano G, Camacho Ayala M (2020) The reducible disulfide proteome of synaptosomes supports a role for reversible oxidations of protein thiols in the maintenance of neuronal redox homeostasis. Neurochem Res 45:1825–1838. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-020-03046-7
Forman HJ, Torres M (2002) Reactive oxygen species and cell signaling: respiratory burst in macrophage signaling. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 166:4–8. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.2206007
Gollamudi R, Ali SF, Lipe G, Newport G, Webb P, Lopez M, Leakey JE, Kolta M, Slikker WJ (1989) Influence of inducers and inhibitors on the metabolism in vitro and neurochemical effects in vivo of MDMA. Neurotoxicology 10:455–466
Hernández J (1987) Brain Na+, K+-ATPase activity possibly regulated by a specific serotonin receptor. Brain Res 408:399–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(87)90414-8
Hernández-Rodríguez J, Chagoya G (1986) Brain serotonin synthesis and Na+, K+-ATPase activity are increased postnatally after prenatal administration of L-tryptophan. Brain Res 390:221–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-8993(86)80230-x
Hrometz SL, Brown AW, Nichols DE, Sprague JE (2004) 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, ecstasy)-mediated production of hydrogen peroxide in an in vitro model: the role of dopamine, the serotonin-reuptake transporter, and monoamine oxidase-B. Neurosci Lett 367:56–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2004.05.075
Jones DC, Duvauchelle C, Ikegami A, Olsen CM, Lau SS, de la Torre R, Monks TJ (2005) Serotonergic neurotoxic metabolites of ecstasy identified in rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 313:422–431. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.104.077628
Kehr J, Ichinose F, Yoshitake S, Goiny M, Sievertsson T, Nyberg F, Yoshitake T (2011) Mephedrone, compared with MDMA (ecstasy) and amphetamine, rapidly increases both dopamine and 5-HT levels in nucleus accumbens of awake rats. Br J Pharmacol 164:1949–1958. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01499.x
Khedr NF, Talkan OFA (2022) New insights into arsenic, lead, and iron neurotoxicity: Activation of MAPK signaling pathway and oxidative stress. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 36:e23040. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.23040
Kinoshita PF, Orellana AMM, Nakao VW, de Souza Port’s NM, Quintas LEM, Kawamoto EM, Scavone C (2022) The Janus face of ouabain in Na+/K+-ATPase and calcium signalling in neurons. Br J Pharmacol 179:1512–1524. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.15419
Liu L, Li J, Liu J, Yuan Z, Pierre SV, Qu W, Zhao X, Xie Z (2006) Involvement of Na+/K+-ATPase in hydrogen peroxide-induced hypertrophy in cardiac myocytes. Free Radic Biol Med 41:1548–1556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2006.08.018
Liu J, Kennedy DJ, Yan Y, Shapiro JI (2012) Reactive oxygen species modulation of Na/K-ATPase regulates fibrosis and renal proximal tubular sodium handling. Int J Nephrol. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/381320
Liu J, Yan Y, Nie Y, Shapiro JI (2017) Na/K-ATPase signaling and salt sensitivity: the role of oxidative stress. Antioxidants 6:18. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox6010018
Macedo C, Branco PS, Ferreira LM, Lobo AM, Capela JP, Fernandes E, Bastos ML, Carvalho F (2007) Synthesis and cyclic voltammetry studies of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) human metabolites. J Health Sci 53:31–42
Magee CP, Le BD, Siripathane YH, Wilkins DG, Hanson GR, Fleckenstein AE (2021) Methcathinone decreases dopamine transporter function: role of protein kinase C. J Neurochem 159:116–127. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.15483
Maya-López M, Mireles-García MV, Ramírez-Toledo M, Colín-González AL, Galván-Arzate S, Túnez I, Santamaría A (2018) Thallium-induced toxicity in rat brain crude synaptosomal/mitochondrial fractions is sensitive to anti-excitatory and antioxidant agents. Neurotox Res 33:634–640. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-017-9863-1
Nahar M, Jat D (2021) Long-term exposure of alcohol induced behavioral impairments and oxidative stress in the brain mitochondria and synaptosomes of adult zebrafish. Zebrafish 18:110–124. https://doi.org/10.1089/zeb.2020.1913
Nicholls DG (1993) The glutamatergic nerve terminal. Eur J Biochem 212:613–631. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17700.x
Pendyala G, Buescher JL, Fox HS (2012) Methamphetamine and inflammatory cytokines increase neuronal Na+/K+-ATPase Isoform 3: relevance for HIV associated neurocognitive disorders. PLoS ONE 7:e37604. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0037604
Pimentel VC, Zanini D, Cardoso AM, Schmatz R, Bagatini MD, Gutierres JM, Carvalho F, Gomes JL, Rubin M, Morsch VM et al (2013) Hypoxia–ischemia alters nucleotide and nucleoside catabolism and Na+, K+-ATPase activity in the cerebral cortex of newborn rats. Neurochem Res 38:886–894. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-013-0994-3
Ridge KM, Dada L, Lecuona E, Bertorello AM, Katz AI, Mochly-Rosen D, Sznajder JI (2002) Dopamine-induced exocytosis of Na, K-ATPase is dependent on activation of protein Kinase C-ε and -δ. Mol Biol Cell 13:1381–1389. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.01-07-0323
Robledo P (2010) Cannabinoids, opioids and MDMA: neuropsychological interactions related to addiction. Curr Drug Targets 11:429–439. https://doi.org/10.2174/138945010790980330
Rodríguez-Moreno A, Sihra TS (2013) Presynaptic kainate receptor-mediated facilitation of glutamate release involves Ca2+–calmodulin and PKA in cerebrocortical synaptosomes. FEBS Lett 587:788–792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2013.01.071
Schmidt CJ, Levin JA, Lovenberg W (1987) In vitro and in vivo neurochemical effects of methylenedioxymethamphetamine on striatal monoaminergic systems in the rat brain. Biochem Pharmacol 36:747–755. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-2952(87)90729-5
Shrivastava AN, Triller A, Melki R (2020) Cell biology and dynamics of neuronal Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase in health and diseases. Neuropharmacology 169:107461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.12.008
Skou JC (1965) Enzymatic basis for active transport of Na+ and K+ across cell membrane. Physiol Rev 45:596–617. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.1965.45.3.596
Stahl WL (1986) The Na, K-ATPase of nervous tissue. Neurochem Int 8:449–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/0197-0186(86)90179-8
Whittaker VP (1993) Thirty years of synaptosome research. J Neurocytol 22:735–742. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01181319
Xie ZJ, Wang YH, Askari A, Huang WH, Klaunig JE, Askari A (1990) Studies on the specificity of the effects of oxygen metabolites on cardiac sodium pump. J Mol Cell Cardiol 22:911–920. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-2828(90)90122-I
Yin W, Yin F, Shen W, Cai B, Hua Z (2008) Requirement of hydrogen peroxide and Sp1 in the stimulation of Na, K-ATPase by low potassium in MDCK epithelial cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 40:942–953. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2007.10.036
Zaitseva T, Shen J, Schears G, Creed J, Wilson DF, Pastuszko A (2002) Effect of catecholamines on activity of Na+, K+-ATPase in neonatal piglet brain during posthypoxic reoxygenation. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 132:139–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1095-6433(01)00540-2
Zhou X, Yin W, Doi SQ, Robinson SW, Takeyasu K, Fan X (2003) Stimulation of Na, K-ATPase by low potassium requires reactive oxygen species. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 285:319–326. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00536.2002
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by “Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia”, Portugal (Project PTDC/SAU-FCF/102958/2008). The NMR spectrometers are part of “The National NMR Facility”, supported by “Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia” (RECI/BBB-BQB/0230/2012). DJB was supported by a PhD fellowship (SFRH/BD/64939/2009) from “Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia”, Portugal.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Barbosa, D.J., Capela, J.P., Ferreira, L.M. et al. Ecstasy metabolites and monoamine neurotransmitters upshift the Na+/K+ ATPase activity in mouse brain synaptosomes. Arch Toxicol 96, 3279–3290 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-022-03370-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-022-03370-7