Abstract
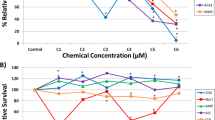
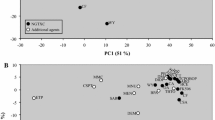
Although the value of the regulatory accepted batteries for in vitro genotoxicity testing is recognized, they result in a high number of false positives. This has a major impact on society and industries developing novel compounds for pharmaceutical, chemical, and consumer products, as afflicted compounds have to be (prematurely) abandoned or further tested on animals. Using the metabolically competent human HepaRG™ cell line and toxicogenomics approaches, we have developed an upgraded, innovative, and proprietary gene classifier. This gene classifier is based on transcriptomic changes induced by 12 genotoxic and 12 non-genotoxic reference compounds tested at sub-cytotoxic concentrations, i.e., IC10 concentrations as determined by the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. The resulting gene classifier was translated into an easy-to-handle qPCR array that, as shown by pathway analysis, covers several different cellular processes related to genotoxicity. To further assess the predictivity of the tool, a set of 5 known positive and 5 known negative test compounds for genotoxicity was evaluated. In addition, 2 compounds with debatable genotoxicity data were tested to explore how the qPCR array would classify these. With an accuracy of 100%, when equivocal results were considered positive, the results showed that combining HepaRG™ cells with a genotoxin-specific qPCR array can improve (geno)toxicological hazard assessment. In addition, the developed qPCR array was able to provide additional information on compounds for which so far debatable genotoxicity data are available. The results indicate that the new in vitro tool can improve human safety assessment of chemicals in general by basing predictions on mechanistic toxicogenomics information.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 2NF :
-
2-nitrofluorene
- AFB :
-
Aflatoxin B1
- AMP :
-
Ampicillin trihydrate
- ANT :
-
Anthranilic acid
- B[α]P :
-
Benzo[α]pyrene
- BLE :
-
Bleomycin sulfate
- BOR :
-
Basic orange 31
- CAP :
-
Caprolactam
- CAvit :
-
In vitro chromosome aberration test
- CdCl 2 :
-
Cadmium chloride
- CHF :
-
Chloramphenicol
- CIS :
-
Cisplatin
- CLI :
-
Climbazole
- CLR :
-
4chlororesorcinol
- CND :
-
Clonidine
- CYC :
-
Cyclophosphamide
- DAT :
-
2,4-diaminotoluene
- DMN :
-
Dimethylnitrosamine
- EMS :
-
Ethyl methanesulphonate
- ENU :
-
1-ethyl-1-nitrosourea
- ETO :
-
Etoposide
- FAM :
-
6-carboxyfluorescein
- FDR :
-
False discovery rate
- HBM :
-
Hydroxybenzomorpholine
- HCA :
-
Hierarchical cluster analysis
- HKG :
-
Housekeeping genes
- MAN :
-
d-mannitol
- MAP :
-
m-aminophenol
- MELA :
-
Melamine
- MMS :
-
Methyl methanesulphonate
- MNvit :
-
In vitro micronucleus test
- MNviv :
-
In vivo micronucleus test
- MTT :
-
3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide
- NAC :
-
No amplification control
- NaCl :
-
Sodium chloride
- NAP :
-
1-naphthol
- NIF :
-
Nifedipine
- NNK :
-
4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone
- NTC :
-
No template control
- OECD :
-
Organisation for economic co-operation and development
- PAM :
-
Prediction analysis of micorarrays
- pCA :
-
p-chloroaniline
- PCA :
-
Principal component analysis
- RIN :
-
RNA integrity number
- SCCS :
-
Scientific Committee on Consumer Safety
- SDF :
-
Sodium diclofenac
- SOR :
-
Sorbitol
- SVM :
-
Support vector machine
- TAMRA :
-
Tetramethylrhodamine
- TOL :
-
Tolbutamide
- TRI :
-
Triclosan
- VIN :
-
Vinblastine sulfate
- WHO :
-
World Health Organization
- ZID :
-
Zidovudine
References
Ates G, Doktorova TY, Pauwels M, Rogiers V (2014) Retrospective analysis of the mutagenicity/genotoxicity data of the cosmetic ingredients present on the Annexes of the Cosmetic EU legislation (2000-12). Mutagenesis 29:115–121. https://doi.org/10.1093/mutage/get068
Ates G, Raitano G, Heymans A et al (2016) In silico tools and transcriptomics analyses in the mutagenicity assessment of cosmetic ingredients: a proof-of-principle on how to add weight to the evidence. Mutagenesis 31:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1093/mutage/gew008
Aubrecht J, Caba E (2005) Gene expression profile analysis: an emerging approach to investigate mechanisms of genotoxicity. Pharmacogenomics 6:419–428. https://doi.org/10.1517/14622416.6.4.419
Bakhtyari NG, Raitano G, Benfenati E et al (2013) Comparison of in silico models for prediction of mutagenicity. J Environ Sci Health C Environ Carcinog Ecotoxicol Rev 31:45–66. https://doi.org/10.1080/10590501.2013.763576
Boehme K, Dietz Y, Hewitt P, Mueller SO (2011) Genomic profiling uncovers a molecular pattern for toxicological characterization of mutagens and promutagens in vitro. Toxicol Sci 122:185–197. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfr090
Boehncke DA, Kielhorn J, Könnecker G et al (2003) Concise international chemical assessment document 48: 4-Chloroaniline, WHO, ISSN 1020–6167
Buick JK, Moffat I, Williams A et al (2015) Integration of metabolic activation with a predictive toxicogenomics signature to classify genotoxic versus nongenotoxic chemicals in human TK6 cells. Environ Mol Mutagen 56:520–534. https://doi.org/10.1002/em
Cahill PA, Knight AW, Billinton N et al (2004) The GreenScreen(R) genotoxicity assay: a screening validation programme. Mutagenesis 19:105–119. https://doi.org/10.1093/mutage/geh015
Ceelen L, De Spiegelaere W, David M et al (2011) Critical selection of reliable reference genes for gene expression study in the HepaRG cell line. Biochem Pharmacol 81:1255–1261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2011.03.004
COM (2011) Guidance on a strategy for genotoxicity testing of chemical substances guidance on a strategy for genotoxicity testing of chemical substances. pp 1–84
Corvi R, Madia F, Worth A, Whelan M (2013) EURL ECVAM strategy to avoid and reduce animal use in genotoxicity testing. JRC, Luxemburg
Doktorova TY, Yildirimman R, Vinken M et al (2013) Transcriptomic responses generated by hepatocarcinogens in a battery of liver-based in vitro models. Carcinogenesis 34:1393–1402. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgt054
Doktorova TY, Ates G, Vinken M et al (2014a) Way forward in case of a false positive in vitro genotoxicity result for a cosmetic substance? Toxicol Vitr 28:54–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2013.09.022
Doktorova TY, Yildirimman R, Ceelen L et al (2014b) Testing chemical carcinogenicity by using a transcriptomics heparg-based model? EXCLI J 13:623–637
EC (2009) Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 30 November 2009 on cosmetic products. Off J Eur Communion L342:59–209
Garcia-Canton C, Anadon A, Meredith C (2013) Assessment of the in vitro yH2AX assay by High Content Screening as a novel genotoxicity test. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 757:158–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2013.08.002
Greene EJ, Friedman MA, Sherrod JA (1979) In vitro mutagenicity and cell transformation screening of caprolactam. Environ Mutagen 407:399–407
Hastwell PW, Chai LL, Roberts KJ et al (2006) High-specificity and high-sensitivity genotoxicity assessment in a human cell line: validation of the GreenScreen HC GADD45a-GFP genotoxicity assay. Mutat Res - Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 607:160–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2006.04.011
Hendriks G, Derr RS, Misovic B et al (2016) The extended ToxTracker assay discriminates between induction of DNA damage, oxidative stress and protein misfolding. Toxicol Sci 150:190–203. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfv323
Hughes C, Rabinowitz A, Tate M et al (2012) Development of a high-throughput Gaussia luciferase reporter assay for the activation of the GADD45a gene by mutagens, promutagens, clastogens, and aneugens. J Biomol Screen 17:1302–1315. https://doi.org/10.1177/1087057112453312
Kamber M, Fluckiger-Isler S, Engelhardt G et al (2009) Comparison of the Ames II and traditional Ames test responses with respect to mutagenicity, strain specificities, need for metabolism and correlation with rodent carcinogenicity. Mutagenesis 24:359–366. https://doi.org/10.1093/mutage/gep017
Khoury L, Zalko D, Audebert M (2013) Validation of high-throughput genotoxicity assay screening using yH2AX in-cell western assay on HepG2 cells. Environ Mol Mutagen 54:737–746. https://doi.org/10.1002/em.21817
Kirkland D (2011) Improvements in the reliability of in vitro genotoxicity testing. Toxicol Lett 205:S7–S7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2011.05.029
Kirkland D, Speit G (2008) Evaluation of the ability of a battery of three in vitro genotoxicity tests to discriminate rodent carcinogens and non-carcinogens. III. Appropriate follow-up testing in vivo. Mutat Res - Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 654:114–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2008.05.002
Kirkland D, Aardema M, Henderson L, Müller L (2005) Evaluation of the ability of a battery of three in vitro genotoxicity tests to discriminate rodent carcinogens and non-carcinogens. I. Sensitivity, specificity and relative predicticity. Mutat Res - Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 584:1–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2008.05.002
Kirkland D, Aardema M, Banduhn N, Carmichael P, Fautz R, Meunier JR, Pfuhler S (2007) In vitro approaches to develop weight of evidence (WoE) and mode of action (MoA) discussions with positive in vitro genotoxicity results. Mutagenesis 22:161–175. https://doi.org/10.1093/mutage/gem006
Kirkland D, Kasper P, Müller L et al (2008) Recommended lists of genotoxic and non-genotoxic chemicals for assessment of the performance of new or improved genotoxicity tests: A follow-up to an ECVAM workshop. Mutat Res - Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 653:99–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2008.03.008
Kirkland D, Reeve L, Gatehouse D, Vanparys P (2011) A core in vitro genotoxicity battery comprising the Ames test plus the in vitro micronucleus test is sufficient to detect rodent carcinogens and in vivo genotoxins. Mutat Res - Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 721:27–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2010.12.015
Kirkland D, Kasper P, Martus HJ et al (2016) Updated recommended lists of genotoxic and non-genotoxic chemicals for assessment of the performance of new or improved genotoxicity tests. Mutat Res - Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 795:7–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2015.10.006
Lee SJ, Yum YN, Kim SC et al (2013) Distinguishing between genotoxic and non-genotoxic hepatocarcinogens by gene expression profiling and bioinformatic pathway analysis. Sci Rep 3:34–41. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep02783
Li H-H, Hyduke DR, Chen R et al (2015) Development of a toxicogenomics signature for genotoxicity using a dose-optimization and informatics strategy in human cells. Environ Mol Mutagen 56:229–262. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-5915-6
Mathijs K, Brauers KJJ, Jennen DGJ et al (2010) Gene expression profiling in primary mouse hepatocytes discriminates true from false-positive genotoxic compounds. Mutagenesis 25:561–568. https://doi.org/10.1093/mutage/geq040
Mi H, Huang X, Muruganujan A et al (2017) PANTHER version 11: expanded annotation data from Gene Ontology and Reactome pathways, and data analysis tool enhancements. Nucleic Acids Res 45:D183–D189. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw1138
Miller K (1991) Clastogenic effects of bleomycin, cyclophosphamide, and ethyl methanesulfonate on resting and proliferating human B- and T-lymphocytes. Mutat Res Mol Mech Mutagen 251:241–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/0027-5107(91)90079-4
Mizota T, Ohno K, Yamada T (2011) Validation of a genotoxicity test based on p53R2 gene expression in human lymphoblastoid cells. Mutat Res 724:76–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2011.06.003
Mozdarani H, Saberi AH (1994) Induction of cytogenetic adaptive response of mouse bone marrow cells to radiation by therapeutic doses of bleomycin sulfate and actinomycin D as assayed by the micronucleus test. Cancer Lett 78:141–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3835(94)90043-4
Phipson B, Lee S, Majewski IJ et al (2016) Robust hyperparameter estimation protects against hypervariable genes and improves power to detect differential expression. Ann Appl Stat 10:946–963. https://doi.org/10.1214/16-AOAS920
Pottenger LH, Bus JS, Gollapudi BB (2007) Genetic Toxicity Assessment: Employing the Best Science for Human Safety Evaluation Part VI: When Salt and Sugar and Vegetables Are Positive, How Can Genotoxicity Data Serve to Inform Risk Assessment? Toxicol Sci 98:327–331. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfm068
Provenzano M, Mocellin S (2007) Complementary techniques: Validation of gene expression data by quantitative real time PCR. Adv Exp Med Biol 593:66–73. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-39978-2_7
Rieswijk L, Brauers KJJ, Coonen MLJ et al (2016) Exploiting microRNA and mRNA profiles generated in vitro from carcinogen-exposed primary mouse hepatocytes for predicting in vivo genotoxicity and carcinogenicity. Mutagenesis 31:603–615. https://doi.org/10.1093/mutage/gew027
SCCP (2005) Opinion on hydroxybenzomorpholine. 0965/05:pp 1–39
SCCP (2008a) Opinion on triclosan. 1192/08:p 136
SCCP (2008b) Opinion on 1-Naphthol. 1123/07:pp 1–26
SCCP (2008c) Opinion on Climbazole. 1204/08:pp 1–33
SCCS (2006) Opinion on m-aminophenol. 0978/06:p 26
SCCS (2010a) Opinion on Basic Orange 31. 1334/10:31
SCCS (2010b) Opinion on 4-chlororesorcinol. 1224/09:p 26
SCCS (2016) The SCCS Notes of Guidance for the testing of cosmetic ingredients and their safety evaluation 9th revision. 1564/15:pp 1–151
Suenaga K, Takasawa H, Watanabe T et al (2013) Differential gene expression profiling between genotoxic and non-genotoxic hepatocarcinogens in young rat liver determined by quantitative real-time PCR and principal component analysis. Mutat Res Toxicol Environ Mutagen 751:73–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2012.11.003
Teixeira do Amaral R, Ansell J, Aptula N et al (2014) In silico approaches for safety assessment of cosmetic ingredients. In: Rep. Int. Coop. Cosmet. Regul. http://www.iccrnet.org/topics/. Accessed 9 Sep 2016
Tibshirani R, Hastie T, Narasimhan B, Chu G (2002) Diagnosis of multiple cancer types by shrunken centroids of gene expression. PNAS 99:6567–6572. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.082099299
Tinker A, Boussioutas A, Bowtell D (2006) The challenges of gene expression microarrays for the study of human cancer. Cancer Cell 9(5):333–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2006.05.001
Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn I et al (2002) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 3:34–31. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2002-3-7-research0034
Vinken M, Doktorova T, Ellinger-Ziegelbauer H et al (2008) The carcinoGENOMICS project: critical selection of model compounds for the development of omics-based in vitro carcinogenicity screening assays. Mutat Res - Rev Mutat Res 659:202–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrrev.2008.04.006
Watanabe T, Tanaka G, Hamada S et al (2009) Dose-dependent alterations in gene expression in mouse liver induced by diethylnitrosamine and ethylnitrosourea and determined by quantitative real-time PCR. Mutat Res Toxicol Environ Mutagen 673:9–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2008.11.004
Westerink WM, Schirris TJJ, Horbach GJ, Schoonen WGEJ. (2011) Development and validation of a high-content screening in vitro micronucleus assay in CHO-k1 and HepG2 cells. Mutat Res Toxicol Environ Mutagen 724:7–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2011.05.007
Williams A, Buick JK, Moffat I et al (2015) A predictive toxicogenomics signature to classify genotoxic versus non-genotoxic chemicals in human TK6 cells. Data Br 5:77–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2015.08.013
Zeiger E, Gollapudi B, Aardema MJ et al (2015) Opportunities to integrate new approaches in genetic toxicology: An ILSI-HESI workshop report. Environ Mol Mutagen 56:277–285. https://doi.org/10.1002/em.21923
Zhou X, Zhang T, Song D et al (2017) Comparison and evaluation of conventional RT-PCR, SYBR green I and TaqMan real-time RT-PCR assays for the detection of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus. Mol Cell Probes 33:36–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcp.2017.02.002
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Vrije Universiteit Brussel (VUB) and the Scientific Institute of Public Health (WIV-ISP), Belgium.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ates, G., Mertens, B., Heymans, A. et al. A novel genotoxin-specific qPCR array based on the metabolically competent human HepaRG™ cell line as a rapid and reliable tool for improved in vitro hazard assessment. Arch Toxicol 92, 1593–1608 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-018-2172-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-018-2172-5