Abstract
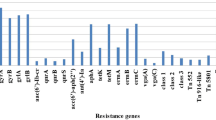
Staphylococcus aureus has been described as the most common cause of human and animal diseases and has emerged as a superbug due to multidrug resistance. Considering these, a total of 175 samples were collected from pyogenic cases of humans (75) and animals (100), to establish the drug resistance pattern and also for molecular characterization of human and animal isolates. Thermonuclease (nuc) gene amplification was used to confirm all presumptive S. aureus isolates and then, antibiotic sensitivity and slide Coagulase tests were used for phenotypic characterization of isolates. Following that, all the isolates were subjected to PCR amplification to detect the existence of the Methicillin-resistant (mecA) and Coagulase (coa) genes. Lastly, typing was done using the Randomly Amplified Polymorphic DNA-PCR. The overall prevalence of S. aureus in human and animal samples was found to be 39.4%. Drug sensitivity revealed the highest resistance against the β-lactam antibiotics such as ampicillin (94.8%) and penicillin (90.6%), followed by cephalosporin (cefixime—67.7%) and quinolone (ciprofloxacin—52.1%) group of drugs. The drug sensitivity was the highest against antibiotics like chloramphenicol (95%) followed by gentamicin (90%). Among the 69 S. aureus isolates, the overall presence of MRSA was 40.5% (27.5% and 50% in human and animal isolates, respectively). Total 33 isolates exhibited coa genes amplification of more than one amplicons and variable in size of 250, 450, 800, and 1100 bp. The RAPD typing revealed amplification of five and six different band patterns in humans and animals, respectively, with two common patterns suggesting a common phylogenetic profile.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdulghany HM, Khairy RM (2014) The frequency of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase gene polymorphism in Egypt. Int J Bacteriol 2014:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/680983
Barbier N, Saulnier P, Chachaty E et al (1996) Random amplified polymorphic DNA typing versus pulsed-field gel electrophoresis for epidemiological typing of vancomycin-resistant enterococci. J Clin Microbiol 34:1096–1099. https://doi.org/10.1128/jcm.34.5.1096-1099.1996
Blumberg HM, Rimland D, Carroll DJ et al (1991) Rapid development of ciprofloxacin resistance in methicillin-susceptible and -resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis 163:1279–1285. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/163.6.1279
Brakstad OG, Aasbakk K, Maeland JA (1992) Detection of Staphylococcus aureus by polymerase chain reaction amplification of the nuc gene. J Clin Microbiol 30:1654–1660. https://doi.org/10.1128/jcm.30.7.1654-1660.1992
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) (2011) Performance standards for antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. An informational supplement for global application developed through the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute
Corrente M, Monno R, Totaro M et al (2005) Characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolated at the Policlinico Hospital of Bari (Italy). New Microbiol 28:57–65
Devriese LA, Hommez J (1975) Epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in dairy herds. Res Vet Sci 19:23–27
Devriese LA, Van Damme LR, Fameree L (1972) Methicillin (Cloxacillin)-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from bovine mastitis cases. Zentralblatt Für Veterinärmedizin R B 19:598–605. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0450.1972.tb00439.x
Fox LK, Gershman M, Hancock DD, Hutton CT (1991) Fomites and reservoirs of Staphylococcus aureus causing intramammary infections as determined by phage typing: the effect of milking time hygiene practices. Cornell Vet 81:183–193
Franklin D, Lowy MD (1998) Staphylococcus aureus infections. N Engl J Med 339:520–532. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199808203390806
Frénay H, Theelen J, Schouls L et al (1994) Discrimination of epidemic and nonepidemic. J Clin Microbiol 32:846–847
Hartman BJ, Tomasz A (1984) Low-affinity penicillin-binding protein associated with β-lactam resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol 158:513–516. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.158.2.513-516.1984
Iliya S, Mwangi J, Maathai R, Muriuki M (2020) Phenotypic analysis and antibiotic susceptibility of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Kiambu County, Kenya. J Infect Dev Ctries 14(6):597–605. https://doi.org/10.3855/jidc.12174
Izadpanah MR, Asadpour L (2018) Investigation of coa gene polymorphism in clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus in North of Iran. J Cell Mol Res 10:27–31. https://doi.org/10.22067/jcmr.v10i1.52730
Jayatilleke K, Bandara P (2012) Antibiotic sensitivity pattern of Staphylococcus aureus in a tertiary care hospital of Sri Lanka. Sri Lankan J Infect Dis 2:13. https://doi.org/10.4038/sljid.v2i2.4162
Kateete DP, Kimani CN, Katabazi FA et al (2010) Identification of Staphylococcus aureus: DNase and Mannitol salt agar improve the efficiency of the tube Coagulase test. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob 9:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-0711-9-23
Kluytmans J, Van Leeuwen W, Goessens W et al (1995) Food-initiated outbreak of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus analyzed by pheno- and genotyping. J Clin Microbiol 33:1121–1128. https://doi.org/10.1128/jcm.33.5.1121-1128.1995
Kumari N, Mohapatra TM, Singh YI (2008) Prevalence of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in a tertiary-care hospital in eastern Nepal. J Nepal Med Assoc 47:53–56. https://doi.org/10.31729/jnma.309
Lee JH (2003) Methicillin (oxacillin)-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from major food animals and their potential transmission to humans. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:6489–6494. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.69.11.6489-6494.2003
Montesinos I, Salido E, Delgado T et al (2002) Epidemiologic genotyping of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis at a University Hospital and comparison with antibiotyping and protein A and Coagulase gene polymorphisms. J Clin Microbiol 40:2119–2125. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.40.6.2119-2125.2002
Palma M, Haggar A, Flock JI (1999) Adherence of Staphylococcus aureus is enhanced by an endogenous secreted protein with broad binding activity. J Bacteriol 181:2840–2845. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.181.9.2840-2845.1999
Predari SC, Ligozzi M, Fontana R (1991) Genotypic identification of methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative staphylococci by polymerase chain reaction. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 35:2568–2573. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.35.12.2568
Quinn PJ, Markey BK, Carter ME et al (2002) Veterinary microbiology and microbial disease. Blackwell Science, Oxford
Reinoso EB, El-Sayed A, Lämmler C et al (2008) Genotyping of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from humans, bovine subclinical mastitis, and food samples in Argentina. Microbiol Res 163:314–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2006.05.013
Roberson JR, Fox LK, Hancock DD et al (1994) Ecology of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from various sites on dairy farms. J Dairy Sci 77:3354–3364. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(94)77277-5
Robinson DA, Enright MC (2004) Evolution of Staphylococcus aureus by large chromosomal replacements. J Bacteriol 186:1060–1064. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.186.4.1060-1064.2004
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2021) Molecular Cloning: a Laboratory Manual 1:2021
Tambic A, Power EGM, Talsania H et al (1997) Analysis of an outbreak of non-phage-typeable methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by using a Randomly Amplified Polymorphic DNA assay. J Clin Microbiol 35:3092–3097. https://doi.org/10.1128/jcm.35.12.3092-3097.1997
Tiwari S, Sahu M, Rautaraya B et al (2011) Prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and its antibiotic susceptibility pattern in a tertiary care hospital. J Indian Med Assoc 109:800–801
Van Leeuwen WB, Jay C, Snijders S et al (2003) Multilocus sequence typing of Staphylococcus aureus with DNA array technology. J Clin Microbiol 41:3323–3326. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.41.7.3323-3326.2003
Yadav R, Kumar A, Singh VK et al (2018a) Molecular determination of Methicillin-resistance mecA and virulence coa genes in Staphylococcus aureus from pyogenic clinical cases of companion animals in India. Turkish J Vet Anim Sci 42:371–375. https://doi.org/10.3906/vet-1705-13
Yadav R, Kumar A, Singh VK et al (2018b) Prevalence and antibiotyping of Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) in domestic animals in India. J Glob Antimicrob Resist 15:222–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgar.2018.08.001
Zadoks R, Van Leeuwen W, Barkema H et al (2000) Application of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and binary typing as tools in veterinary clinical microbiology and molecular epidemiologic analysis of bovine and human Staphylococcus aureus isolates. J Clin Microbiol 38:1931–1939. https://doi.org/10.1128/jcm.38.5.1931-1939.2000
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all parents and hospital managements who participated in the study. The authors also acknowledge the assistance of hospital staff, laboratory staff, Dean, College of Biotechnology, and Vice-chancellor of DUVASU, Mathura for rendering all facilities and funds for the study.
Funding
This research work received no specific grant from any funding agency.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
No ethical clearance was required as samples were collected from the clinical cases of both humans and animals.
Additional information
Communicated by Jorge Membrillo-Hernández.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, J., Kumar, A., Yadav, S.K. et al. Study of antibiotics sensitivity pattern and molecular characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from human and animal pyogenic cases. Arch Microbiol 204, 245 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-02855-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-02855-4