Abstract
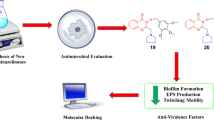
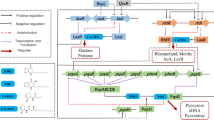
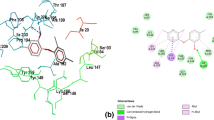
Inhibition of quorum sensing is considered to be an effective strategy of control and treatment of a wide range of acute and persistent infections. Pseudomonas aeruginosa is an opportunistic bacterium with a high adaptation potential that contributes to healthcare-associated infections. In the present study, the effects of the synthesized hybrid structures bearing sterically hindered phenolic and heterocyclic moieties in a single scaffold on the production of virulence factors by P. aeruginosa were determined. It has been shown that the obtained compounds significantly reduce both pyocyanin and alginate production and stimulate the biosynthesis of siderophores in vitro, which may be attributed to their iron-chelating properties. The results of docking-based inverse high-throughput virtual screening indicate that transcription regulator LasR and Cu-transporter OPRC could be potential molecular targets for these compounds. Investigation of the impact small molecules exert on the molecular mechanisms of the production of bacterial virulence factors may pave the way for the design and development of novel antibacterial agents.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data supporting the findings of this study are available within the paper and its Supplementary Information.
References
Allan JR, Paton AD, Pendlowski MJ (1985) The preparation, characterisation and thermal analysis studies on complexes of cobalt (II), nickel (II), and copper (II) with 3-picolylamine. J Therm Anal 30:579–586
Aminov RI (2009) The role of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance in nature. Environ Microbiol 11:2970–2988
Aziz NH, Farag SE, Mousa LA, Abo-Zaid MA (1998) Comparative antibacterial and antifungal effects of some phenolic compounds. Microbios 93:43–54
Balasundram N, Sundram K, Samman S (2006) Phenolic compounds in plants and agri-industrial by-products: antioxidant activity, occurrence, and potential uses. Food Chem 99:191–203
Barreteau H, Bouhss A, Fourgeaud M, Mainardi J, Touzé T, Gérard F, Blanot D, Arthur M, Mengin-Lecreulx DJ (2009) Human-and plant-pathogenic Pseudomonas species produce bacteriocins exhibiting colicin M-like hydrolase activity towards peptidoglycan precursors. J Bacteriol 191:3657–3664
Daina A, Michielin O, Zoete V (2017) SwissADME: a free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep42717
Das T, Kutty SK, Tavallaie R, Ibugo AI, Panchompoo J, Sehar S, Aldous L, Yeung AWS, Thomas SR, Kumar N, Gooding JJ, Manefield M (2015) Phenazine virulence factor binding to extracellular DNA is important for Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation. Sci Rep 5:8398
Dharshini RS, Manickam R, Curtis WR, Rathinasabapathi P, Ramya M (2021) Genome analysis of alginate synthesizing Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain SW1 isolated from degraded seaweeds. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 114:2205–2217
Dumas Z, Ross-Gillespie A, Kummerli R (2013) Switching between apparently redundant iron-uptake mechanisms benefits bacteria in changeable environments. Proc R Soc B. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2013.1055
Durrant JD, McCammon JA (2011) BINANA: a novel algorithm for ligand-binding characterization. J Mol Graph Model. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmgm.2011.01.004
Franklin MJ, Nivens DE, Weadge JT, Howell PL (2011) Biosynthesis of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa extracellular polysaccharides, alginate, Pel, and Psl. Front Microbiol 2:167
Gao L, Kim KJ, Yankaskas JR, Forman HJ (1999) Abnormal glutathione transport in cystic fibrosis airway epithelia. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol 277:L113–L118
Gao P, Guo K, Pu Q, Wang Z, Lin P, Qin S, Khan N, Hur J, Liang H, Wu M (2020) oprC impairs host defense by increasing the quorum-sensing-mediated virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front Immunol 11:1696
Ghannay S, Kadri A, Aouadi K (2020) Synthesis, in vitro antimicrobial assessment, and computational investigation of pharmacokinetic and bioactivity properties of novel trifluoromethylated compounds using in silico ADME and toxicity prediction tools. Monatsh Chem. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00706-020-02550-4
Ghssein G, Ezzeddine Z (2002) A review of Pseudomonas aeruginosa metallophores: pyoverdine, pyochelin and pseudopaline. Biology 11:1711
Hanwell MD, Curtis DE, Lonie DC, Vandermeersch T, Zurek E, Hutchison GR (2012) Avogadro: an advanced semantic chemical editor, visualization, and analysis platform. J Cheminform. https://doi.org/10.1186/1758-2946-4-17
Heidari A, Noshiranzadeh N, Haghi F, Bikas R (2017) Inhibition of quorum sensing related virulence factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by pyridoxal lactohydrazone. Microb Pathog 112:103–110
Hentzer M, Teitzel GM, Balzer GJ, Heydorn A, Molin S, Givskov M, Parsek MR (2001) Alginate overproduction affects Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm structure and function. J Bacteriol 183:5395–5401
Hoegy F, Mislin GLA, Schalk IJ (2014) Pyoverdine and pyochelin measurements. Pseudomonas Methods Protoc. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-0473-0_24
Hoffmann N, Lee B, Hentzer M, Rasmussen TB, Song Z, Johansen HK, Givskov M, Høiby N (2007) Azithromycin blocks quorum sensing and alginate polymer formation and increases the sensitivity to serum and stationary-growth-phase killing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and attenuates chronic P. aeruginosa lung infection in Cftr(−/−) mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.01011-06
Jagani S, Chelikani R, Kim DS (2009) Effects of phenol and natural phenolic compounds on biofilm formation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biofouling 25:321–324
Jia CY, Li JY, Hao GF, Yang GF (2020) A drug-likeness toolbox facilitates ADMET study in drug discovery. Drug Discov Today 25:248–258
Kerr KG, Snelling AM (2009) Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a formidable and ever-present adversary. J Hosp Infect. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhin.2009.04.020
Kidambi SP, Sundin GW, Palmer DA, Chakrabarty AM, Bender CL (1995) Copper as a signal for alginate synthesis in Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:2172–2179
Kim SK, Ngo HX, Dennis EK, Thamban Chandrika N, DeShong P, Garneau-Tsodikova S, Lee VT (2021) Inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa alginate synthesis by ebselen oxide and its analogues. ACS Infect Dis. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsinfecdis.1c00045
Lagorce D, Douguet D, Miteva M, Villoutreix BO (2017) Computational analysis of calculated physicochemical and ADMET properties of protein-protein interaction inhibitors. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep46277
Lau GW, Hassett DJ, Ran H, Kong F (2004) The role of pyocyanin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. Trends Mol Med. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2004.10.002
Ledgham F, Ventre I, Soscia C, Foglino M, Sturgis JN, Lazdunski A (2003) Interactions of the quorum sensing regulator QscR: interaction with itself and the other regulators of Pseudomonas aeruginosa LasR and RhlR. Mol Microbiol 48:199–210
Li Q, Mao S, Wang H, Ye X (2022) The molecular architecture of Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing inhibitors. Mar Drugs. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20080488
Loginova N, Gvozdev M, Osipovich N, Khodosovskaya A, Koval’chuk-Rabchinskaya T, Ksendzova G, Kotsikau D, Evtushenkov A (2022) Silver(I) complexes with phenolic Schiff bases: synthesis, antibacterial evaluation and interaction with biomolecules. ADMET DMPK. https://doi.org/10.5599/admet.1167
Lyczak JB, Cannon CL, Pier GB (2000) Establishment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection: lessons from a versatile opportunist. Microbes Infect 2:1051–1060
Miller LC, O’Loughlin CT, Zhang Z, Siryaporn A, Silpe JE, Bassler BL, Semmelhack MF (2015) Development of potent inhibitors of pyocyanin production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Med Chem 58:1298–1306
Min KB, Hwang W, Lee KM, Kim JB, Yoon SS (2021) Chemical inhibitors of the conserved bacterial transcriptional regulator DksA1 suppressed quorum sensing-mediated virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Biol Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100576
Mishra R, Kushveer J, Khan MIK, Pagal S, Meena CK, Murali A, Dhayalan A, Sarma V (2020) 2,4-Di-tert-butylphenol isolated from an endophytic fungus, Daldinia eschscholtzii, reduces virulence and quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front Microbiol 11:1668
Müh U, Schuster M, Heim R, Singh A, Olson ER, Greenberg EP (2006) Novel Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing inhibitors identified in an ultra-high-throughput screen. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 50:3674–3679
Panda SS, Kumari S, Dixit M, Sharma NK (2023) N-salicyl-AA n-picolamide foldameric peptides exhibit quorum sensing inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PA14). ACS Omega 8:30349–30358
Qais FA, Khan MS, Ahmad I, Husain FM, Khan RA, Hassan I, Shahzad SA, AlHarbi W (2021) Coumarin exhibits broad-spectrum antibiofilm and antiquorum sensing activity against Gram-negative bacteria: in vitro and in silico investigation. ACS Omega 6:18823–18835
Sanner MF (1999) Python: a programming language for software integration and development. J Mol Graph Mod 17:57–61
Santos JS, Alvarenga Brizola VR, Granato D (2017) High-throughput assay comparison and standardization for metal chelating capacity screening: a proposal and application. Food Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.07.09
Simanek KA, Taylor IR, Richael EK, Lasek-Nesselquist E, Bassler BL, Paczkowski JE (2022) The PqsE-RhlR interaction regulates RhlR DNA binding to control virulence factor production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiol Spectr 10:e02108-e2121
Singh A, Mishra AK, Singh SS, Sarma HK, Shukla E (2008) Influence of iron and chelator on siderophore production in Frankia strains nodulating Hippophae salicifolia D. Don J Basic Microbiol 48:104–111
Trott O, Olson AJ (2010) AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J Comp Chem. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.21334
Williams P, Cámara M (2009) Quorum sensing and environmental adaptation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a tale of regulatory networks and multifunctional signal molecules. Curr Opin Microbiol 12:182–191
Wood LG (2003) Improved antioxidant and fatty acid status of patients with cystic fibrosis after antioxidant supplementation is linked to improved lung function. Am J Clin Nutr 77:150–159
Xiong G, Wu Z, Yi J, Fu L, Yang Z, Hsieh C, Yin M, Zeng X, Wu C, Lu A, Chen X, Hou T, Cao D (2021) ADMETlab 2.0: an integrated online platform for accurate and comprehensive predictions of ADMET properties. Nucleic Acids Res. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab255
Yakovets P, Staravoitava V, Faletrov Y, Shkumatov V (2022) High-throughput virtual screening of compounds with electrophilic fragments for new potential covalent inhibitors of bacterial proteins. Chem Proc. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-26-13574
Zeng YF, Su YL, Liu WL, Chen HG, Zeng SG, Zhou HB, Chen W, Zheng J, Sun PH (2022) Design and synthesis of caffeic acid derivatives and evaluation of their inhibitory activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Med Chem Res 31:177–194
Zhou E, Seminara AB, Kim S-K, Hall CL, Wang Y, Lee VT (2017) Thiol-benzo-triazolo-quinazolinone Inhibits Alg44 Binding to c-di-GMP and reduces alginate production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. ACS Chem Biol. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.7b00826
Acknowledgements
The work was carried out within the framework of the task 2.2.01.05 SRP «Chemical processes, reagents and technologies, bioregulators and bioorgchemistry» and BRFFR grant X21-131 (governmental registration number 20213306).
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MY and IS wrote the main manuscript text and MY and YV prepared graphics, MY and IS completed the conceptualization of the manuscript, N.V. supervised the work and performed the validation and formal analysis of the manuscript. Y.V. provided necessary resources for molecular docking studies. Bacterial cultures for biological assays were supplied by V.V. and A.V. Project administration was carried out by N.V. and V.M. All authors reviewed the manuscript and agreed to its published version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Communicated by Yusuf Akhter.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gvozdev, M.Y., Turomsha, I.S., Savich, V.V. et al. Sterically hindered phenolic derivatives: effect on the production of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence factors, high-throughput virtual screening and ADME properties prediction. Arch Microbiol 206, 91 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03827-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03827-y