Abstract
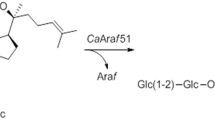
The α-L-arabinofuranosidase enzyme plays a crucial role in the degradation of ginsenosides. In this study, we successfully cloned and expressed a novel α-L-arabinofuranosidase bsafs gene (1503 bp, 501 amino acids, 55 kDa, and pI = 5.4) belonging to glycosyl hydrolase (GH) family 51 from Bacillus subtilis genome in Escherichia coli BL21 cells. The recombinant protein Bsafs was purified using Ni2+ sepharose fastflow affinity chromatography and exhibited a specific activity of 2.91 U/mg. Bsafs effectively hydrolyzed the α-L-arabinofuranoside at C20 site of ginsenoside Rc to produce Rd as the product. The Km values for hydrolysis of pNP-α-L-arabinofuranoside (pNPαAraf) and ginsenoside Rc were determined as 0.74 and 4.59 mmol/L, respectively; while the Vmax values for these substrates were found to be 24 and 164 μmol/min/mg, respectively; furthermore, the Kcat values for these enzymes were calculated as 22.3 and 1.58 S−1 correspondingly.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy.
References
An DS, Cui CH, Sung BH, Yang HC, Kim SC, Lee ST, Im WT, Kim SG (2012) Characterization of a novel ginsenoside-hydrolyzing α-L-arabinofuranosidase, AbfA, from Rhodanobacter ginsenosidimutans Gsoil 3054T. Appl Microbiol Biotechno 94:672–682
An DS, Cui CH, Siddiqi MZ, Yu HS (2017) Gram-scale production of ginsenoside F1 using a recombinant bacterial β-glucosidase. J Microbiol Biotechnol 27:1559–1565
Chen Y, Nose M, Ogihara Y (1987) Alkaline cleavage of ginsenosides. Chem Pharm Bull 35:1653–1655
Cleland WW (1967) The statistical analysis of enzyme kinetic data. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol 29:1–32
Fu Y (2019) Biotransformation of ginsenoside Rb1 to Gyp-XVII and minor ginsenoside Rg3 by endophytic bacterium Flavobacterium sp. GE 32 isolated from Panax ginseng. Lett Appl Microbio 68:134–141
Fuzzati N (2004) Analysis methods of ginsenosides. J Chromatogr B 812:119–133
Han BH, Park MH, Han YN, Woo LK, Sankawa U, Yahara S, Tanaka O (1982) Degradation of ginseng saponins under mild acidic conditions. Planta Med 44:146–149
Hollinger J, Wu JB, Awayda KM, O’Connell MR, Yao P (2023) Expression and purification of the mitochondrial transmembrane protein FAM210A in Escherichia coli. Protein Expression Purif 106:322
Inacio JM, Correia IL, de Sa-Nogueira I (2008) Two distinct arabinofuranosidases contribute to arabino-oligosaccharide degradation in Bacillus subtili. Microbiol 154:2719–2729
Jia L, Zhao Y (2009) Current evaluation of themillennium phytomedicine ginseng[I]; etymology, pharmacognosy, phytochemistry, market and regulations. Curr Med Chem 16:2475–2484
Kim DH (2012) Chemical diversity of panax ginseng, panax quinquifolium, and panax notoginseng. J Ginseng Res 36:1–15
Lee JH, Hyun YJ, Kim DH (2011) Cloning and characterization of α-L-arabinofuranosidase and bifunctional α-L-arabinopyranosidase/β-D-galactopyranosidase from Bifidobacterium longum H-1. J Appl Microbiol 111:1097–1107
Lin WM, Zhang YM, Moldzio R (2007) Ginsenoside Rd attenuates neuroinflammation of dopaminergic cells in culture. J Neural Transm 72:105–112
Liu QM, Jung HM, Cui CH, Sung BH, Kim JK, Kim SG, Lee ST, Kim SC, Im WT (2013) Bioconversion of ginsenoside Rc into Rd by a novel α-L-arabinofuranosidase, Abf 22–3 from Leuconostoc sp. 22–3: cloning, expression, and enzyme characterization. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 103:747–754
Matrawy AA, Khalil AI, Embaby AM (2022) Molecular study on recombinant cold-adapted, detergent- and alkali stable esterase (EstRag) from Lysinibacillus sp: a member of family VI. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 38:217
Qu CL, Bai YP, Jin XQ et al (2009) Study on ginsenosides in different parts and ages of Panax quinquefolius. Food Chem 115:340–346
Quan LH, Min JW, Sathiyamoorthy S, Yang DU, Kim YJ, Yang DC (2012) Biotransformation of ginsenosides Re and Rg1 into ginsenosides Rg2 and Rh1 by recombinant β-glucosidase. Biotechnol Lett 34:913–917
Scaglione F, Ferrara F, Dugnani S (1990) Immunomodulatory effects of two etracts of Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer Drugs Exp Clin Res 16:537–542
Shi W, Wang YT, Li J, Zhang HQ, Ding L (2007) Investigation of ginsenosides in different parts and ages of Panax ginseng. Food Chem 102:664–668
Shin KC, Oh DK (2016) Classification of glycosidases that hydrolyze the specific positions and types of sugar moieties in ginsenosides. Crit Rev Biotechnol 36:1036–1049
Shin HY, Park SY, Sung JH, Kim DH (2003) Purification and characterization of α-L-arabinopyranosidase and α-Larabinofuranosidase from Bifdobacterium breve K-110, a human intestinal anaerobic bacterium metabolizing ginsenoside Rb2 and Rc. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:7116–7123
Shin KC, Lee GW, Oh DK (2013a) Production of ginsenoside Rd from ginsenoside Rc by α-L-arabinofuranosidase from Caldicellulosiruptor saccharolyticus. J Microbiol Biotechnol 23:483–490
Shin KC, Oh HJ, Kim BJ, Oh DK (2013b) Complete conversion of major protopanaxadiol ginsenosides to compound K by the combined use of α-L-arabinofuranosidase and β-galactosidase from Caldicellulosiruptor saccharolyticus and β-glucosidase from Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. J Biotechnol 167:33–40
Singh VK, Agarwal SS, Gupta BM (1984) Immunomodulatory activity of Panax ginseng extract. Planta Med 50:462–465
Tawab MA, Bahr U, Karas M, Wurglics M, Schubert-Zsilavecz M (2003) Degradation of ginsenosides in humans after oral administration. Drug Metab Dispos 31:1065–1071
Wandrey C, Liese A, Kihumbu D (2000) Industrial biocatalysis: past, present, and future. Org Process Res Dev 4:286–290
Yang ZG, Sun HX, Ye YP (2006) Ginsenoside Rd from Panax notoginseng is cytotoxic towards HeLa cancer cells and induces apoptosis. Chem Biodivers 3:187–197
Yang ZG, Chen A, Sun HX, Ye YP, Fang WH (2007) Ginsenoside Rd elicits Th1 and Th2 immune responses to ovalbumin in mice. Vaccine 25:161–169
Yang WZ, Hu Y, Wu WY, Ye M, Gao DA (2014) Saponins in the genus Panax L. (Araliaceae): A systematic review of their chemical diversity. Phytochemistry 106:7–24
Yokozawa T, Satoh A, Cho EJ (2004) Ginsenoside-Rd attenuates oxidative damage related to aging in senescence-accelerated mice. J Pharm Pharmacol 56:107–113
Zhang C, Yu H, Bao Y (2002) Purification and characterization of ginsenoside-α-arabinofuranase hydrolyzing ginsenoside Rc into Rd form the fresh root of Panax ginseng. Process Biochem 37:793–798
Zhu L, Wang YC, Zhao JY, Wen ML, Li MG, Han XL (2020) Transformation of ginsenoside Rb3 and C-Mx by recombinant beta-xylosidase. Chem J Chin Univ 41:1010–1017
Zuo SS, Wang YC, Zhu L, Zhao JY, Li MG, Han XL, Wen ML (2020) Cloning and characterization of a ginsenoside-hydrolyzing α-L-arabinofuranosidase, CaAraf51, From Cellulosimicrobium aquatile Lyp51. Curr Microbiol 77:2783–2791
Funding
This work is supported by Special Basic Cooperative Research Programs of Yunnan Provincial Undergraduate Universities’ Association (Grant NO. 202301BA070001-081), Yunnan Fundamental Research Projects (Grant NO. 202301AU070012), Special Basic Cooperative Research Innovation Programs of Qujing Science and Technology Bureau & Qujing Normal University (Grant NO. KJLH2023ZD06, KJLH2022YB07).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L. Z and Y. C. W conceived the study and supervised the project. J C cloned and expressed Bsafs. L. Z tudy of the enzymatic activity of Bsafs. L. Z wrote the main manuscript. All authors participated in preparation of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by PANKAJ BHATT.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, L., Wang, Y. & Cai, J. Molecular cloning, expression, purification, and characterization of Bacillus subtilis hydrolyzed ginsenoside Rc of α-L-arabinofuranosidase in Escherichia coli. Arch Microbiol 206, 181 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-024-03902-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-024-03902-y