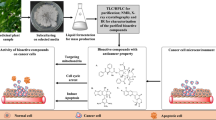
Abstract
Endophytes are considered one of the major sources of bioactive compounds used in different aspects of health care including cancer treatment. When colonized, they either synthesize these bioactive compounds as a part of their secondary metabolite production or augment the host plant machinery in synthesising such bioactive compounds. Hence, the study of endophytes has drawn the attention of the scientific community in the last few decades. Among the endophytes, endophytic fungi constitute a major portion of endophytic microbiota. This review deals with a plethora of anti-cancer compounds derived from endophytic fungi, highlighting alkaloids, lignans, terpenes, polyketides, polyphenols, quinones, xanthenes, tetralones, peptides, and spirobisnaphthalenes. Further, this review emphasizes modern methodologies, particularly omics-based techniques, asymmetric dihydroxylation, and biotic elicitors, showcasing the dynamic and evolving landscape of research in this field and describing the potential of endophytic fungi as a source of anticancer drugs in the future.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdalla MA, Matasyoh JC (2014) Endophytes as producers of peptides: an overview about the recently discovered peptides from endophytic microbes. Nat Prod Bioprospecting 4(5):257–270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13659-014-0038-y
Acuna UM, Shen Q, Ren Y, Lantvit DD, Wittwer JA, Kinghorn AD, Swanson SM, Blanco EJC (2013) Goyazensolide induces apoptosis in cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Int J Cancer Res 9(2):36–53. https://doi.org/10.3923/ijcr.2013.36.53
Adeleke BS, Babalola OO (2021) pharmacological potential of fungal endophytes associated with medicinal plants: a review. J Fungi 7(2):147. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7020147
Adorisio S, Fierabracci A, Muscari I, Liberati AM, Cannarile L, Thuy TT, Sung TV, Sohrab H, Hasan CM, Ayroldi E, Riccardi C, Mazid A, Delfino DV (2019) Fusarubin and anhydrofusarubin isolated from a Cladosporium species inhibit cell growth in human cancer cell lines. Toxins 11(9):503. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11090503
Adpressa DA, Loesgen S (2016) Bioprospecting chemical diversity and bioactivity in a marine derived Aspergillus terreus. Chem Biodivers 13(2):253–259. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbdv.201500310
Afrin S, Giampieri F, Gasparrini M, Forbes-Hernández TY, Cianciosi D, Reboredo-Rodriguez P, Zhang J, Manna PP, Daglia M, Atanasov AG, Battino M (2020) Dietary phytochemicals in colorectal cancer prevention and treatment: a focus on the molecular mechanisms involved. Biotechnol Adv 38:107322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2018.11.011
Albright JC, Henke MT, Soukup AA, McClure RA, Thomson RJ, Keller NP, Kelleher NL (2015) Large-scale metabolomics reveals a complex response of Aspergillus nidulans to epigenetic perturbation. ACS Chem Biol 10(6):1535–1541. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.5b00025
Ali GS, El-Sayed ASA, Patel JS, Green KB, Ali M, Brennan M, Norman D (2016) Ex vivo application of secreted metabolites produced by soil-inhabiting bacillus spp efficiently controls foliar diseases caused by Alternaria spp. Appl Environ Microbiol 82(2):478–490. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02662-15
Anders C, Carey LA (2008) Understanding and treating triple-negative breast cancer. Oncology (williston Park) 22(11):1233–1243
Anderson AC, Yanai I, Yates LR, Wang L, Swarbrick A, Sorger P, Santagata S, Fridman WH, Gao Q, Jerby L, Izar B, Shang L, Zhou X (2022) Spatial transcriptomics. Cancer Cell 40(9):895–900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2022.08.021
Ardalani H, Avan A, Ghayour-Mobarhan M (2017) Podophyllotoxin: a novel potential natural anticancer agent. Avicenna J Phytomedicine 7(4):285–294
Ashraf J, Sharma MK, Biswas D (2021) Separation, purification and characterization of vincristine and vinblastine from fusarium oxysporum, an endophytic fungus present in Catharanthus roseus leaves. J Adv Sci Res 12(01 Suppl 2):Article 01 Suppl 2
Aswini A, Soundhari C (2018) Production of camptothecin from endophytic fungi and characterization by high-performance liquid chromatography and anticancer activity against colon cancer cell line. Asian J Pharm Clin Res 11(3):166. https://doi.org/10.22159/ajpcr.2018.v11i3.18921
Barbulovic-Nad I, Lucente M, Sun Y, Zhang M, Wheeler AR, Bussmann M (2006) Bio-microarray fabrication techniques—a review. Crit Rev Biotechnol 26(4):237–259. https://doi.org/10.1080/07388550600978358
Bayraktar O, Erdoğan İ, Köse MD, Kalmaz G (2017) Chapter 17—Nanocarriers for plant-derived natural compounds. In: Ficai A, Grumezescu AM (eds) Nanostructures for antimicrobial therapy. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 395–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-46152-8.00017-2
Bhagobaty RK, Joshi SR (2011) Fungal endophytes of five medicinal plants prevalent in the traditionally preserved ‘Sacred forests’ of Meghalaya, India. Forest Sci Technol 7(4):151–154. https://doi.org/10.1080/21580103.2011.621381
Bhardwaj A, Agrawal P (2014) A review fungal endophytes: as a store house of bioactive compound. World J Pharm Pharm Sci 3:228–237
Bhaskar R, Xavier LSE, Udayakumaran G, Kumar DS, Venkatesh R, Nagella P (2022) Biotic elicitors: a boon for the in-vitro production of plant secondary metabolites. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 149(1):7–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-021-02131-1
Birat K, Binsuwaidan R, Siddiqi TO, Mir SR, Alshammari N, Adnan M, Nazir R, Ejaz B, Malik MQ, Dewangan RP, Ashraf SA, Panda BP (2022a) Report on vincristine-producing endophytic fungus Nigrospora zimmermanii from leaves of Catharanthus roseus. Metabolites 12(11):1119. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12111119
Birat K, Siddiqi TO, Mir SR, Aslan J, Bansal R, Khan W, Dewangan RP, Panda BP (2022b) Enhancement of vincristine under in vitro culture of Catharanthus roseus supplemented with Alternaria sesami endophytic fungal extract as a biotic elicitor. Int Microbiol 25(2):275–284. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-021-00213-w
Blessie EJ, Wruck W, Abbey BA, Ncube A, Graffmann N, Amarh V, Arthur PK, Adjaye J (2020) Transcriptomic analysis of marine endophytic fungi extract identifies highly enriched anti-fungal fractions targeting cancer pathways in HepG2 cell lines. BMC Genomics 21(1):265. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-020-6684-z
Bode HB, Walker M, Zeeck A (2000) Structure and biosynthesis of mutolide, a novel macrolide from a UV mutant of the fungus F-24′707. Eur J Org Chem 2000(8):1451–1456. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-0690(200004)2000:8%3c1451::AID-EJOC1451%3e3.0.CO;2-F
Brakhage AA (2013) Regulation of fungal secondary metabolism. Nat Rev Microbiol 11(1):21–32. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2916
Brakhage AA, Schuemann J, Bergmann S, Scherlach K, Schroeckh V, Hertweck C (2008) Activation of fungal silent gene clusters: a new avenue to drug discovery. In: Petersen F, Amstutz R (eds) Natural compounds as drugs, vol 2. Birkhäuser, Basel, pp 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7643-8595-8_1
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J Clin 68(6):394–424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492
Brown DW, Yu JH, Kelkar HS, Fernandes M, Nesbitt TC, Keller NP, Adams TH, Leonard TJ (1996) Twenty-five coregulated transcripts define a sterigmatocystin gene cluster in Aspergillus nidulans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93(4):1418–1422. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.93.4.1418
Bruckdorfer T, Marder O, Albericio F (2004) From production of peptides in milligram amounts for research to multi-tons quantities for drugs of the future. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 5(1):29–43. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389201043489620
Brvar M, Ploj T, Kozelj G, Mozina M, Noc M, Bunc M (2004) Case report: fatal poisoning with Colchicum autumnale. Crit Care 8(1):R56. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc2427
Buchfink B, Xie C, Huson DH (2015) Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat Methods 12(1):Article 1. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3176
Bunyapaiboonsri T, Yoiprommarat S, Srikitikulchai P, Srichomthong K, Lumyong S (2010) Oblongolides from the endophytic fungus Phomopsis sp. BCC 9789. J Nat Prod 73(1):55–59. https://doi.org/10.1021/np900650c
Butnariu M, Quispe C, Herrera-Bravo J, Sharifi-Rad J, Singh L, Aborehab NM, Bouyahya A, Venditti A, Sen S, Acharya K, Bashiry M, Ezzat SM, Setzer WN, Martorell M, Mileski KS, Bagiu I-C, Docea AO, Calina D, Cho WC (2022) The pharmacological activities of Crocus sativus L.: a review based on the mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities of its phytoconstituents. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022:8214821. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/8214821
Cai Y-S, Sarotti AM, Zhou T-L, Huang R, Qiu G, Tian C, Miao Z-H, Mándi A, Kurtán T, Cao S, Yang S-P (2018) Flabellipparicine, a flabelliformide-apparicine-type bisindole alkaloid from Tabernaemontana divaricata. J Nat Prod 81(9):1976–1983. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.8b00191
Carreira EM, Pfaff P (2020) Total synthesis of (+)-formosalides A and B. Synfacts 16(12):1387. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0040-1719535
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Side effects of cancer treatment. https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/survivors/patients/side-effects-of-treatment.html
Cháirez-Ramírez MH, de la Cruz-López KG, García-Carrancá A (2021) Polyphenols as antitumor agents targeting key players in cancer-driving signaling pathways. Front Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.710304
Charpentier MS, Whipple RA, Vitolo MI, Boggs AE, Slovic J, Thompson KN, Bhandary L, Martin SS (2014) Curcumin targets breast cancer stem-like cells with microtentacles that persist in mammospheres and promote reattachment. Cancer Res 74(4):1250–1260. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-1778
Chen Q-H, Kingston DGI (2014) Zampanolide and dactylolide: cytotoxic tubulin assembly agents and promising anticancer leads. Nat Prod Rep 31:1202. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4np00024b
Chen J-Y, Tang Y-A, Li W-S, Chiou Y-C, Shieh J-M, Wang Y-C (2013) A synthetic podophyllotoxin derivative exerts anti-cancer effects by inducing mitotic arrest and pro-apoptotic ER stress in lung cancer preclinical models. PLoS ONE 8(4):e62082. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0062082
Chen Z, Chen H-P, Li Y, Feng T, Liu J-K (2015) Cytochalasins from cultures of endophytic fungus Phoma multirostrata EA-12. J Antibiot 68(1):23–26. https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2014.87
Cheng Z, Lu X, Feng B (2020) A review of research progress of antitumor drugs based on tubulin targets. Transl Cancer Res 9(6):4020–4027. https://doi.org/10.21037/tcr-20-682
Cheng T, Kolařík M, Quijada L, Stadler M (2022) A re-assessment of Taxomyces andreanae, the alleged taxol-producing fungus, using comparative genomics. IMA Fungus 13(1):17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43008-022-00103-4
Chokpaiboon S, Sommit D, Teerawatananond T, Muangsin N, Bunyapaiboonsri T, Pudhom K (2010) Cytotoxic nor-chamigrane and chamigrane endoperoxides from a basidiomycetous fungus. J Nat Prod 73(5):1005–1007. https://doi.org/10.1021/np100103j
Chowdhury NS, Sohrab MdH, Rana MdS, Hasan CM, Jamshidi S, Rahman KM (2017) Cytotoxic naphthoquinone and azaanthraquinone derivatives from an endophytic Fusarium solani. J Nat Prod 80(4):1173–1177
Christensen SB (2022) Drugs that changed society: microtubule-targeting agents belonging to taxanoids, macrolides and non-ribosomal peptides. Molecules 27(17):Article 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175648
Clish CB (2015) Metabolomics: an emerging but powerful tool for precision medicine. Cold Spring Harb Mol Case Stud 1(1):a000588. https://doi.org/10.1101/mcs.a000588
Cooper JA (1987) Effects of cytochalasin and phalloidin on actin. J Cell Biol 105(4):1473–1478. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.105.4.1473
Cores Á, Carmona-Zafra N, Clerigué J, Villacampa M, Menéndez JC (2023) Quinones as neuroprotective agents. Antioxidants 12(7):Article 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12071464
Cox RJ (2023) Curiouser and curiouser: progress in understanding the programming of iterative highly-reducing polyketide synthases. Nat Prod Rep 40(1):9–27. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2np00007e
Cox G, Wright GD (2013) Intrinsic antibiotic resistance: mechanisms, origins, challenges and solutions. Int J Med Microbiol 303(6):287–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmm.2013.02.009
Cragg GM, Newman DJ (2005) Plants as a source of anti-cancer agents. J Ethnopharmacol 100(1–2):72–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2005.05.011
Crispino GA, Jeong KS, Kolb HC, Wang ZM, Xu D, Sharpless KB (1993) Improved enantioselectivity in asymmetric dihydroxylations of terminal olefins using pyrimidine ligands. J Org Chem 58(15):3785–3786. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo00067a002
D’Costa VM, King CE, Kalan L, Morar M, Sung WWL, Schwarz C, Froese D, Zazula G, Calmels F, Debruyne R, Golding GB, Poinar HN, Wright GD (2011) Antibiotic resistance is ancient. Nature 477(7365):Article 7365. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10388
Das A, Sarkar S, Bhattacharyya S, Gantait S (2020) Biotechnological advancements in Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104(11):4811–4835. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10592-1
de Jong A, van Heel AJ, Kok J, Kuipers OP (2010) BAGEL2: mining for bacteriocins in genomic data. Nucleic Acids Res 38(suppl_2):W647–W651. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkq365
de Ruijter TC, Veeck J, de Hoon JPJ, van Engeland M, Tjan-Heijnen VC (2011) Characteristics of triple-negative breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 137(2):183–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-010-0957-x
Deepika VB, Vohra M, Mishra S, Dorai K, Rai P, Satyamoorthy K, Murali TS (2020) DNA demethylation overcomes attenuation of colchicine biosynthesis in an endophytic fungus Diaporthe. J Biotechnol 323:33–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2020.07.019
Degambada KD, Kumara PAASP, Salim N, Abeysekera AM, Chandrika UG (2023) Diaporthe sp. F18; a new source of camptothecin-producing endophytic fungus from Nothapodytes nimmoniana growing in Sri Lanka. Nat Prod Res 37(1):113–118. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2021.1946535
Demain AL, Vaishnav P (2011) Natural products for cancer chemotherapy. Microb Biotechnol 4(6):687–699. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-7915.2010.00221.x
Deshmukh SK, Mishra PD, Kulkarni-Almeida A, Verekar S, Sahoo MR, Periyasamy G, Goswami H, Khanna A, Balakrishnan A, Vishwakarma R (2009) Anti-inflammatory and anticancer activity of ergoflavin isolated from an endophytic fungus. Chem Biodivers 6(5):784–789. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbdv.200800103
Devari S, Jaglan S, Kumar M, Deshidi R, Guru S, Bhushan S, Kushwaha M, Gupta AP, Gandhi SG, Sharma JP, Taneja SC, Vishwakarma RA, Shah BA (2014) Capsaicin production by Alternaria alternata, an endophytic fungus from Capsicum annum; LC–ESI–MS/MS analysis. Phytochemistry 98:183–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2013.12.001
Devi N (2014) Bioactive metabolites from an endophytic fungus Penicillium s.p isolated from Centella asiatica. Curr Res Environ Appl Mycol 4(1):34–43. https://doi.org/10.5943/cream/4/1/3
Dewick PM (2002) Medicinal natural products: a biosynthetic approach. Wiley, Hoboken
Dhyani P, Quispe C, Sharma E, Bahukhandi A, Sati P, Attri DC, Szopa A, Sharifi-Rad J, Docea AO, Mardare I, Calina D, Cho WC (2022) Anticancer potential of alkaloids: a key emphasis to colchicine, vinblastine, vincristine, vindesine, vinorelbine and vincamine. Cancer Cell Int 22(1):206. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-022-02624-9
Dong Z, Chen Y (2013) Transcriptomics: advances and approaches. Sci China Life Sci 56(10):960–967. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-013-4557-2
dos Santos Baliza DDM, da Silva JFM, Ferreira EMS, Ferreira IM, da Silva EO, do Nascimento JLM, Pimenta RS (2023) Screening of endophytes for anticancer compounds. In: Sankaranarayanan A, Amaresan N, Dwivedi MK (eds) Endophytic microbes: isolation, identification, and bioactive potentials. Springer US, New York, pp 255–268. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2827-0_27
Duconseil P, Gilabert M, Gayet O, Loncle C, Moutardier V, Turrini O, Calvo E, Ewald J, Giovannini M, Gasmi M, Bories E, Barthet M, Ouaissi M, Goncalves A, Poizat F, Raoul JL, Secq V, Garcia S, Viens P, Dusetti N (2015) Transcriptomic analysis predicts survival and sensitivity to anticancer drugs of patients with a pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Am J Pathol 185(4):1022–1032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2014.11.029
El Khalki L, Maire V, Dubois T, Zyad A (2020) Berberine impairs the survival of triple negative breast cancer cells: cellular and molecular analyses. Molecules 25(3):506. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030506
Elkhayat ES, Goda AM (2017) Antifungal and cytotoxic constituents from the endophytic fungus Penicillium sp. Bull Fac Pharm Cairo Univ 55(1):85–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bfopcu.2017.03.001
El-Sayed ASA, Abdel-Azeim S, Ibrahim HM, Yassin MA, Abdel-Ghany SE, Esener S, Ali GS (2015) Biochemical stability and molecular dynamic characterization of Aspergillus fumigatus cystathionine γ-lyase in response to various reaction effectors. Enzyme Microb Technol 81:31–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2015.08.004
El-Sayed ASA, Abdel-Ghany SE, Ali GS (2017a) Genome editing approaches: manipulating of lovastatin and taxol synthesis of filamentous fungi by CRISPR/Cas9 system. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101(10):3953–3976. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8263-z
El-Sayed ASA, Ruff LE, Ghany SEA, Ali GS, Esener S (2017b) Molecular and spectroscopic characterization of Aspergillus flavipes and Pseudomonas putida L-methionine γ-lyase in vitro. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 181(4):1513–1532. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-016-2299-x
El-Sayed ASA, Safan S, Mohamed NZ, Shaban L, Ali GS, Sitohy MZ (2018) Induction of Taxol biosynthesis by Aspergillus terreus, endophyte of Podocarpus gracilior Pilger, upon intimate interaction with the plant endogenous microbes. Process Biochem 71:31–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2018.04.020
El-Sayed ASA, Ali DMI, Yassin MA, Zayed RA, Ali GS (2019) Sterol inhibitor “Fluconazole” enhance the Taxol yield and molecular expression of its encoding genes cluster from Aspergillus flavipes. Process Biochem 76:55–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2018.10.008
Erhirhie EO, Ezeagha CC, Okafor GC, Ikegbune C, Mohammad M (2023) Endophytes—untapped resources and pharmacological prospects against coronaviruses. Eur J Clin Exp Med 21(1):145–151. https://doi.org/10.15584/ejcem.2023.1.18
Exposito O, Bonfill M, Moyano E, Onrubia M, Mirjalili MH, Cusido RM, Palazon J (2009) Biotechnological production of taxol and related taxoids: current state and prospects. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 9(1):109–121
Eyberger AL, Dondapati R, Porter JR (2006) Endophyte fungal isolates from Podophyllum peltatum produce podophyllotoxin. J Nat Prod 69(8):1121–1124. https://doi.org/10.1021/np060174f
Franciosa G, Kverneland AH, Jensen AWP, Donia M, Olsen JV (2023) Proteomics to study cancer immunity and improve treatment. Semin Immunopathol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-022-00980-2
Frattaruolo L, Lacret R, Cappello AR, Truman AW (2017) A genomics-based approach identifies a thioviridamide-like compound with selective anticancer activity. ACS Chem Biol 12(11):2815–2822. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.7b00677
Gallego-Jara J, Lozano-Terol G, Sola-Martínez RA, Cánovas-Díaz M, de Diego Puente T (2020) A compressive review about Taxol®: history and future challenges. Molecules 25(24):Article 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25245986
Gallo M, Falso M, Balem F, Menezes D, Rocha N, Balachandran R, Sturgeon T, Pupo M, Day B (2014) The anti-promyelocytic leukemia mode of action of two endophytic secondary metabolites unveiled by a proteomic approach. Planta Med 80(06):473–481. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0034-1368301
Ganesan N, Rajendran R, Ilanchezhiyan S (2015) Nyctanthes arbor-tristis Linn. associated fungal endophyte Aspergillus niger derived isolation of Camptothecin for its antimicrobial and cytotoxic activity. Scigen J Sci Technol 1:6–13
Ganguly A, Yang H, Zhang H, Cabral F, Patel KD (2013) Microtubule dynamics control tail retraction in migrating vascular endothelial cells. Mol Cancer Ther 12(12):2837–2846. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0401
Ghosh S, Khanam R, Acharya Chowdhury A (2021) The evolving roles of Bacopa monnieri as potential anti-cancer agent: a review. Nutr Cancer 73(11–12):2166–2176. https://doi.org/10.1080/01635581.2020.1841248
Gonzalez-Covarrubias V, Martínez-Martínez E, del Bosque-Plata L (2022) The potential of metabolomics in biomedical applications. Metabolites 12(2):Article 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12020194
González-Menéndez V, Pérez-Bonilla M, Pérez-Victoria I, Martín J, Muñoz F, Reyes F, Tormo JR, Genilloud O (2016) Multicomponent analysis of the differential induction of secondary metabolite profiles in fungal endophytes. Molecules 21(2):Article 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21020234
Gouda S, Das G, Sen SK, Shin H-S, Patra JK (2016) Endophytes: a treasure house of bioactive compounds of medicinal importance. Front Microbiol 7:1538. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01538
Guo B, Wang Y, Sun X, Tang K (2008) Bioactive natural products from endophytes: a review. Appl Biochem Microbiol 44(2):136–142. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0003683808020026
Gutierrez RM, Gonzalez AM, Ramirez AM (2012) Compounds derived from endophytes: a review of phytochemistry and pharmacology. Curr Med Chem 19(18):2992–3030. https://doi.org/10.2174/092986712800672111
Habli Z, Toumieh G, Fatfat M, Rahal ON, Gali-Muhtasib H (2017) emerging cytotoxic alkaloids in the battle against cancer: overview of molecular mechanisms. Molecules 22(2):250. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22020250
Hasan AEZ, Julistiono H, Bermawie N, Riyanti EI, Arifni FR (2022) Soursop leaves (Annona muricata L.) endophytic fungi anticancer activity against HeLa cells. Saudi J Biol Sci 29(8):103354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2022.103354
Hashimshony T, Wagner F, Sher N, Yanai I (2012) CEL-Seq: single-cell RNA-Seq by multiplexed linear amplification. Cell Rep 2(3):666–673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2012.08.003
Hawksworth DL, Lücking R (2017) Fungal diversity revisited: 2.2 to 3.8 million species. Microbiol Spectr 5(4):5.4.10. https://doi.org/10.1128/microbiolspec.FUNK-0052-2016
Haworth RD (1942) The chemistry of the lignan group of natural products. J Chem Soc. https://doi.org/10.1039/jr9420000448
Heinig U, Scholz S, Jennewein S (2013) Getting to the bottom of Taxol biosynthesis by fungi. Fungal Divers 60(1):161–170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13225-013-0228-7
Heravi MM, Zadsirjan V, Esfandyari M, Lashaki TB (2017) Applications of sharpless asymmetric dihydroxylation in the total synthesis of natural products. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 28(8):987–1043. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetasy.2017.07.004
Hertweck C (2009) The biosynthetic logic of polyketide diversity. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 48(26):4688–4716. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200806121
Holton RA, Biediger RJ, Boatman PD (1995) Semisynthesis of taxol and taxotere. In: Taxol, 1 edn. CRC Press, p 25. https://doi.org/10.1201/9780429275792
Houbraken J, Visagie CM, Frisvad JC (2021) Recommendations to prevent taxonomic misidentification of genome-sequenced fungal strains. Microbiol Resour Announc 10(48):e01074-e1120. https://doi.org/10.1128/MRA.01074-20
Hridoy Md, Gorapi MdZH, Noor S, Chowdhury NS, Rahman MdM, Muscari I, Masia F, Adorisio S, Delfino DV, Mazid MdA (2022) Putative anticancer compounds from plant-derived endophytic fungi: a review. Molecules 27(1):296. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27010296
Huang W-Y, Cai Y-Z, Xing J, Corke H, Sun M (2007) A potential antioxidant resource: endophytic fungi from medicinal plants. Econ Bot 61(1):14–30. https://doi.org/10.1663/0013-0001(2007)61[14:APAREF]2.0.CO;2
Huang C-H, Pan J-H, Chen B, Yu M, Huang H-B, Zhu X, Lu Y-J, She Z-G, Lin Y-C (2011) Three bianthraquinone derivatives from the mangrove endophytic fungus Alternaria sp. ZJ9-6B from the South China Sea. Mar Drugs 9(5):832–843. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9050832
Huang C, Jin H, Song B, Zhu X, Zhao H, Cai J, Lu Y, Chen B, Lin Y (2012) The cytotoxicity and anticancer mechanisms of alterporriol L, a marine bianthraquinone, against MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93(2):777–785. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3463-4
Huang S, Chen H, Li W, Zhu X, Ding W, Li C (2016) Bioactive chaetoglobosins from the mangrove endophytic fungus Penicillium chrysogenum. Mar Drugs 14(10):172. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14100172
Indian Council of Medical Research - Regional Medical Research Centre. Research areas. Retrieved from https://rmrcne.org.in/index.php/research-areas
Ionkova I (2011) Anticancer lignans—from discovery to biotechnology. Mini-Rev Med Chem 11(10):843–856. https://doi.org/10.2174/138955711796575425
Iqbal J, Abbasi BA, Mahmood T, Kanwal S, Ali B, Shah SA, Khalil AT (2017) Plant-derived anticancer agents: a green anticancer approach. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 7(12):1129–1150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apjtb.2017.10.016
Isah T, Mujib A (2015) Camptothecin from Nothapodytes nimmoniana: review on biotechnology applications. Acta Physiol Plant 37(6):106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-015-1854-3
Isaka M, Chinthanom P, Boonruangprapa T, Rungjindamai N, Pinruan U (2010) Eremophilane-type sesquiterpenes from the fungus Xylaria sp. BCC 21097. J Nat Prod 73(4):683–687. https://doi.org/10.1021/np100030x
Isaq M, Somu P, Acharya D, Gomez LA, Thathapudi JJ, Ramachandra YL, Rudraiah SB, Ravi P, Rai PS, Rosalin R, Poojari CC, Lee YR (2022) Phytochemical screening and bioactivity studies of endophytes Cladosporium sp. isolated from the endangered plant Vateria indica using in silico and in vitro analysis. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 194(10):4546–4569. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-03933-5
Jeyasri R, Muthuramalingam P, Karthick K, Shin H, Choi SH, Ramesh M (2023) Methyl jasmonate and salicylic acid as powerful elicitors for enhancing the production of secondary metabolites in medicinal plants: an updated review. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-023-02485-8
Jiao RH, Xu S, Liu JY, Ge HM, Ding H, Xu C, Zhu HL, Tan RX (2006) Chaetominine, a cytotoxic alkaloid produced by endophytic Chaetomium sp. IFB-E015. Org Lett 8(25):5709–5712. https://doi.org/10.1021/ol062257t
Jordan MA (2002) Mechanism of action of antitumor drugs that interact with microtubules and tubulin. Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents 2(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568011023354290
Joseph B, Priya R (2011) Bioactive compounds from endophytes and their potential in pharmaceutical effect: a review. Am J Biochem Mol Biol 1(3):291–309. https://doi.org/10.3923/ajbmb.2011.291.309
Kampan N, Madondo M, McNally O, Quinn M, Plebanski M (2015) Paclitaxel and its evolving role in the management of ovarian cancer. Biomed Res Int 2015:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/413076
Karahalil B, Yardım-Akaydin S, Nacak Baytas S (2019) An overview of microtubule targeting agents for cancer therapy. Arh Hig Rada Toksikol 70(3):160–172. https://doi.org/10.2478/aiht-2019-70-3258
Kato S, Mizukami D, Sugai T, Tsuda M, Fuwa H (2020) Total synthesis and complete configurational assignment of amphirionin-2. Chem Sci 12(3):872–879. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0sc06021f
Kawada M, Inoue H, Ohba S-I, Masuda T, Momose I, Ikeda D (2010) Leucinostatin A inhibits prostate cancer growth through reduction of insulin-like growth factor-I expression in prostate stromal cells. Int J Cancer 126(4):810–818. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.24915
Keller EF (2011) Genes, genomes, and genomics. Biol Theory 6(2):132–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13752-012-0014-x
Keller NP (2019) Fungal secondary metabolism: regulation, function and drug discovery. Nat Rev Microbiol 17(3):Article 3. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-018-0121-1
Keshri PK, Rai N, Verma A, Kamble SC, Barik S, Mishra P, Singh SK, Salvi P, Gautam V (2021) Biological potential of bioactive metabolites derived from fungal endophytes associated with medicinal plants. Mycol Prog 20(5):577–594. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11557-021-01695-8
Khaldi N, Seifuddin FT, Turner G, Haft D, Nierman WC, Wolfe KH, Fedorova ND (2010) SMURF: genomic mapping of fungal secondary metabolite clusters. Fungal Genet Biol 47(9):736–741. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2010.06.003
Khalil MW, Sasse F, Lünsdorf H, Elnakady YA, Reichenbach H (2006) Mechanism of action of tubulysin, an antimitotic peptide from myxobacteria. ChemBioChem 7(4):678–683. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.200500421
Kharde A, Kore S, Khetmalas M (2018) Elicitation of bacoside content using plant growth regulators in cell suspension culture of Bacopa monnieri (L.) Wettst. Plant Tissue Cult Biotechnol 28(2):191–199. https://doi.org/10.3329/ptcb.v28i2.39678
Kharwar RN, Mishra A, Gond SK, Stierle A, Stierle D (2011) Anticancer compounds derived from fungal endophytes: their importance and future challenges. Nat Prod Rep 28(7):1208–1228. https://doi.org/10.1039/C1NP00008J
Klassen A, Faccio AT, Canuto GAB, da Cruz PLR, Ribeiro HC, Tavares MFM, Sussulini A (2017) Metabolomics: definitions and significance in systems biology. In: Sussulini A (ed) Metabolomics: from fundamentals to clinical applications. Springer, Cham, pp 3–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-47656-8_1
Klopfleisch R, Gruber AD (2012) Transcriptome and proteome research in veterinary science: what is possible and what questions can be asked? Sci World J 2012:e254962. https://doi.org/10.1100/2012/254962
Kobayashi J, Tsuda M (2004) Amphidinolides, bioactive macrolides from symbiotic marine dinoflagellates. ChemInform. https://doi.org/10.1002/chin.200420239
König IR, Fuchs O, Hansen G, von Mutius E, Kopp MV (2017) What is precision medicine? Eur Respir J 50(4):1700391. https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.00391-2017
Koul M, Singh S (2017) Penicillium spp.: prolific producer for harnessing cytotoxic secondary metabolites. Anticancer Drugs 28(1):11–30. https://doi.org/10.1097/CAD.0000000000000423
Koul M, Meena S, Kumar A, Sharma PR, Singamaneni V, Riyaz-Ul-Hassan S, Hamid A, Chaubey A, Prabhakar A, Gupta P, Singh S (2016) Secondary metabolites from endophytic fungus Penicillium pinophilum induce ROS-mediated apoptosis through mitochondrial pathway in pancreatic cancer cells. Planta Med 82(4):344–355. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0035-1558308
Koul M, Kumar A, Deshidi R, Sharma V, Singh RD, Singh J, Sharma PR, Shah BA, Jaglan S, Singh S (2017) Cladosporol A triggers apoptosis sensitivity by ROS-mediated autophagic flux in human breast cancer cells. BMC Cell Biol 18(1):26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12860-017-0141-0
Kousar R, Naeem M, Jamaludin MI, Arshad A, Shamsuri AN, Ansari N, Akhtar S, Hazafa A, Uddin J, Khan A, Al-Harrasi A (2022) Exploring the anticancer activities of novel bioactive compounds derived from endophytic fungi: mechanisms of action, current challenges and future perspectives. Am J Cancer Res 12(7):2897–2919
Krohn K (2003) Natural products derived from naphthalenoid precursors by oxidative dimerization. In: Chakraborty DP, Krohn K, Messner P, Roy S, Schäffer C (eds) Fortschritte der Chemie organischer Naturstoffe/progress in the chemistry of organic natural products. Springer, Berlin, pp 1–49. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-6051-0_1
Krown SE, Moser CB, MacPhail P, Matining RM, Godfrey C, Caruso SR, Hosseinipour MC, Samaneka W, Nyirenda M, Busakhala NW, Okuku FM, Kosgei J, Hoagland B, Mwelase N, Oliver VO, Burger H, Mngqibisa R, Nokta M, Campbell TB, Gottshall B (2020) Treatment of advanced AIDS-associated Kaposi sarcoma in resource-limited settings: a three-arm, open-label, randomised, non-inferiority trial. Lancet 395(10231):1195–1207. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(19)33222-2
Kumagai K, Minamida M, Akakabe M, Tsuda M, Konishi Y, Tominaga A, Tsuda M, Fukushi E, Kawabata J (2015) Amphirionin-2, a novel linear polyketide with potent cytotoxic activity from a marine dinoflagellate Amphidinium species. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 25(3):635–638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2014.12.003
Kumar A, Ahmad A (2013) Biotransformation of vinblastine to vincristine by the endophytic fungus Fusarium oxysporum isolated from Catharanthus roseus. Biocatal Biotransformation 31(2):89–93. https://doi.org/10.3109/10242422.2013.776544
Kumaran RS, Kim HJ, Hur B-K (2010) Taxol-producing [corrected] fungal endophyte, Pestalotiopsis species isolated from Taxus cuspidata. J Biosci Bioeng 110(5):541–546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2010.06.007
Kumari R, Kotecha M (2016) A review on the standardization of herbal medicines. Int J Pharm Sci Res (IJPSR) 7(2):97–106
Kurobane I, Vining LC, McInnes AG (1979) Biosynthetic relationships among the secalonic acids Isolation of emodin, endocrocin and secalonic acids from Pyrenochaeta terrestris and Aspergillus aculeatus. J Antibiot 32(12):1256–1266. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.32.1256
Kusari S, Pandey SP, Spiteller M (2013) Untapped mutualistic paradigms linking host plant and endophytic fungal production of similar bioactive secondary metabolites. Phytochemistry 91:81–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2012.07.021
Lakshmi N, Bhuvaneswari V, Kathiravan G, Shanmugapriya B (2015) Endophytic fungal communities associated with ethnomedicinal plants from India and their potential production of anticancer drug camptothecin. Life Sci Arch 1(2):142–156
Lal M, Parasar NR, Singh AK, Akhtar MS (2018) Potentiality of anticancer plant-derived compounds of North-East India. In: Akhtar M, Swamy M (eds) Anticancer plants: properties and application. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-8548-2_4
Leung YY, Hui LLY, Kraus VB (2015) Colchicine—update on mechanisms of action and therapeutic uses. Semin Arthritis Rheum 45(3):341–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semarthrit.2015.06.013
Li H-L, Li X-M, Mándi A, Antus S, Li X, Zhang P, Liu Y, Kurtán T, Wang B-G (2017a) Characterization of cladosporols from the marine algal-derived endophytic fungus Cladosporium cladosporioides EN-399 and configurational revision of the previously reported cladosporol derivatives. J Org Chem 82(19):9946–9954. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.7b01277
Li Q, Zhang Y, Shi J-L, Wang Y-L, Zhao H-B, Shao D, Huang Q-S, Yang H, Jin M-L (2017b) Mechanism and anticancer activity of the metabolites of an endophytic fungi from Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. Anti-Cancer Agents Med Chem 17(7):982–989. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871520616666160923094814
Li L, Chen Z, Zhang X, Jia Y (2018) Divergent strategy in natural product total synthesis. Chem Rev 118(7):3752–3832. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00653
Li S, Chen J-F, Qin L-L, Li X-H, Cao Z-X, Gu Y-C, Guo D-L, Deng Y (2020) Two new sesquiterpenes produced by the endophytic fungus Aspergillus fumigatus from Ligusticum wallichii. J Asian Nat Prod Res 22(2):138–143. https://doi.org/10.1080/10286020.2018.1540606
Li L, Shan T, Zhang D, Ma F (2022) Nowcasting and forecasting global aging and cancer burden: analysis of data from the Globocan and Global Burden of Disease Study. SSRN Electron J. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4313699
Liang Z, Zhang T, Zhang X, Zhang J, Zhao C (2015) An alkaloid and a steroid from the endophytic fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. Molecules 20(1):Article 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20011424
Lima NNdC, Faustino DC, Allahdadi KJ, França LSdA, Pinto LC (2022) Acetogenins from Annonaceae plants: potent antitumor and neurotoxic compounds. PharmaNutrition 20:100295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phanu.2022.100295
Lin Z-Y, Kuo C-H, Wu D-C, Chuang W-L (2016) Anticancer effects of clinically acceptable colchicine concentrations on human gastric cancer cell lines. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 32(2):68–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kjms.2015.12.006
Liu L, Liu S, Niu S, Guo L, Chen X, Che Y (2009) Isoprenylated chromone derivatives from the plant endophytic fungus Pestalotiopsis fici. J Nat Prod 72(8):1482–1486. https://doi.org/10.1021/np900308s
Liu S-C, Ye X, Guo L-D, Liu L (2011) Cytotoxic isoprenylated epoxycyclohexanediols from the plant endophyte Pestalotiopsis fici. Chin J Nat Med 9(5):374–379. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1009.2011.00374
Liu J-F, Sang C-Y, Xu X-H, Zhang L-L, Yang X, Hui L, Zhang J-B, Chen S-W (2013) Synthesis and cytotoxic activity on human cancer cells of carbamate derivatives of 4β-(1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)podophyllotoxin. Eur J Med Chem 64:621–628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2013.03.068
Lorico A, Long BH (1993) Biochemical characterisation of elsamicin and other coumarin-related antitumour agents as potent inhibitors of human topoisomerase II. Eur J Cancer 29(14):1985–1991. https://doi.org/10.1016/0959-8049(93)90459-S
Lowe R, Shirley N, Bleackley M, Dolan S, Shafee T (2017) Transcriptomics technologies. PLoS Comput Biol 13(5):e1005457. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005457
Lu Y, Chen J, Xiao M, Li W, Miller DD (2012) An overview of tubulin inhibitors that interact with the colchicine binding site. Pharm Res 29(11):2943–2971. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-012-0828-z
Lü Y, Han B, Yu H, Cui Z, Li Z, Wang J (2018) Berberine regulates the microRNA-21-ITGΒ4-PDCD4 axis and inhibits colon cancer viability. Oncol Lett 15(4):5971–5976. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2018.7997
Luo M, Liu X, Zu Y, Fu Y, Zhang S, Yao L, Efferth T (2010) Cajanol, a novel anticancer agent from Pigeonpea [Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp.] roots, induces apoptosis in human breast cancer cells through a ROS-mediated mitochondrial pathway. Chem Biol Interact 188(1):151–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2010.07.009
Luo J, Liu X, Li E, Guo L, Che Y (2013) Arundinols A–C and arundinones A and B from the plant endophytic fungus Microsphaeropsis arundinis. J Nat Prod 76(1):107–112. https://doi.org/10.1021/np300806a
Ma Y-M, Zhang H-C, Zhao J, Li X-Q (2012) Secondary anti-fungi metabolites from the endophytic fungus Fusarium sp. in Eucommia Ulmoides. Chem Nat Compd 48(1):170–171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10600-012-0195-3
Maia M, Resende DISP, Durães F, Pinto MMM, Sousa E (2021) Xanthenes in medicinal chemistry—synthetic strategies and biological activities. Eur J Med Chem 210:113085. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.113085
Maldonado EN, Patnaik J, Mullins MR, Lemasters JJ (2010) Free Tubulin modulates mitochondrial membrane potential in cancer cells. Cancer Res 70(24):10192–10201. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-2429
Malik S, Cusidó RM, Mirjalili MH, Moyano E, Palazón J, Bonfill M (2011) Production of the anticancer drug taxol in Taxus baccata suspension cultures: a review. Process Biochem 46(1):23–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2010.09.004
Mallath MK, Taylor DG, Badwe RA, Rath GK, Shanta V, Pramesh CS, Digumarti R, Sebastian P, Borthakur BB, Kalwar A, Kapoor S, Kumar S, Gill JL, Kuriakose MA, Malhotra H, Sharma SC, Shukla S, Viswanath L, Chacko RT, Sullivan R (2014) The growing burden of cancer in India: epidemiology and social context. Lancet Oncol 15(6):e205–e212. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70115-9
Mallebrera B, Prosperini A, Font G, Ruiz MJ (2018) In vitro mechanisms of Beauvericin toxicity: a review. Food Chem Toxicol 111:537–545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2017.11.019
Mandhare A, Banerjee P (2016) Therapeutic use of colchicine and its derivatives: a patent review. Expert Opin Ther Pat 26(10):1157–1174. https://doi.org/10.1080/13543776.2016.1214268
Martino E, Della Volpe S, Terribile E, Benetti E, Sakaj M, Centamore A, Sala A, Collina S (2017) The long story of camptothecin: from traditional medicine to drugs. Bioorganic Med Chem Lett 27(4):701–707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2016.12.085
Marx V (2021) Method of the year: spatially resolved transcriptomics. Nat Methods 18(1):Article 1. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-020-01033-y
Mastrangelopoulou M, Grigalavicius M, Berg K, Ménard M, Theodossiou TA (2019) Cytotoxic and photocytotoxic effects of cercosporin on human tumor cell lines. Photochem Photobiol 95(1):387–396. https://doi.org/10.1111/php.12997
Medema MH, Blin K, Cimermancic P, de Jager V, Zakrzewski P, Fischbach MA, Weber T, Takano E, Breitling R (2011) antiSMASH: rapid identification, annotation and analysis of secondary metabolite biosynthesis gene clusters in bacterial and fungal genome sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 39(suppl_2):W339–W346. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr466
Medema MH, Kottmann R, Yilmaz P, Cummings M, Biggins JB, Blin K, de Bruijn I, Chooi YH, Claesen J, Coates RC, Cruz-Morales P, Duddela S, Düsterhus S, Edwards DJ, Fewer DP, Garg N, Geiger C, Gomez-Escribano JP, Greule A, Glöckner FO (2015) Minimum information about a biosynthetic gene cluster. Nat Chem Biol 11(9):Article 9. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.1890
Mishra J, Verma N (2017) A brief study on Catharanthus roseus: a review. Int J Res Pharm Pharm Sci 2:20–23
Mishra PD, Verekar SA, Deshmukh SK, Joshi KS, Fiebig HH, Kelter G (2015) Altersolanol A: a selective cytotoxic anthraquinone from a Phomopsis sp. Lett Appl Microbiol 60(4):387–391. https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.12384
Moni F, Saifullah N, Afroz F, Rony SR, Sharmin S, Shahinuzzaman A, Al-Mansur MA, Al-Reza SMd, Sohrab MdH (2022) Antibacterial and cytotoxic compounds from endophyte Fusarium solani isolated from Centella asiatica (L.). J Biol Act Prod Nat 12(5):436–449. https://doi.org/10.1080/22311866.2022.2144947
Moreno E, Varughese T, Spadafora C, Arnold AE, Coley PD, Kursar TA, Gerwick WH, Cubilla-Rios L (2011) Chemical constituents of the new endophytic fungus Mycosphaerella sp. Nov. and their anti-parasitic activity. Nat Prod Commun 6(6):1934578X1100600620. https://doi.org/10.1177/1934578X1100600620
Moss GP (2000) Nomenclature of lignans and neolignans (IUPAC Recommendations 2000). Pure Appl Chem 72(8):1493–1523. https://doi.org/10.1351/pac200072081493
Moudi M, Go R, Yien CYS, Nazre M (2013) Vinca alkaloids. Int J Prev Med 4(11):1231–1235
Mushtaq A, Zahoor AF, Bilal M, Hussain SM, Irfan M, Akhtar R, Irfan A, Kotwica-Mojzych K, Mojzych M (2023) Sharpless asymmetric dihydroxylation: an impressive gadget for the synthesis of natural products: a review. Molecules 28(6):Article 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062722
Nadeem M (2012) Fusarium solani, P1, a new endophytic podophyllotoxin-producing fungus from roots of Podophyllum hexandrum. Afr J Microbiol Res. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJMR11.1596
Narayanan Z, Glick BR (2022) Secondary metabolites produced by plant growth-promoting bacterial endophytes. Microorganisms 10(10):Article 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10102008
National Cancer Institute. Side effects of cancer treatment. National Institute of Health. https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/side-effects
Nataraj HR, Rao P, Apoorva JM (2017) Anticancerous potentials of Nothapodytes nimmoniana (Grah.) Mabb—a review. Int J Med Pharm Sci 4(5):24. https://doi.org/10.5281/ZENODO.572993
Nicolaou KC, Erande RD, Yin J, Vourloumis D, Aujay M, Sandoval J, Munneke S, Gavrilyuk J (2018) Improved total synthesis of tubulysins and design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of new tubulysins with highly potent cytotoxicities against cancer cells as potential payloads for antibody-drug conjugates. J Am Chem Soc. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.7b12692
Nishad JH, Singh A, Bharti R, Prajapati P, Sharma VK, Gupta VK, Kharwar RN (2021) Effect of the histone methyltransferase specific probe BRD4770 on metabolic profiling of the endophytic fungus Diaporthe longicolla. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.725463
Niu Q, Hou W, Yan Y, Sun S, Lin Y, Fang H, Ma C, Dong C, Cheng Y, Xu Y, Ding M, Wang S, Cui Z, Chen Y, Li H, Li H, Xiao N (2022) Antileukemic effects of topoisomerase I inhibitors mediated by de-SUMOylase SENP1. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 1868(12):166492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2022.16649
Nugraha AS, Damayanti YD, Wangchuk P, Keller PA (2019) Anti-infective and anti-cancer properties of the Annona species: their ethnomedicinal uses, alkaloid diversity, and pharmacological activities. Molecules 24(23):4419. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24234419
Ogishi H, Chiba N, Mikawa T, Sasaki T, Miyaji S, Sezaki M (1990) Mitsubishi Kasei Corp., JP 01294686. In: Chem. Abstr, vol 113, p 38906q
Ojima I, Lichtenthal B, Lee S, Wang C, Wang X (2016) Taxane anticancer agents: a patent perspective. Expert Opin Ther Pat 26(1):1–20. https://doi.org/10.1517/13543776.2016.1111872
Osbourn A (2010) Secondary metabolic gene clusters: evolutionary toolkits for chemical innovation. Trends Genet 26(10):449–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2010.07.001
Ozdemir N, Dogan M, Sendur MAN, Yazici O, Abali H, Yazilitas D, Akinci MB, Aksoy S, Zengin N (2014) Efficacy and safety of first line vincristine with doxorubicin, bleomycin and dacarbazine (ABOD) for Hodgkin’s lymphoma: a single institute experience. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 15(20):8715–8718. https://doi.org/10.7314/apjcp.2014.15.20.8715
Ozsolak F, Milos PM (2011) RNA sequencing: advances, challenges and opportunities. Nat Rev Genet 12(2):87–98. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2934
Palanichamy P, Kannan S, Murugan D, Alagusundaram P, Marudhamuthu M (2019) Purification, crystallization and anticancer activity evaluation of the compound alternariol methyl ether from endophytic fungi Alternaria alternata. J Appl Microbiol 127(5):1468–1478. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.14410
Palem PPC, Kuriakose GC, Jayabaskaran C (2015) An endophytic fungus, Talaromyces radicus, isolated from Catharanthus roseus, produces vincristine and vinblastine, which induce apoptotic cell death. PLoS ONE 10(12):e0144476. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0144476
Pandeti S, Sharma K, Bathula SR, Tadigoppula N (2014) Synthesis of novel anticancer iridoid derivatives and their cell cycle arrest and caspase dependent apoptosis. Phytomedicine 21(3):333–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2013.08.023
Pandey SS, Singh S, Babu CSV, Shanker K, Srivastava NK, Shukla AK, Kalra A (2016) Fungal endophytes of Catharanthus roseus enhance vindoline content by modulating structural and regulatory genes related to terpenoid indole alkaloid biosynthesis. Sci Rep 6(1):Article 1. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep26583
Parashiva J, Nuthan BR, Rakshith D, Satish S (2023) Endophytic fungi as a promising source of anticancer l-asparaginase: a review. Curr Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-023-03392-z
Partida-Martínez LP, Heil M (2011) The microbe-free plant: fact or artifact? Front Plant Sci 2:100. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2011.00100
Paul BN, Saxena AK (1997) Depletion of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in mice by Nyctanthes arbor-tristis. J Ethnopharmacol 56(2):153–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-8741(97)01525-0
Perez-Matas E, Hidalgo-Martinez D, Escrich A, Alcalde MA, Moyano E, Bonfill M, Palazon J (2023) Genetic approaches in improving biotechnological production of taxanes: an update. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2023.1100228
Perveen S, Al-Taweel A (eds) (2018) Terpenes and terpenoids. IntechOpen. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.71175
Pettit GR, Orr B, Ducki S (2000) Antineoplastic agents 453. Synthesis of pancratistatin prodrugs. Anticancer Drug Des 15(6):389–395
Priebe S, Linde J, Albrecht D, Guthke R, Brakhage AA (2011) FungiFun: a web-based application for functional categorization of fungal genes and proteins. Fungal Genet Biol 48(4):353–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2010.11.001
Pu X, Qu X, Chen F, Bao J, Zhang G, Luo Y (2013) Camptothecin-producing endophytic fungus Trichoderma atroviride LY357: isolation, identification, and fermentation conditions optimization for camptothecin production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(21):9365–9375. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5163-8
Pu X, Zhang C-R, Zhu L, Li Q-L, Huang Q-M, Zhang L, Luo Y-G (2019) Possible clues for camptothecin biosynthesis from the metabolites in camptothecin-producing plants. Fitoterapia 134:113–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2019.02.014
Pundir RK, Yadav D, Jain P (2020) Production, optimization and partial purification of L-asparaginase from endophytic fungus Aspergillus sp., isolated from Cassia fistula. Appl Biol Res 22(1):26–33. https://doi.org/10.5958/0974-4517.2020.00008.7
Puri SC, Verma V, Amna T, Qazi GN, Spiteller M (2005) An endophytic fungus from Nothapodytes foetida that produces camptothecin. J Nat Prod 68(12):1717–1719. https://doi.org/10.1021/np0502802
Puri SC, Nazir A, Chawla R, Arora R, Riyaz-ul-Hasan S, Amna T, Ahmed B, Verma V, Singh S, Sagar R, Sharma A, Kumar R, Sharma RK, Qazi GN (2006) The endophytic fungus Trametes hirsuta as a novel alternative source of podophyllotoxin and related aryl tetralin lignans. J Biotechnol 122(4):494–510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2005.10.015
Ragab AE, Badawy ET, Aboukhatwa SM, Kabbash A, Abo El-Seoud KA (2022) In vitro characterization of inhibitors for lung A549 and leukemia K562 cell lines from fungal transformation of arecoline supported by in silico docking to M3-mAChR and ADME prediction. Pharmaceuticals 15(10):Article 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15101171
Rai N, Gupta P, Keshri PK, Verma A, Mishra P, Kumar D, Kumar A, Singh SK, Gautam V (2022a) Fungal endophytes: an accessible source of bioactive compounds with potential anticancer activity. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 194(7):3296–3319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-03872-1
Rai N, Keshri PK, Gupta P, Verma A, Kamble SC, Singh SK, Gautam V (2022b) Bioprospecting of fungal endophytes from Oroxylum indicum (L.) Kurz with antioxidant and cytotoxic activity. PLoS ONE 17(3):e0264673. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0264673
Rai N, Gupta P, Verma A, Singh SK, Gautam V (2023) Isolation and characterization of N-(2-Hydroxyethyl)hexadecanamide from Colletotrichum gloeosporioides with apoptosis-inducing potential in breast cancer cells. BioFactors (oxford, England). https://doi.org/10.1002/biof.1940
Ramesha BT, Suma HK, Senthilkumar U, Priti V, Ravikanth G, Vasudeva R, Kumar TRS, Ganeshaiah KN, Shaanker RU (2013) New plant sources of the anti-cancer alkaloid, camptothecine from the Icacinaceae taxa, India. Phytomedicine 20(6):521–527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2012.12.003
Rauf A, Abu-Izneid T, Khalil AA, Imran M, Shah ZA, Emran TB, Mitra S, Khan Z, Alhumaydhi FA, Aljohani ASM, Khan I, Rahman MdM, Jeandet P, Gondal TA (2021) Berberine as a potential anticancer agent: a comprehensive review. Molecules 26(23):7368. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26237368
Rehman S, Shawl AS, Kour A, Andrabi R, Sudan P, Sultan P, Verma V, Qazi GN (2008) An endophytic Neurospora sp. from Nothapodytes foetida producing camptothecin. Appl Biochem Microbiol 44(2):203–209. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0003683808020130
Reita D, Bour C, Benbrika R, Groh A, Pencreach E, Guérin E, Guenot D (2019) Synergistic anti-tumor effect of mTOR inhibitors with irinotecan on colon cancer cells. Cancers 11(10):1581. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11101581
Romanov V, Davidoff SN, Miles AR, Grainger DW, Gale BK, Brooks BD (2014) A critical comparison of protein microarray fabrication technologies. Analyst 139(6):1303–1326. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3AN01577G
Rubtsova SN, Kondratov RV, Kopnin PB, Chumakov PM, Kopnin BP, Vasiliev JM (1998) Disruption of actin microfilaments by cytochalasin D leads to activation of p53. FEBS Lett 430(3):353–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0014-5793(98)00692-9
Ryavalad C, Melappa G (2014) First report of anticancer agent, lapachol producing endophyte, Aspergillus niger of Tabebuia argentea and its in vitro cytotoxicity assays. Bangladesh J Pharmacol 9:129–139. https://doi.org/10.3329/bjp.v9i1.15622
Saeed S, Ali H, Khan T, Kayani W, Khan MA (2017) Impacts of methyl jasmonate and phenyl acetic acid on biomass accumulation and antioxidant potential in adventitious roots of Ajuga bracteosa Wall ex Benth., a high valued endangered medicinal plant. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 23(1):229–237. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-016-0406-7
Salas X, Portugal J (1991) Map of chartreusin and elsamicin binding sites on DNA. FEBS Lett 292(1):223–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-5793(91)80872-Z
Sana T, Siddiqui BS, Shahzad S, Farooq AD, Siddiqui F, Sattar S, Begum S (2019) Antiproliferative activity and characterization of metabolites of Aspergillus nidulans: an endophytic fungus from Nyctanthes arbor-tristis Linn against three human cancer cell lines. Med Chem (shariqah (united Arab Emirates)) 15(4):352–359. https://doi.org/10.2174/1573406414666180828124252
Sana T, Qayyum S, Jabeen A, Siddiqui BS, Begum S, Siddiqui RA, Hadda TB (2022) Isolation and characterization of anti-inflammatory and anti-proliferative compound, for B-cell Non-Hodgkin lymphoma, from Nyctanthes arbor-tristis Linn. J Ethnopharmacol 293:115267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2022.115267
Santoyo G, Moreno-Hagelsieb G, del Carmen Orozco-Mosqueda M, Glick BR (2016) Plant growth-promoting bacterial endophytes. Microbiol Res 183:92–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2015.11.008
Saraiva NN, Rodrigues BSF, Jimenez PC, Guimarães LA, Torres MCM, Rodrigues-Filho E, Pfenning LH, Abreu LM, Mafezoli J, de Mattos MC, Costa-Lotufo LV, de Oliveira MDCF (2015) Cytotoxic compounds from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. recovered from the sediments of the Brazilian coast. Nat Prod Rep 29(16):1545–1550. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2014.987772
Satish L, Seher Y, Rakkammal K, Muthuramalingam P, Lakshmi CR, Hemasundar A, Prasanth K, Shamili S, Swamy MK, Dhanarajan MS, Ramesh M (2022) 9—Metabolic engineering strategies to enhance the production of anticancer drug, paclitaxel. In: Swamy MK, Pullaiah T, Chen Z-S (eds) Paclitaxel. Academic Press, pp 229–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-90951-8.00003-5
Schiff PB, Horwitz SB (1980) Taxol stabilizes microtubules in mouse fibroblast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77(3):1561–1565. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.77.3.1561
Shan T, Tian J, Wang X, Mou Y, Mao Z, Lai D, Dai J, Peng Y, Zhou L, Wang M (2014) Bioactive spirobisnaphthalenes from the endophytic fungus Berkleasmium sp. J Nat Prod 77(10):2151–2160. https://doi.org/10.1021/np400988a
Sharma M, Ahuja A, Gupta R, Mallubhotla S (2015) Enhanced bacoside production in shoot cultures of Bacopa monnieri under the influence of abiotic elicitors. Nat Prod Rep 29(8):745–749. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2014.986657
Sharma N, Kushwaha M, Arora D, Jain S, Singamaneni V, Sharma S, Shankar R, Bhushan S, Gupta P, Jaglan S (2018) New cytochalasin from Rosellinia sanctae-cruciana, an endophytic fungus of Albizia lebbeck. J Appl Microbiol 125(1):111–120. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.13764
Shastry RP, Welch M, Rai VR, Ghate SD, Sandeep K, Rekha PD (2020) The whole-genome sequence analysis of Enterobacter cloacae strain Ghats 1: insights into endophytic lifestyle-associated genomic adaptations. Arch Microbiol 202(6):1571–1579. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-020-01848-5
Shen S, Tong Y, Luo Y, Huang L, Gao W (2022) Biosynthesis, total synthesis, and pharmacological activities of aryltetralin-type lignan podophyllotoxin and its derivatives. Nat Prod Rep 39(9):1856–1875. https://doi.org/10.1039/D2NP00028H
Shrivastava A, Khan AA, Khurshid M, Kalam MA, Jain SK, Singhal PK (2016) Recent developments in l-asparaginase discovery and its potential as anticancer agent. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 100:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2015.01.002
Shrivastava N, Jiang L, Li P, Sharma AK, Luo X, Wu S, Pandey R, Gao Q, Lou B (2018) Proteomic approach to understand the molecular physiology of symbiotic interaction between Piriformospora indica and Brassica napus. Sci Rep 8(1):5773. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-23994-z
Shweta S, Zuehlke S, Ramesha BT, Priti V, Mohana Kumar P, Ravikanth G, Spiteller M, Vasudeva R, Uma Shaanker R (2010) Endophytic fungal strains of Fusarium solani, from Apodytes dimidiata E. Mey. Ex. Arn (Icacinaceae) produce camptothecin, 10-hydroxycamptothecin and 9-methoxycamptothecin. Phytochemistry 71(1):117–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2009.09.030
Singh S, Awasthi M, Pandey VP, Dwivedi UN (2018) Natural products as anticancerous therapeutic molecules with special reference to enzymatic targets topoisomerase, COX, LOX and aromatase. Curr Protein Pept Sci 19(3):238–274. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389203718666170106102223
Strobel GA, Hess WM (1997) Glucosylation of the peptide leucinostatin A, produced by an endophytic fungus of European yew, may protect the host from leucinostatin toxicity. Chem Biol 4(7):529–536. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1074-5521(97)90325-2
Strobel G, Stierle A, Stierle D, Hess WM (1993) Taxomyces andreanae, a proposed new taxon for a bulbilliferous hyphomycete associated with Pacific yew (Taxus brevifolia). Mycotaxon 47:71–80
Svejstrup JQ, Christiansen K, Gromova II, Andersen AH, Westergaard O (1991) New technique for uncoupling the cleavage and religation reactions of eukaryotic topoisomerase I. The mode of action of camptothecin at a specific recognition site. J Mol Biol 222(3):669–678. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-2836(91)90503-x
Takeda N, Seo S, Ogihara Y, Sankawa U, Iitaka I, Kitagawa I, Shibata S (1973) Studies on fungal metabolites—XXXI: anthraquinonoid colouring matters of Penicillium islandicum sopp and some other fungi (−)luteoskyrin, (−)rubroskyrin, (+)rugulosin and their related compounds. Tetrahedron 29(22):3703–3719. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-4020(01)93536-7
Talukdar R, Wary S, Mili C, Roy S, Tayung K (2020) Antimicrobial secondary metabolites obtained from endophytic fungi inhabiting healthy leaf tissues of Houttuynia cordata Thunb., an ethnomedicinal plant of Northeast India. J Appl Pharm Sci. https://doi.org/10.7324/JAPS.2020.10912
Tao Y, Lin Y, She Z, Lin M, Chen P, Zhang J (2015) Anticancer activity and mechanism investigation of beauvericin isolated from secondary metabolites of the mangrove endophytic fungi. Anti-Cancer Agents Med Chem 15(2):258–266. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871520614666140825112255
Taufiq MMJ, Darah I (2018) Fungal endophytes isolated from the leaves of a medicinal plant, Ocimum sanctum Linn and evaluation of their antimicrobial activities. Afr J Microbiol Res 12(26):616–622. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJMR2018.8812
Tawfike A, Abbott G, Young L, Edrada-Ebel R (2018) Metabolomic-guided isolation of bioactive natural products from Curvularia sp., an endophytic fungus of Terminalia laxiflora. Planta Med 84(03):182–190. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0043-118807
Tawfike AF, Romli M, Clements C, Abbott G, Young L, Schumacher M, Diederich M, Farag M, Edrada-Ebel R (2019) Isolation of anticancer and anti-trypanosome secondary metabolites from the endophytic fungus Aspergillus flocculus via bioactivity guided isolation and MS based metabolomics. J Chromatogr B 1106–1107:71–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2018.12.032
Thakur M, Bhattacharya S, Khosla PK, Puri S (2019) Improving production of plant secondary metabolites through biotic and abiotic elicitation. J Appl Res Med Aromat Plants 12:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jarmap.2018.11.004
Thirumaran R, Prendergast GC, Gilman PB (2007) Cytotoxic chemotherapy in clinical treatment of cancer. In: Prendergast GC, Jaffee EM (eds) Cancer immunotherapy. Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-012372551-6/50071-7
Thomson R (2012) Naturally occurring quinones. Elsevier Science, London
Tong Y, Charusanti P, Zhang L, Weber T, Lee SY (2015) CRISPR-Cas9 based engineering of actinomycetal genomes. ACS Synth Biol 4(9):1020–1029. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.5b00038
Trost BM, Knopf JD, Brindle CS (2016) Synthetic strategies employed for the construction of fostriecin and related natural products. Chem Rev 116(24):15035–15088. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00488
Uzma F, Mohan CD, Hashem A, Konappa NM, Rangappa S, Kamath PV, Singh BP, Mudili V, Gupta VK, Siddaiah CN, Chowdappa S, Alqarawi AA, Abd-Allah EF (2018) Endophytic fungi—alternative sources of cytotoxic compounds: a review. Front Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00309
Van Goietsenoven G, Mathieu V, Andolfi A, Cimmino A, Lefranc F, Kiss R, Evidente A (2011) In vitro growth inhibitory effects of cytochalasins and derivatives in cancer cells. Planta Med 77(7):711–717. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0030-1250523
Vantangoli MM, Madnick SJ, Huse SM, Weston P, Boekelheide K (2015) MCF-7 human breast cancer cells form differentiated microtissues in scaffold-free hydrogels. PLoS ONE 10(8):e0135426. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0135426
Vasundhara M, Kumar A, Reddy MS (2016) Molecular approaches to screen bioactive compounds from endophytic fungi. Front Microbiol 7:1774. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01774
Wang Z, Gerstein M, Snyder M (2009) RNA-Seq: a revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat Rev Genet 10(1):57–63. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2484
Wang Q-X, Li S-F, Zhao F, Dai H-Q, Bao L, Ding R, Gao H, Zhang L-X, Wen H-A, Liu H-W (2011) Chemical constituents from endophytic fungus Fusarium oxysporum. Fitoterapia 82(5):777–781. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2011.04.002
Wang X, Zhang X, Liu L, Xiang M, Wang W, Sun X, Che Y, Guo L, Liu G, Guo L, Wang C, Yin W-B, Stadler M, Zhang X, Liu X (2015) Genomic and transcriptomic analysis of the endophytic fungus Pestalotiopsis fici reveals its lifestyle and high potential for synthesis of natural products. BMC Genom 16(1):28. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-014-1190-9
Wang J, Márquez-Cadena MA, Tong R (2020) Asymmetric total syntheses of (+)-penostatins A and C. Org Lett. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.0c01649
Weber HA, Gloer JB (1991) The preussomerins: novel antifungal metabolites from the coprophilous fungus preussia isomera cain. J Org Chem 56(14):4355–4360. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo00014a007
Weber T, Rausch C, Lopez P, Hoof I, Gaykova V, Huson DH, Wohlleben W (2009) CLUSEAN: a computer-based framework for the automated analysis of bacterial secondary metabolite biosynthetic gene clusters. J Biotechnol 140(1):13–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2009.01.007
Wei H, Xu Y, Espinosa-Artiles P, Liu MX, Luo J-G, U’Ren JM, Elizabeth Arnold A, Leslie Gunatilaka AA (2015) Sesquiterpenes and other constituents of Xylaria sp. NC1214, a fungal endophyte of the moss Hypnum sp. Phytochem 118:102–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2015.08.010
Wu K, Yang Q, Mu Y, Zhou L, Liu Y, Zhou Q, He B (2012) Berberine inhibits the proliferation of colon cancer cells by inactivating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Int J Oncol 41(1):292–298. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2012.1423
Wu Q, Patocka J, Nepovimova E, Kuca K (2018) A review on the synthesis and bioactivity aspects of beauvericin, a fusarium mycotoxin. Front Pharmacol 9:1338. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.01338
Xia Y, Xiang L, Yao M, Ai Z, Yang W, Guo J, Fan S, Liu N, Yang X (2023) Proteomics, transcriptomics, and phosphoproteomics reveal the mechanism of talaroconvolutin-A suppressing bladder cancer via blocking cell cycle and triggering ferroptosis. Mol Cell Proteom. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcpro.2023.100672
Xu J, Kjer J, Sendker J, Wray V, Guan H, Edrada RA, Lin W, Proksch P (2009) Chromones from the endophytic fungus Pestalotiopsis sp isolated from the Chinese mangrove plant rhizophora mucronata. J Nat Prod 72(4):662–665. https://doi.org/10.1021/np800748u
Yang Y, Zhao H, Barrero RA, Zhang B, Sun G, Wilson IW, Xie F, Walker KD, Parks JW, Bruce R, Guo G, Chen L, Zhang Y, Huang X, Tang Q, Liu H, Bellgard MI, Qiu D, Lai J, Hoffman A (2014) Genome sequencing and analysis of the paclitaxel-producing endophytic fungus Penicillium aurantiogriseum NRRL 62431. BMC Genom 15(1):69. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-15-69
Yang Y, Liu X, Cai J, Chen Y, Li B, Guo Z, Huang G (2019) Genomic characteristics and comparative genomics analysis of the endophytic fungus Sarocladium brachiariae. BMC Genomics 20:782. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-019-6095-1
Yang X, Wu P, Xue J, Li H, Wei X (2020) Cytochalasans from endophytic fungus Diaporthe sp. SC-J0138. Fitoterapia 145:104611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2020.104611
Yao J, Jiao R, Liu C, Zhang Y, Yu W, Lu Y, Tan R (2016) Assessment of the cytotoxic and apoptotic effects of chaetominine in a human leukemia cell line. Biomol Ther 24(2):147–155. https://doi.org/10.4062/biomolther.2015.093
Yedukondalu N, Arora P, Wadhwa B, Malik FA, Vishwakarma RA, Gupta VK, Riyaz-Ul-Hassan S, Ali A (2017) Diapolic acid A-B from an endophytic fungus, Diaporthe terebinthifolii depicting antimicrobial and cytotoxic activity. J Antibiot 70(2):Article 2. https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2016.109
Yin X, Han L, Zheng W, Cai L, Qin M, He Z, Kang J (2022) Global regulatory factor AaLaeA upregulates the production of antitumor substances in endophytic Alternaria alstroemeria, PREPRINT (Version 1) available at Research Square. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-1721421/v1
Zazali KE, Abdullah H, Noor Jamil NI (2013) Methanol extract of Oroxylum indicum leaves induces G1/S cell cycle arrest in HeLa cells via p53-mediated pathway. Int J Med Plant Res 2(7):225–237
Zhan J, Burns AM, Liu MX, Faeth SH, Gunatilaka AAL (2007) Search for cell motility and angiogenesis inhibitors with potential anticancer activity: beauvericin and other constituents of two endophytic strains of Fusarium oxysporum. J Nat Prod 70(2):227–232. https://doi.org/10.1021/np060394t
Zhang L, Bo G, Haiyan L et al (2000) Preliminary study on the isolation of endophytic fungus of Catharanthus roseus and its fermentation to produce products of therapeutic value. Zhong Cao Yao Chin Tradit Herb Drugs 31(11):805–807
Zhang J, Tao L-Y, Liang Y-j, Yan Y-Y, Dai C-L, Xia X-K, She Z-G, Lin Y-C, Li-wu Fu (2009) Secalonic acid D induced leukemia cell apoptosis and cell cycle arrest of G1 with involvement of GSK-3β/β-catenin/c-Myc pathway. Cell Cycle 8(15):2444–2450. https://doi.org/10.4161/cc.8.15.9170
Zhang H-C, Ma Y-M, Liu R, Zhou F (2012) Endophytic fungus Aspergillus tamarii from Ficus carica L., a new source of indolyl diketopiperazines. Biochem Syst Ecol 45:31–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bse.2012.07.020
Zhang F-H, Xiang J-H, Cui W-X, Yu J, Wang Y, Li Q-F (2016) Isolation and identification of berberine from endophytic fungi HL-Y-3. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi = Zhongguo Zhongyao Zazhi = China J Chin Mater Med 41(16):2998–3001. https://doi.org/10.4268/cjcmm20161609
Zhang M, Fu W, Zhu L-Z, Liu X-F, Li L, Peng L-Z, Kai G-Y, Liu Y-Q, Zhang Z-J, Xu C-R (2022) Anti-tumor effects and mechanism of a novel camptothecin derivative YCJ100. Life Sci 311:121105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2022.121105
Zhao J-L, Zhou L-G, Wu J-Y (2010) Effects of biotic and abiotic elicitors on cell growth and tanshinone accumulation in Salvia miltiorrhiza cell cultures. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87(1):137–144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2443-4
Zhao J, Li C, Wang W, Zhao C, Luo M, Mu F, Fu Y, Zu Y, Yao M (2013) Hypocrea lixii, novel endophytic fungi producing anticancer agent cajanol, isolated from pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan [L.] Millsp.). J Appl Microbiol 115(1):102–113. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.12195
Zhao H, Chen X, Chen X, Zhu Y, Kong Y, Zhang S, Deng X, Ouyang P, Zhang W, Hou S, Wang X, Xie T (2020) New peptidendrocins and anticancer chartreusin from an endophytic bacterium of Dendrobium officinale. Ann Transl Med 8(7):Article 7. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm.2020.03.227
Zheng W, Seletsky BM, Palme MH, Lydon PJ, Singer LA, Chase CE, Lemelin CA, Shen Y, Davis H, Tremblay L, Towle MJ, Salvato KA, Wels BF, Aalfs KK, Kishi Y, Littlefield BA, Yu MJ (2004) Macrocyclic ketone analogues of halichondrin B. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 14(22):5551–5554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2004.08.069
Zhu L, Chen L (2019) Progress in research on paclitaxel and tumor immunotherapy. Cell Mol Biol Lett 24(1):40. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11658-019-0164-y
Ziemert N, Alanjary M, Weber T (2016) The evolution of genome mining in microbes—a review. Nat Prod Rep 33(8):988–1005. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6np00025h
Zompra AA, Galanis AS, Werbitzky O, Albericio F (2009) Manufacturing peptides as active pharmaceutical ingredients. Future Med Chem 1(2):361–377. https://doi.org/10.4155/fmc.09.23
Zurlo D, Assante G, Moricca S, Colantuoni V, Lupo A (2014) Cladosporol A, a new peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) ligand, inhibits colorectal cancer cells proliferation through β-catenin/TCF pathway inactivation. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj 1840(7):2361–2372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2014.04.007
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the Dept. of Life Sciences, Dibrugarh University for providing the infrastructure facilities. We are also thankful to all the research scholars of the Microbiology Laboratory for their constant help and support.
Funding
No funding was received to assist with the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have equally contributed to the preparation of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical statement
No special permit was required for this work.
Additional information
Communicated by Yusuf Akhter.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sonowal, S., Gogoi, U., Buragohain, K. et al. Endophytic fungi as a potential source of anti-cancer drug. Arch Microbiol 206, 122 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-024-03829-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-024-03829-4