Abstract
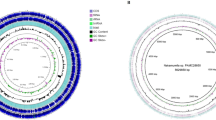
The A. sendaiensis PA2 is a polyextremophile bacterium. In this study, we analyze the A. sendaiensis PA2 genome. The genome was assembled and annotated. The A. sendaiensis PA2 genome structure consists of a 2,956,928 bp long chromosome and 62.77% of G + C content. 3056 CDSs were predicted, and 2921 genes were assigned to a putative function. The ANIm and ANIb value resulted in 97.17% and 96.65%, the DDH value was 75.5%, and the value of TETRA (Z-score) was 0.98. Comparative genomic analyses indicated that three systems are enriched in A. sendaiensis PA2. This strain has phenotypic changes in cell wall during batch culture at 65 °C, pH 5.0 and without carbon and nitrogen source. The presence of unique genes of cell wall and sporulation subsystem could be related to the adaptation of A. sendaiensis PA2 to hostile conditions.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article. Genome sequence of strain PA2 is deposited in the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) database. The whole-genome shotgun project for PA2 have been deposited at DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank under the GenBank accession number JASGCB000000000 BioProject PRJNA962085, BioSample SAMN33326909.
References
Adhikary A, Biswal S, Chatterjee D, Ghosh AS (2022) A NiCoT family metal transporter of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Rv2856/NicT) behaves as a drug efflux pump that facilitates cross-resistance to antibiotics. Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.001260
Albuquerque L, Rainey FA, Chung AP, Sunna A, Nobre R, Grote R, Antranikian G, Costa MS (2000) Alicyclobacillus hesperidum sp .nov and a related genomic species from solfataric soils of Sao Miguel in the Azores. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50(1):451–457. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-50-2-451
Andryukov BG, Karpenko AA, Lyapun IN, Matosova EV, Bynina MP (2019) Bacterial spores: mechanisms of stability and targets for modern biotechnologies. Biomed J Sci Tech Res 20:15329–15343. https://doi.org/10.26717/bjstr.2019.20.003500
Armienta MA, De Cruz-reyna S, Macı JL (2000) Chemical characteristics of the crater lakes of Popocatetetl, El Chichon, and Nevado de Toluca volcanoes, Mexico. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 97:105–125
Arnold JW, Simpson JB, Roach J, Kwintkiewicz J, Azcarate-Peril MA (2018) Intra-species genomic and physiological variability impact stress resistance in strains of probiotic potential. Front Microbiol 9:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.00242
Auch AF, von Jan M, Klenk HP, Göker M (2010) Digital DNA-DNA hybridization for microbial species delineation by means of genome-to-genome sequence comparison. Stand Genom Sci 2(1):117–134. https://doi.org/10.4056/sigs.531120
Aulitto M, Gallo G, Puopolo R, Mormone A, Limauro D, Contursi P, Piochi M, Bartolucci S, Fiorentino G (2021) Genomic insight of Alicyclobacillus mali FL18 isolated from an arsenic-rich hot spring. Front Microbiol 12:1–18. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.639697
Aziz RK, Bartels D, Best A, DeJongh M, Disz T, Edwards RA, Formsma K, Gerdes S, Glass EM, Kubal M, Meyer F, Olsen GJ, Olson R, Osterman AL, Overbeek RA, McNeil LK, Paarmann D, Paczian T, Parrello B, Zagnitko O (2008) The RAST server: rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genom 9:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-9-75
Bankevich A, Nurk S, Antipov D, Gurevich AA, Dvorkin M, Kulikov AS, Lesin VM, Nikolenko SI, Pham S, Prjibelski AD, Pyshkin AV, Sirotkin AV, Vyahhi N, Tesler G, Alekseyev MA, Pevzner PA (2012) SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J Comput Biol 19(5):455–477. https://doi.org/10.1089/cmb.2012.0021
Barák I (2017) Editorial: spores and spore formers. Front Microbiol 8:1–2. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.01046
Beveridge TJ (1990) Mechanism of gram variability in select bacteria. J Bacteriol 172(3):1609–1620. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.172.3.1609-1620.1990
Bevilacqua A, Mischitelli M, Pietropaolo V, Ciuffreda E, Sinigaglia M, Corbo MR (2015) Genotypic and phenotypic heterogeneity in Alicyclobacillus acidoterrestris: a contribution to species characterization. PLoS ONE 10:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0141228
Bischer AP, Kovacs CK, Faustoferri RC, Quivey RG (2020) Disruption of L-rhamnose biosynthesis results in severe growth defects in Streptococcus mutans. Am Soc Microbiol 202:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00728-19
Borroni B, Benussi A (2019) Recent advances in understanding frontotemporal degeneration [version 1; peer review: 2 approved]. F1000Research 8:1–8. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.20330.1
Brüser T, Sanders C (2003) An alternative model of the twin arginine translocation system. Microbiol Res 158:7–17. https://doi.org/10.1078/0944-5013-00176
Casillo A, Lanzetta R, Parrilli M, Corsaro MM (2018) Exopolysaccharides from marine and marine extremophilic bacteria: structures, properties, ecological roles and applications. Mar Drugs 16(2):1–34. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16020069
Chen GQ, Jiang XR (2018) Next generation industrial biotechnology based on extremophilic bacteria. Curr Opin Biotechnol 50:94–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2017.11.016
Ciuffreda E, Bevilacqua A, Sinigaglia M, Corbo M (2015) Alicyclobacillus spp.: new insights on ecology and preserving food quality through new approaches. Microorganisms 3(4):625–640. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms3040625
Dhakar K, Pandey A (2016) Wide pH range tolerance in extremophiles: towards understanding an important phenomenon for future biotechnology. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(6):2499–2510. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7285-2
Dörr T, Moynihan PJ, Mayer C (2019) Editorial: bacterial cell wall structure and dynamics. Front Microbiol 10:4–7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.02051
Drori E, Levy D, Smirin-Yosef P, Rahimi O, Salmon-Divon M (2017) CIRCOS VCF: CIRCOS visualization of whole-genome sequence variations stored in VCF files. Bioinformatics 33(9):1392–1393. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btw834
Egan K, Field D, Ross RP, Cotter PD, Hill C (2018) In silicoprediction and exploration of potential bacteriocin gene clusters within the bacterial genus Geobacillus. Front Microbiol 284:851–867. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.02116
Fisher JF, Mobashery S (2020) Constructing and deconstructing the bacterial cell wall. Protein Sci 29(3):629–646. https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.3737
Gasteiger E, Hoogland C, Gattiker A, Duvaud S, Wilkins MR, Appel RD, Bairoch A (2003) Protein Identification and analysis tools on the ExPASy server. Nucleic Acids Res 31(13):571–607. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkg563
Gauvry E, Mathot AG, Leguérinel I, Couvert O, Postollec F, Broussolle V, Coroller L (2017) Knowledge of the physiology of spore-forming bacteria can explain the origin of spores in the food environment. Res Microbiol 168(4):369–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resmic.2016.10.006
Goto K, Tanimoto Y, Tamura T, Mochida K, Arai D, Asahara M, Suzuki M, Tanaka H, Inagaki K (2002) Identification of thermoacidophilic bacteria and a new Alicyclobacillus genomic species isolated from acidic environments in Japan. Extremophiles 6(4):333–340. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-001-0262-3
Gottesman S (2019) Trouble is coming: signaling pathways that regulate general stress responses in bacteria. J Biol Chem 294(31):11685–11700. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.REV119.005593
Graninger M, Kneidinger B, Bruno K, Scheberl A, Messner P (2002) Homologs of the Rml enzymes from Salmonella enterica are responsible for dTDP-beta-L-rhamnose biosynthesis in the gram-positive thermophile Aneurinibacillus thermoaerophilus DSM 10155. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(8):3708–3715. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.68.8.3708
Grosu-Tudor SS, Brown L, Hebert EM, Brezeanu A, Brinzan A, Fadda S, Mozzi F, Zamfir M (2016) S-layer production by Lactobacillus acidophilus IBB 801 under environmental stress conditions. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(10):4573–4583. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7355-5
Guérin H, Kulakauskas S (2022) Structural variations and roles of rhamnose-rich cell wall polysaccharides in Gram-positive bacteria. J Biol Chem 298(10):102488–102504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102488
Han N, Qiang Y, Zhang W (2016) ANItools web: a web tool for fast genome comparison within multiple bacterial strains. Database 2016:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1093/database/baw084
Hu EZ, Lan XR, Liu ZL, Gao J, Niu DK (2022) A positive correlation between GC content and growth temperature in prokaryotes. BMC Genom 23(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-022-08353-7
Hussey MA (2007) Endospore stain protocol. Am Soc Microbiol 8:1–11
Hyatt D, Chen G, Locascio PF, Land ML, Larimer FW, Hauser LJ (2010) Prodigal: prokaryotic gene recognition and translation initiation site identification. BMC Bioinf 11(119):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-11-119
Isticato R (2023) Bacterial spore-based delivery system: 20 years of a versatile approach for innovative vaccines. Biomolecules 13(6):1–20. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13060947
Jensen LJ, Julien P, Kuhn M, von Mering C, Muller J, Doerks T, Bork P (2008) eggNOG: automated construction and annotation of orthologous groups of genes. Nucleic Acids Res 36:250–254. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkm796
Jiang CY, Guo X, You XY, Liu YY, Liu SJ (2009) Some physiological properties of three novel Fe (II)- And sulfur-oxidizing strains affiliated to Alicyclobacillus. Adv Mater Res 59:247–250. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.71-73.247
Kanehisa M, Sato Y, Morishima K (2016) BlastKOALA and GhostKOALA: KEGG tools for functional characterization of genome and metagenome sequences. J Mol Biol 428(4):726–731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2015.11.006
Karley D, Shukla SK, Rao TS (2023) Sequestration of cobalt and nickel by biofilm forming bacteria isolated from spent nuclear fuel pool water. Environ Monit Assess 195:699. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11266-x
Kaur N, Dey P (2023) Bacterial exopolysaccharides as emerging bioactive macromolecules: from fundamentals to applications. Res Microbiol 174(4):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resmic.2022.104024
Klingl A (2014) S layer and cytoplasmic membrane - exceptions from the typical archaeal cell wall with a focus on double membranes. Front Microbiol 5:1–7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2014.00624
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35(6):1547–1549. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy096
Lee PA, Tullman-ercek D, Georgiou G (2006) The bacterial translocation pathway. Annu Rev Microbiol 60:373–395. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.micro.60.080805.142212
Li S, Chen F, Li Y, Wang L, Li H, Gu G, Li E (2022) Rhamnose-containing compounds: biosynthesis and applications. Molecules 27:1–20. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27165315
Liu Z, Liang Z, Gu Y, Huang Y, Liu X, Yang Z, Drewniak L, Liu T, Liu Y, Liu S, Wang J, Jiang C (2021) Mobile genetic elements mediate the mixotrophic evolution of novel Alicyclobacillus species for acid mine drainage adaptation. Environ Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.15543
Merino N, Aronson HS, Bojanova DP, Feyhl-Buska J, Wong ML, Zhang S, Giovannelli D (2019) Living at the extremes: extremophiles and the limits of life in a planetary context. Front Microbiol 10:1–25. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.00780
Mistou MY, Sutcliffe IC, Van Sorge NM (2016) Bacterial glycobiology: rhamnose-containing cell wall polysaccharides in gram-positive bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 40(4):464–479. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsre/fuw006
Nguema-Ona E, Vicré-Gibouin M, Gotté M, Plancot B, Lerouge P, Bardor M, Driouich A (2014) Cell wall O-glycoproteins and N-glycoproteins: aspects of biosynthesis and function. Front Plant Sci 5:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2014.00499
Ortiz-Cortés LY, Ventura-Canseco LMC, Abud-Archila M, Ruíz-Valdiviezo VM, Velázquez-Ríos IO, Alvarez-Gutiérrez PE (2021) Evaluation of temperature, pH and nutrient conditions in bacterial growth and extracellular hydrolytic activities of two Alicyclobacillus spp. strains. Arch Microbiol 203(7):4557–4570. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-021-02332-4
Palmer T, Stansfeld PJ (2020) Targeting of proteins to the twin-arginine translocation pathway. Mol Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1111/mmi.14461
Panja AS, Maiti S, Bandyopadhyay B (2020) Protein stability governed by its structural plasticity is inferred by physicochemical factors and salt bridges. Sci Rep 10:1822–1830. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-58825-7
Parks DH, Imelfort M, Skennerton CT, Hugenholtz P, Tyson GW (2015) CheckM: assessing the quality of microbial genomes recovered from isolates, single cells, and metagenomes. Genome Res 25(7):1043–1055. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.186072.114
Paul C, Filippidou S, Jamil I, Kooli W, House GL, Estoppey A, Hayoz M, Junier T, Palmieri F, Wunderlin T, Lehmann A, Bindschedler S, Vennemann T, Chain PSG, Junier P (2019) Bacterial spores, from ecology to biotechnology. Advances in applied microbiology, 1st edn. Elsevier Inc, Amsterdam, pp 79–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.aambs.2018.10.002
Richter M, Rosselló-Móra R, Oliver Glöckner F, Peplies J (2016) JSpeciesWS: a web server for prokaryotic species circumscription based on pairwise genome comparison. Bioinformatics 32(6):929–931. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btv681
Rosa Martins PH, Rabinovitch L, de Orem JC, Silva WMC, de Araujo MF, de Magalhães MIA, de Andrade CD, Vivoni AM, de Oliveira EJ, de Lima RA, Izzotti A, Pulliero A, Bast A, Rattan SIS, De-Souza MT (2023) Biochemical, physiological, and molecular characterisation of a large collection of aerobic endospore-forming bacteria isolated from Brazilian soils. Neotropical Biol Conserv 18(1):53–72. https://doi.org/10.3897/neotropical.18.e86548
Rossnerova P (2020) The molecular mechanisms of adaptive response related to environmental stress. Int J Mol Sci 21(19):1–15. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197053
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The Neigbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4(4):406–425. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454
Shi H, Westfall CS, Kao J, Odermatt PD, Anderson SE, Cesar S, Sievert M, Moore J, Gonzalez CG, Zhang L, Elias JE, Chang F, Huang KC, Levin PA (2021) Starvation induces shrinkage of the bacterial cytoplasm. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 24:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2104686118
Sibinelli-Sousa S, Hespanhol JT, Bayer-Santos E (2021) Targeting the achilles’ heel of bacteria: different mechanisms to break down the peptidoglycan cell wall during bacterial warfare. J Bacteriol 203(7):1–45. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00478-20
Siliakus MF, van der Oost J, Kengen SWM (2017) Adaptations of archaeal and bacterial membranes to variations in temperature, pH and pressure. Extremophiles 21(4):651–670. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-017-0939-x
Simbahan J, Drijber R, Blum P (2004) Alicyclobacillus vulcanalis sp. nov., a thermophilic acidophilic bacterium isolated from Coso Hot Springs, California, USA. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54(5):1703–1707. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.03012-0
Simonsen AK (2021) Environmental stress leads to genome streamlining in a widely distributed species of soil bacteria. ISME J 16:423–434. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-021-01082-x
Singh P, Jain K, Desai C, Tiwari O, Madamwar D (2018) Microbial community dynamics of extremophiles/extreme environment. Microbial diversity in the genomic era. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 326–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-814849-5.00018-6
Smit Y, Cameron M, Venter P, Witthuhn RC (2011) Alicyclobacillus spoilage and isolation - a review. Food Microbiol 28(3):331–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2010.11.008
Terano H, Takahashi K, Sakakibara Y (2005) Characterization of spore germination of a thermoacidophilic spore-forming bacterium. Alicyclobacillus Acidoterrestris Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 69(6):1217–1220. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.69.1217
Tsuruoka N, Isono Y, Shida O, Hemmi H, Nakayama T, Nishino T (2003) Alicyclobacillus sendaiensis sp. Nov., a novel acidophilic, slightly thermophilic species isolated from soil in Sendai, Japan. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53(4):1081–1084. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.02409-0
Ultee E, Ramijan K, Dame RT, Briegel A, Claessen D (2019) Stress-induced adaptive morphogenesis in bacteria. Advances in microbial physiology, vol 74. Elsevier Ltd, Amsterdam. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.ambps.2019.02.001
Van der Beek SL, Zorzoli A, Çanak E, Chapman RN, Lucas K, Meyer BH, Evangelopoulos D, de Carvalho LPS, Boons GJ, Dorfmueller HC, van Sorge NM (2019) Streptococcal dTDP-L-rhamnose biosynthesis enzymes: functional characterization and lead compound identification. Mol Microbiol 111(4):951–964. https://doi.org/10.1111/mmi.14197
Vohradsky J, Schwarz M, Ramaniuk O, Ruiz-larrabeiti O, Va V (2021) Kinetic modeling and meta-analysis of the bacillus subtilis SigB regulon during spore germination and outgrowth. Microorganisms 9(112):1–13. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9010112
Waterhouse A, Bertoni M, Bienert S, Studer G, Tauriello G, Gumienny R, Heer FT, De Beer TAP, Rempfer C, Bordoli L, Lepore R, Schwede T (2018) SWISS-MODEL: homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res 46(W1):W296–W303. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky427
Wingett SW, Andrews S, Donaldson IJ (2018) FastQ Screen: a tool for multi-genome mapping and quality control [version 2; peer review: 4 approved]. F1000Research 7:1–14. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.15931.1
Yabe S, Aiba Y, Sakai Y, Hazaka M, Yokota A (2011) Thermogemmatispora onikobensis gen. nov., sp. nov. and Thermogemmatispora foliorum sp. nov., isolated from fallen leaves on geothermal soils, and description of Thermogemmatisporaceae fam. nov. and Thermogemmatisporales nov. within the class Ktedonob. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61(4):903–910. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.024877-0
Zeng X, Zhang X, Shao Z (2020) Metabolic adaptation to sulfur of Hyperthermophilic Palaeococcus pacificus DY20341 T from deep-sea hydrothermal sediments. Int J Mol Sci 21(368):2–18. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21010368
Zhang J, Madden TL (1997) PowerBLAST: a new network BLAST application for interactive or automated sequence analysis and annotation. Genome Res 7(6):649–656. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.7.6.649
Zhu D, Adebisi WA, Ahmad F, Sethupathy S (2020) Recent development of extremophilic bacteria and their application in biorefinery front bioeng. Biotechnol 8:1–18. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2020.00483
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Jorge Roberto Velázquez Milanes for bioinformatics support. David Emmanuel Roblero Toledo for protein modeling.
Funding
This research was funded by Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnologia (National Council of Science and Technology, México) for the scholarship granted 853058. Institute of Science, Technology and Innovation of Chiapas (ICTI-México) and National Technology of Mexico (TecNM).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LYO-C and PEA-G carried out the conceptualization, and investigation of the project, designed and developed methodology, and wrote the original draft. LYO-C, ETA-C, and PEA-G carried out the data curation, critical review, and editing of the manuscript. ETA-C and LYO-C. Carried out the implementation of the computer code and supporting algorithms and formal analysis. PEA-G and LMCV-C carried out the acquisition of financial support. FAG-M and VMR-V carried out the visualization and critical review of the manuscript. PEA-G carried out leadership responsibility for the research activity, planning, and execution, including mentorship of the external to core team. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Yusuf Akhter.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ortiz-Cortés, L.Y., Aréchiga-Carvajal, E.T., Ventura-Canseco, L.M.C. et al. Analysis of phenotypic changes in high temperature and low pH extreme conditions of Alicyclobacillus sendaiensis PA2 related with the cell wall and sporulation genes. Arch Microbiol 206, 53 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03735-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03735-1