Abstract
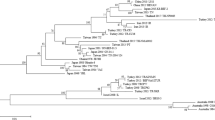
Bovine ephemeral fever virus (BEFV) is an economically important arthropod-borne virus of cattle and water buffaloes which is enzootic in Africa, Australia, and Asia. We characterized the entire length of BEFV BA/RZ/IR strain genome isolated in Iran and compared to the all BEFV full genomes available in the GenBank. The BEFV genomes were phylogenetically classified as 4 lineages including the Middle Eastern, East Asian, Australian, and South African lineages. The Iranian BA/RZ/IR strain, which displayed maximum sequence identity (96.72%) to the Chinese JT02L strain was clustered as a separate branch in the East Asian lineage of the virus. Using Shannon entropy analysis, amino acid variations were detected in the all proteins encoded by BEFV genomes. Particularly, the polymerase L and the accessory proteins Gns, α2 and β exhibited the highest amino acid variations suggesting their significance in the viral replication efficiency. Our bioinformatics analyses also predict the occurrence of recombination event within the East Asian lineage of BEFV genomes. Our data show that the Chinese Henan 1 may be a hybrid strain constructed of the Chinese JT02L and Iranian BA/RZ/IR BEFV strains as the major and minor parents, respectively. These computational analyses suggest that the homologous recombination may be an evolutionary mechanism for BEFV as a member of the Rhabdoviridae family.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated and analyzed for this study are included the published article.
References
Abayli H, Tonbak S, Azkur AK, Bulut H (2017) Complete genome analysis of highly pathogenic bovine ephemeral fever virus isolated in Turkey in 2012. Arch Virol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-017-3470-6
Aguado LC, Jordan TX, Hsieh E, Blanco-Melo D, Panis M, Vignuzzi M, tenOver BR (2018) Homologous recombination is an intrinsic defense against antiviral RNA interference. PNAS. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.181022911
Almasi S, Bakhshesh M (2019) Antigenic variation of bovine ephemeral fever viruses isolated in Iran, 2012–2013. Virus Genes. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-019-01688-6
Aziz-Boaron O, Klausner Z, Hasoksuz M, Shenka RJ, Gafni O, Gelman B, David D, Klement E (2012) Circulation of bovine ephemeral fever in the Middle East: strong evidence for transmission by winds and animal transport. Mirobiol, Vet. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2012.03.003
Bakhshesh M, Abdollahi D (2015) Bovine ephemeral fever in Iran: diagnosis, isolation and molecular characterization. J Arthropod Borne Dis 9:195
Chaisirirat T, Sangthong P, Arunvipas P, Petcharat N, Thangthamniyom N, Chumsing W, Lekcharoensuk P (2018) Molecular characterization of bovine ephemeral fever virus in Thailand between 2013 and 2017. Vet Mirobiol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2018.10.013
Constable P, Hinchcliff KW, Done SH, Grunberg W (2017) Veterinary medicine: a textbook of the diseases of cattle, sheep, pigs, goats and horses, 11th edn. WB Saunders Company LTD., London, England, UK, pp 2081–2084
Cybinski D, Walker P, Byrne K, Zakrzewski H (1990) Mapping of antigenic sites on the bovine ephemeral fever virus glycoprotein using monoclonal antibodies. J Gen Virol. https://doi.org/10.1099/0022-1317-71-9-2065
Dorey-Robinson DLW, Fernández de Marco M, Hernández-Triana LM, et al (2019) Complete Genome Sequence of a Bovine Ephemeral Fever Virus Isolate from Israel. Microbiol Resour Announc 8(41). https://doi.org/10.1128/MRA.00822-19
Gao S, Du J et al (2017) Complete genome sequence of a bovine ephemeral fever virus JT02L strain in mainland China. Arch Virol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-017-3520-0
Han G-Z, Worobey M (2011) Homologous recombination in negative sense RNA viruses. Viruses 3:1358–1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/v3081358
He C-Q, Liu Y-X, Wang H-M, Hou P-L, He H-B, Ding N-Z (2016) New genetic mechanism, origin and population dynamic of bovine ephemeral fever virus. Vet. Mirobiol 182:50–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2015.10.029
Hertig C, Pye AD (1996) Vaccinia virus-expressed bovine ephemeral fever virus G but not GNS glycoprotein induces neutralizing antibodies and protects against experimental infection. J Gen Virol. https://doi.org/10.1099/0022-1317-77-4-631
Jiang H, Hou P, He H, Wang H (2020) Cell apoptosis regulated by interaction between viral gene alpha 3 and host heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K facilitates bovine ephemeral fever virus replication. Vet Mirobiol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2019.108510
Johal J, Gresty K, Kongsuwan K, Walker PJ (2008) Antigenic characterization of bovine ephemeral fever rhabdovirus G and GNS glycoproteins expressed from recombinant baculoviruses. Arch Virol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-008-0164-0
Joubert DA, Blasdell KR et al (2014) Bovine ephemeral fever rhabdovirus α1 protein has viroporin-like properties and binds importin β1 and importin 7. J Virol. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01812-13
Kongsuwan K, Cybinski DH, Cooper J, Walker PJ (1998) Location of neutralizing epitopes on the G protein of bovine ephemeral fever rhabdovirus. J Gen Virol 79:2573–2581
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33(7):1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Kuzmin I, Novella I, Dietzgen R, Padhi A, Rupprecht C (2009) The rhabdoviruses: biodiversity, phylogenetics, and evolution. Infect Genet Evol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meegid.2009.02.005
Lee F (2019) Bovine ephemeral fever in Asia: recent status and research gaps. Viruses. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11050412
Martin DP, Varsani A et al (2021) RDP5: a computer program for analyzing recombination in, and removing signals of recombination from, nucleotide sequence datasets. Virus Evol. https://doi.org/10.1093/ve/veaa087
McWilliam SM, Kongsuwan K, Cowley JA, Byrne KA, Walker PJ (1997) Genome organization and transcription strategy in the complex GNS-L intergenic region of bovine ephemeral fever rhabdovirus. J Gen Virol 78:1309–1317. https://doi.org/10.1099/0022-1317-78-6-1309
Mlingo TA, Nthangeni BM, Mokoena NB (2021) Genome sequence of Bovine Ephemeral fever virus vaccine strain of South African origin. Vet Med Sci 7:1611–1615. https://doi.org/10.1002/vms3.517
Omar R, Van SA, Carulei O, Heath L, Douglass N, Williamson A-L (2020) South African bovine ephemeral fever virus glycoprotein sequences are phylogenetically distinct from those from the rest of the world. Arch Virol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-020-04568-9
Pérez-Losada M, Arenas M, Galán JC, Palero F, González-Candelas F (2015) Recombination in viruses: mechanisms, methods of study, and evolutionary consequences. Infect Genet Evol 30:296–307
Pyasi S, Sahu BP, Sahoo P, Dubey PK, Sahoo N, Byrareddy SN, Nayak D (2020) Identification and phylogenetic characterization of bovine ephemeral fever virus (BEFV) of Middle Eastern lineage associated with 2018–2019 outbreaks in India. Transbound Emerg Dis. https://doi.org/10.1111/tbed.13531
Rezatofighi E, Mirzadeh K, Mahmoodi F (2022) Molecular characterization and phylogenetic analysis of bovine ephemeral fever viruses in Khuzestan province of Iran in 2018 and 2020. BMC Vet Res 18:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12917-021-03119-x
Snowdon W (1970) Bovine ephemeral fever: the reaction of cattle to different strains of ephemeral fever virus and the antigenic comparison of two strains of virus. Aust Vet J 46(6):258–266. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-0813.1970.tb15773.x
Tian FG, Jiang CL, Zakrzweski H, Davis SS (1987) A comparison of a Chinese and an Australian strain of bovine ephemeral fever virus. Aust Vet J 64:159. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-0813.1987.tb09670
Trinidad L, Blasdell KR et al (2014) Evolution of bovine ephemeral fever virus in the Australian episystem. J Virol. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.02797-13
Uren MF, Walker PJ, Zakrzewski H, St George TD, Byrne KA (1994) Effective vaccination of cattle using the virion G protein of bovine ephemeral fever virus as an antigen. Vaccine 12:845–852. https://doi.org/10.1016/0264-410X(94)90295
Walker P (2005) Bovine ephemeral fever in Australia and the world. Curr Top Micro Immunol. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-27485-5_4
Walker PJ, Klement E (2015) Epidemiology and control of bovine ephemeral fever. Vet Res 46:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13567-015-0262-4
Walker PJ, Tesh R (2021) Vesicular stomatitis virus and bovine ephemeral fever virus (Rhabdoviridae). In: Bamford DH, Zuckerman M (eds) Encyclopedia of Virology, 4th edn. Academic Press, pp 875–883
Walker PJ, Byrne KA, Cybinski DH, Doolan DL, Wang Y (1991) Proteins of bovine ephemeral fever virus. J Gen Virol 72:67–74. https://doi.org/10.1099/0022-1317-72-1-67
Walker PJ, Byrne KA, Riding GA, Cowley JA, Wang Y, McWilliam S (1992) The genome of bovine ephemeral fever rhabdovirus contains two related glycoprotein genes. Virology 191:46–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/0042-6822(92)90165-l
Wang YH, Walker PJ (1993) Adelaide River rhabdovirus expresses consecutive glycoprotein genes as polycistronic mRNAs: new evidence of gene duplication as an evolutionary process. Virology 195:719–731. https://doi.org/10.1006/viro.1993.1423
Zheng F, Qiu C (2012) Phylogenetic relationships of the glycoprotein gene of bovine ephemeral fever virus isolated from mainland China, Taiwan, Japan, Turkey, Israel and Australia. Virol J 9:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-422X-9-268
Acknowledgements
The author’s thank to Razi Vaccine and Serum Research Institute for financial support of this study.
Funding
Razi Vaccine and Serum Research Institute provided the financial funds for the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MB designed the study, performed the experiments and wrote the manuscript. SM helped in data analyzing. SA helped in conducting experiments. NA helped in clinical examinations and sampling.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Communicated by Yusuf Akhter.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bakhshesh, M., Mollazadeh, S., Almasi, S. et al. Whole genome characterization and evolutionary analysis of bovine ephemeral fever virus isolated in Iran. Arch Microbiol 205, 196 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03527-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03527-7