Abstract
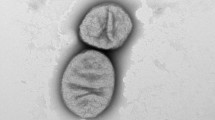
Strain SYSU D01096T was isolated from a sandy soil sample collected from Gurbantunggut Desert in Xinjiang, PR China. Phylogenetic analysis of the nearly full-length 16S rRNA gene sequence revealed that strain SYSU D01096T belonged to the family Acetobacteraceae and was closest to Rubritepida flocculans DSM 14296T (96.0% similarity). Cells of strain SYSU D01096T were observed to be non-motile, short rod-shaped and Gram-staining negative. The colonies were observed to be translucent, reddish orange, circular, convex and smooth. Growth occurred at 15–37 °C (optimum, 28–30 °C), pH 4.0–8.0 (optimum, pH 7.0) and 0–0.5% NaCl (w/v; optimum, 0%) on Reasoner’s 2A medium. The predominant ubiquinone was identified as ubiquinone 9 and the major fatty acids were Summed Feature 8 (C18:1 ω7c and/or C18:1 ω6c) and C16:0. The polar lipids consisted of diphosphatidylglycerol (DPG), phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), phosphatidylcholine (PC), phosphatidylglycerol (PG), one unidentified phospholipid (PL), three unidentified aminolipids (AL1-3) and one unidentified aminophospholipid (APL). The genomic DNA G + C content was 69.1%. Phylogenetic tree based on 16S rRNA gene sequences indicated strain SYSU D01096T represented an individual lineage in the family Acetobacteraceae, which was supported by 30 core gene-based phylogenomic tree. Based on the multi-analysis including physiological, chemotaxonomic and phylogenetic comparison, strain SYSU D01096T was proposed to represent a novel species of a novel genus, named Sabulicella rubraurantiaca gen. nov., sp. nov., within the family Acetobacteraceae. The type strain is SYSU D01096T (= CGMCC 1.8619T = KCTC 82268T = MCCC 1K04998T).


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alarico S, Rainey FA, Empadinhas N, Schumann P, Nobre MF, da Costa MS (2002) Rubritepida flocculans gen. nov., sp. nov., a new slightly thermophilic member of the alpha-1 subclass of the Proteobacteria. Syst Appl Microbiol 25:198–206. https://doi.org/10.1078/0723-2020-00116
Albuquerque L, Rainey FA, Nobre MF, da Costa MS (2008) Elioraea tepidiphila gen. nov., sp. nov., a slightly thermophilic member of the Alphaproteobacteria. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:773–778. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.65294-0
Alcock BP, Raphenya AR, Lau TTY et al (2020) CARD 2020: antibiotic resistome surveillance with the comprehensive antibiotic resistance database. Nucleic Acids Res 48:D517-d525. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz935
Boldareva EN, Turova TP, Kolganova TV, Moskalenko AA, Makhneva ZK, Gorlenko VM (2009) Roseococcus suduntuyensis sp. nov., a new aerobic bacteriochlorophyll A-containing bacterium isolated from a low-mineralized soda lake of Eastern Siberia. Mikrobiologiia 78:106–116
Castresana J (2000) Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol Biol Evol 17:540–552. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a026334
Cerny G (1978) Studies on the aminopeptidase test for the distinction of Gram-negative from Gram-positive bacteria. Appl Microbiol Biot 5:113–122. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00498805
Chen WM, Xie YR, Sheu DS, Tsai JM, Sheu SY (2020) Rhodovarius crocodyli sp. nov., isolated from a crocodile pond. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 70:5141–5148. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.004396
Chun J, Oren A, Ventosa A et al (2018) Proposed minimal standards for the use of genome data for the taxonomy of prokaryotes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 68:461–466. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.002516
Collins MD, Pirouz T, Goodfellow M, Minnikin DE (1977) Distribution of menaquinones in actinomycetes and corynebacteria. J Gen Microbiol 100:221–230. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-100-2-221
Dong L, Ming H, Liu L et al (2014) Zhizhongheella caldifontis gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel member of the family Comamonadaceae. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 105:755–761. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-014-0131-6
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32:1792–1797. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkh340
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01734359
Fitch WM (1971) Toward defining the course of evolution: minimum change for a specific tree topology. Syst Biol 20:406–416. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/20.4.406
Gillis M, De Ley J (1980) Intra- and intergeneric similarities of the ribosomal ribonucleic acid cistrons of Acetobacter and Gluconobacter. Int J Syst Bacteriol 30:7–27. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-30-1-7
Gomes RJ, Borges MF, Rosa MF, Castro-Gómez RJH, Spinosa WA (2018) Acetic acid bacteria in the food industry: systematics, characteristics and applications. Food Technol Biotechnol 56:139–151. https://doi.org/10.17113/ftb.56.02.18.5593
Gonzalez C, Gutierrez C, Ramirez C (1978) Halobacterium vallismortis sp. nov. An amylolytic and carbohydrate-metabolizing, extremely halophilic bacterium. Can J Microbiol 24:710–715. https://doi.org/10.1139/m78-119
Gosselé F, Swings J, Mossel DA, De Ley J (1984) Identification of Acetobacter strains isolated from spoiled lactic acid fermented meat food for pets. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 50:269–274. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02342137
He D, Kim JK, Jiang XY et al (2014) Roseomonas sediminicola sp. nov., isolated from fresh water. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 105:191–197. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-013-0065-4
Kämpfer P, Busse HJ, Rosséllo-Mora R, Kjellin E, Falsen E (2004) Rhodovarius lipocyclicus gen. nov. sp. nov., a new genus of the alpha-1 subclass of the Proteobacteria. Syst Appl Microbiol 27:511–516. https://doi.org/10.1078/0723202041748235
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Kawashima S, Okuno Y, Hattori M (2004) The KEGG resource for deciphering the genome. Nucleic Acids Res 32:D277-280. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkh063
Kim WH, Kim DH, Kang K, Ahn TY (2016) Dankookia rubra gen. nov., sp. nov., an alphaproteobacterium isolated from sediment of a shallow stream. J Microbiol 54:420–425. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-016-6054-3
Konstantinidis KT, Rosselló-Móra R, Amann R (2017) Uncultivated microbes in need of their own taxonomy. ISME J 11:2399–2406. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2017.113
Kroppenstedt RM (1982) Separation of bacterial menaquinones by HPLC using reverse phase (RP18) and a silver loaded ion exchanger as stationary phases. J Liq Chromatogr 5:2359–2367. https://doi.org/10.1080/01483918208067640
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35:1547–1549. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy096
Li WJ, Xu P, Schumann P et al (2007) Georgenia ruanii sp. nov., a novel actinobacterium isolated from forest soil in Yunnan (China), and emended description of the genus Georgenia. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:1424–1428. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.64749-0
Li S, Shi L, Lian WH et al (2021) Arenibaculum pallidiluteum gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel bacterium in the family Azospirillaceae, isolated from desert soil, and reclassification of Skermanella xinjiangensis to a new genus Deserticella as Deserticella xinjiangensis comb. nov., and transfer of the genera Indioceanicola and Oleisolibacter from the family Rhodospirillaceae to the family Azospirillaceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.004874
Lopes A, Espirito Santo C, Grass G, Chung AP, Morais PV (2011) Roseomonas pecuniae sp. nov., isolated from the surface of a copper-alloy coin. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:610–615. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.020966-0
Margesin R, Zhang DC (2013) Humitalea rosea gen. nov., sp. nov., an aerobic bacteriochlorophyll-containing bacterium of the family Acetobacteraceae isolated from soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:1411–1416. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.043018-0
Minnikin DE, Collins MD, Goodfellow M (1979) Fatty acid and polar lipid composition in the classification of Cellulomonas, Oerskoviaand related taxa. J Appl Bacteriol 47:87–95. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.1979.tb01172.x
Mistry J, Chuguransky S, Williams L et al (2021) Pfam: the protein families database in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res 49:D412-d419. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa913
Qu PH, Luo HM, Feng JH et al (2021) Sandaracinobacteroides hominis gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from human skin. Arch Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-021-02454-9
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454
Salam N, Jiao JY, Zhang XT, Li WJ (2020) Update on the classification of higher ranks in the phylum Actinobacteria. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 70:2958. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.003920
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids. USFCC Newsl 20:1–6
Stamatakis A (2006) RAxML-VI-HPC: maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic analyses with thousands of taxa and mixed models. Bioinformatics 22:2688–2690. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btl446
Tatusov RL, Galperin MY, Natale DA, Koonin EV (2000) The COG database: a tool for genome-scale analysis of protein functions and evolution. Nucleic Acids Res 28:33–36. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/28.1.33
Wu L, Ma JC (2019) The Global Catalogue of Microorganisms (GCM) 10K type strain sequencing project: providing services to taxonomists for standard genome sequencing and annotation. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 69(4):895–898. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.003276
Wu M, Scott AJ (2012) Phylogenomic analysis of bacterial and archaeal sequences with AMPHORA2. Bioinformatics 28:1033–1034. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts079
Yoon SH, Ha SM, Lim J, Kwon S, Chun J (2017) A large-scale evaluation of algorithms to calculate average nucleotide identity. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 110(10):1281–1286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-017-0844-4
Yu TT, Zhou EM, Yin YR et al (2013) Vulcaniibacterium tengchongense gen. nov., sp. nov. isolated from a geothermally heated soil sample, and reclassification of Lysobacter thermophilus Wei et al. 2012 as Vulcaniibacterium thermophilum comb. nov. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 104:369–376. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-013-9959-4
Yurkov V, Stackebrandt E, Holmes A et al (1994) Phylogenetic positions of novel aerobic, bacteriochlorophyll a-containing bacteria and description of Roseococcus thiosulfatophilus gen. nov., sp. nov., Erythromicrobium ramosum gen. nov., sp. nov., and Erythrobacter litoralis sp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 44:427–434. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-44-3-427
Zhang YQ, Yu LY, Wang D et al (2008) Roseomonas vinacea sp. nov., a Gram-negative coccobacillus isolated from a soil sample. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:2070–2074. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.65789-0
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 32000005 and 32061143043), Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China (Nos. 2016A030312003 and 2018A030313589), and Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region regional coordinated innovation project (Shanghai cooperation organization science and technology partnership program) (No. 2021E01018). WJ Li was also supported by Introduction project of high-level talents in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ accession number for the 16S rRNA gene sequence and whole genome shotgun project of strain SYSU D01096T is MT527707 and JAFEUU000000000, respectively.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, ZL., Li, S., Wei, QC. et al. Sabulicella rubraurantiaca gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the family Acetobacteraceae, isolated from desert soil. Arch Microbiol 204, 1 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-021-02604-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-021-02604-z