Abstract
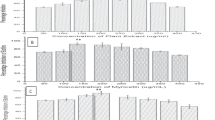
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is an opportunistic bacterium that can form a biofilm with the ability to colonize different surfaces and for increasing resistance to antibiotics. An alternative to solve this problem may be the use of non-glucose/mannose glycosylated proteins from Melipona beecheii honey, which are capable of inhibiting the growth of this pathogen. In this work, the antibiofilm activity of the conA-unbound protein fraction (F1) from M. beecheii was evaluated. The crude protein extract (CPE) and the F1 fraction inhibited the P. aeruginosa biofilm growth above 80% at 4 and 1.3 µg/mL, respectively. These proteins affected the structure of the biofilm, as well as fleQ and fleR gene expressions involved in the formation and regulation of the P. aeruginosa biofilm. The results demonstrated that the F1 fraction proteins of M. beecheii honey inhibit and affect the formation of the P. aeruginosa biofilm.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data is available within the article and supplementary figures.
References
Al-Kafaween MA, Abu Bakar MH, Al-Jamal HAN, Khairi Z, Jaffar N (2020a) Antibacterial and Antibiofilm activities of Malaysian trigona honey against Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 10145 and Streptococcus pyogenes ATCC 19615. Jordan J Biol Sci 13:69–76
Al-Kafaween MA, Alwahsh M, Mohd Hilmi AB, Abulebdah DH (2023) Physicochemical characteristics and bioactive compounds of different types of honey and their biological and therapeutic properties: a comprehensive review. Antibiotics 12:337. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12020337
Al-Kafaween MA, Hilmi ABM, Al-Jamal HAN, Elsahoryi NA, Jaffar N, Zahri MK (2020b) Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Streptococcus pyogenes exposed to Malaysian Trigona honey in vitro demonstrated downregulation of virulence factor. Iran J Biotechnol 18:115–123. https://doi.org/10.30498/IJB.2020.2542
Baraquet C, Harwood CS (2016) FleQ DNA binding consensus sequence revealed by studies of FleQ-dependent regulation of biofilm gene expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 198:178–186. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.00539-15
Blanco-Romero E, Redondo-Nieto M, Martínez-Granero F, Garrido-Sanz D, Ramos-González MI, Martín M, Rivilla R (2018) Genome-wide analysis of the FleQ direct regulon in Pseudomonas fluorescens F113 and Pseudomonas putida KT2440. Sci Rep 8: 13145. 10.1038%2Fs41598-018-31371-z
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1976.9999
Chang CY (2017) Surface sensing for biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front Microbiol 8:2671. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.02671
Fooladi AAI, Aghelimansour A, Nourani MR (2013) Evaluation of the pathogenesis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa’s flagellum before and after flagellar gene knockdown by small interfering RNAs (siRNA). Jundishapur J Microbiol 6:273–278. https://doi.org/10.5812/jjm.5401
Gharieb R, Saad M, Khedr M, El Gohary A, Ibrahim H (2022) Occurrence, virulence, carbapenem resistance, susceptibility to disinfectants and public health hazard of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from animals, humans and environment in intensive farms. J Appl Microbiol 132:256–267. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.15191
Hau-Yama NE, Magaña-Ortiz D, Oliva AI, Ortiz-Vázquez E (2020) Antifungal activity of honey from stingless bee Melipona beecheii against Candida albicans. J Apic Res 59:12–18. https://doi.org/10.1080/00218839.2019.1665247
Jain R, Kazmierczak BI (2014) A conservative amino acid mutation in the master regulator FleQ renders Pseudomonas aeruginosa aflagellate. PLoS ONE 9:e97439. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0097439
Liao C, Huang X, Wang Q, Yao D, Lu W (2022) Virulence Factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and antivirulence strategies to combat its drug resistance. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 12:926758. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2022.926758
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Majtan J, Bohova J, Horniackova M, Klaudiny J, Majtan V (2014) Anti-biofilm effects of honey against wound pathogens Proteus mirabilis and Enterobacter cloacae. Phytother Res 28:69–75. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.4957
Matsuyama BY, Krasteva PV, Baraquet C, Harwood CS, Sondermann H, Navarro MVAS (2016) Mechanistic insights into c-di-GMP-dependent control of the biofilm regulator FleQ from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:E209–E218. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1523148113
Montero MM, Montesinos IL, Knobel H, Molas E, Sorlí L, Siverio-Parés A, Prim N, Segura C, Duran-Jordà X, Grau S, Horcajada JP (2020) Risk factors for mortality among patients with Pseudomonas aeruginosa bloodstream infections: what is the influence of XDR phenotype on outcomes? J Clin Med 9:514. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9020514
Morroni G, Alvarez-Suarez JM, Brenciani A, Simoni S, Fioriti S, Pugnaloni A, Giampieri F, Mazzoni L, Gasparrini M, Marini E, Mingoia M, Battino M, Giovanetti E (2018) Comparison of the antimicrobial activities of four honeys from three countries (New Zealand, Cuba, and Kenya). Front Microbiol 9:1378. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01378
Nursofiah S, Hartoyo Y, Amalia N, Febrianti T, Febriyana D, Saraswati R, Multihartina P (2021) Long-term storage of bacterial isolates by using tryptic soy broth with 15% glycerol in the deep freezer (-70 to-80° c). IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci 913:012070. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/913/1/012070
Park H, Hong M, Hwang S, Park Y, Kwon K, Yoon J, Shin S, Kim J, Park Y (2013) Characterisation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa related to bovine mastitis. Acta Vet Hung 62:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1556/avet.2013.054
Pirnay JP, De Vos D, Cochez C, Bilocq F, Vanderkelen A, Zizi M, Ghysels B, Cornelis P (2002) Pseudomonas aeruginosa displays an epidemic population structure. Environ Microbiol 4:898–911. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1462-2920.2002.00321.x
Pirnay JP, Bilocq F, Pot B, Cornelis P, Zizi M, Van Eldere J, Deschaght P, Vaneechoutte M, Jennes S, Pitt T, De Vos D (2009) Pseudomonas aeruginosa population structure revisited. PLoS ONE 4:e7740. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0007740
Qin S, Xiao W, Zhou C, Pu Q, Deng X, Lan L, Liang H, Song X, Wu M (2022) Pseudomonas aeruginosa: pathogenesis, virulence factors, antibiotic resistance, interaction with host, technology advances and emerging therapeutics. Signal Transduct Target Ther 7:199. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-022-01056-1
Ramón-Sierra JM, Martínez-Guevara JL, Pool-Yam L, Magaña-Ortiz D, Yam-Puc A, Ortiz-Vázquez E (2020) Effects of phenolic and protein extracts from Melipona beecheii honey on pathogenic strains of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Food Sci Biotechnol 29:1013–1021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-020-00744-4
Ramón-Sierra JM, Villanueva MA, Rodríguez-Mendiola M, Reséndez-Pérez D, Ortiz-Vázquez E, Arias-Castro C (2021) Characterization of a non-glycosylated fraction from honey proteins of Melipona beecheii with antimicrobial activity against Escherichia coli O157:H7. J Appl Microbiol 130:1913–1924. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.14921
Ramón-Sierra JM, Villanueva MA, Yam-Puc A, Rodríguez-Mendiola M, Arias-Castro C, Ortiz-Vázquez E (2022) Antimicrobial and antioxidant activity of proteins isolated from Melipona beecheii honey. Food Chem: X 13:100177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fochx.2021.100177
Rasamiravaka T, Labtani Q, Duez P, El Jaziri M (2015) The formation of biofilms by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a review of the natural and synthetic compounds interfering with control mechanisms. BioMed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/759348
Reverdy A, Chen Y, Hunter E, Gozzi K, Chai Y (2018) Protein lysine acetylation plays a regulatory role in Bacillus subtilis multicellularity. PLoS ONE 13:e0204687. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0204687
Sauer K, Camper AK, Ehrlich GD, Costerton JW, Davies DG (2002) Pseudomonas aeruginosa displays multiple phenotypes during development as a biofilm. J Bacteriol 184:1140–1154. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.184.4.1140-1154.2002
Schauer B, Wald R, Urbantke V, Loncaric I, Baumgartner M (2021) Tracing mastitis pathogens-epidemiological investigations of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa mastitis outbreak in an Austrian Dairy Herd. Animals (basel) 11(2):279. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11020279
Schneider CA, Rasband WS, Eliceiri KW (2012) NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods 9:671–675. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2089
Seder N, Abu Bakar MH, Abu Rayyan WS (2021) Transcriptome analysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm following the exposure to Malaysian stingless bee honey. Adv Appl Bioinform Chem 2021:1–11. https://doi.org/10.2147/aabc.s292143
Sio CF, Otten LG, Cool RH, Diggle SP, Braun PG, Bos R, Daykin M, Cámara M, Williams P, Quax WJ (2006) Quorum quenching by an N-acyl-homoserine lactone acylase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Infect Immun 74: 1673–1682. 10.1128%2FIAI.74.3.1673-1682.2006
Taee SR, Khansari Nezhad B, Abtahi H, Najafimosleh M, Ghaznavi-Rad E (2014) Detection of algD, oprL and exoA genes by new specific primers as an efficient, rapid and accurate procedure for direct diagnosis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains in clinical samples. Jundishapur J Microbiol 7:e13583. https://doi.org/10.5812/jjm.13583
Thi MTT, Wibowo D, Rehm BHA (2020) Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Int J Mol Sci 21:8671. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21228671
Tuon FF, Dantas LR, Suss PH, Tasca Ribeiro VS (2022) Pathogenesis of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm: a review. Pathogens 11:300. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11030300
Valentin JD, Straub H, Pietsch F, Lemare M, Ahrens CH, Schreiber F, Ren Q (2022) Role of the flagellar hook in the structural development and antibiotic tolerance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. ISME J 16:1176–1186. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-021-01157-9
Wang J, Liu Q, Li X, Ma S, Hu H, Wu B, Zhang X, Ren H (2020) In-situ monitoring AHL-mediated quorum-sensing regulation of the initial phase of wastewater biofilm formation. Environ Int 135:105326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.105326
Xiao Y, Nie H, Liu H, Chen W, Huang Q (2016) Expression of the diguanylate cyclase GcbA is regulated by FleQ in response to cyclic di-GMP in Pseudomonas putida KT2440. Environ Microbiol Rep 8:993–1002. https://doi.org/10.1111/1758-2229.12478
Yayan J, Ghebremedhin B, Rasche K (2015) Antibiotic resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in pneumonia at a single University Hospital Center in Germany over a 10-Year Period. PLoS ONE 10:e0139836. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0139836
Yeo, WWY, Sundralingam, U, Maran S (2023). Medicinal Properties of Royal Jelly. In M. I. Khalil, S. H. Gan, & B. H. Goh (Eds.), Honey: composition and health benefits (1st edn). John Wiley & Sons. Hoboken NJ USA, pp. 263–277. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119113324.ch20
Yin R, Cheng J, Wang J, Li P, Lin J (2022) Treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infectious biofilms: challenges and strategies. Front Microbiol 13:955286. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.955286
Yinping G, Shankar SU, Jeong-soon K, Nian W (2010) Requirement of the galU gene for polysaccharide production by and pathogenicity and growth in planta of Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:2234–2242. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.02897-09
Zamora LG, Beukelman CJ, van den Berg AJJ, Aerts PC, Quarles van Ufford HC, Nijland R, Arias ML (2017) An insight into the antibiofilm properties of Costa Rican stingless bee honeys. J Wound Care 26: 168–177. https://doi.org/10.12968/jowc.2017.26.4.168
Zhang Y, Pan X, Liao S, Jiang C, Wang L, Tang Y, Wu G, Dai G, Chen L (2020) Quantitative proteomics reveals the mechanism of silver nanoparticles against multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. J Proteome Res 19:3109–3122. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jproteome.0c00114
Zhou T, Huang J, Feng Q, Liu Z, Lin Q, Xu Z, Zhang LH (2021) A Two-Component System FleS/FleR regulates multiple virulence-related traits in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. BioRxiv 2021:2021–2104. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.04.22.441042
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Alvaro Morales for technical assistance; Paola Campa for manuscript revision and Dr. Victor Rejon for his technical help in the use of the Scanning Electron Microscope.
Funding
This study was supported by Tecnológico Nacional de México (TecNM) throught the Grant 17678. The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LPY contributed to conceptualization, design of methodology and formal analysis of results. JRS contributed on formal analysis, writing and review the paper. AIO and RZB contributed to the statistical analysis of the results. EOV contributed to conceptualization, designed the study, supervised the laboratory, writing and review the paper. All the authors have read the final manuscript and approved the submission.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Yusuf Akhter.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pool-Yam, L., Ramón-Sierra, J., Oliva, A.I. et al. Effect of conA-unbound proteins from Melipona beecheii honey on the formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853 biofilm. Arch Microbiol 206, 54 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03783-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03783-7