Abstract
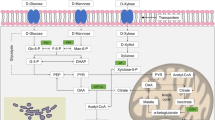
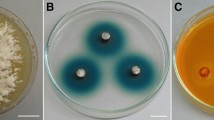
We isolated two Candida pseudointermedia strains from the Atlantic rain forest in Brazil, and analyzed cellobiose metabolization in their cells. After growth in cellobiose medium, both strains had high intracellular β-glucosidase activity [~ 200 U (g cells)−1 for 200 mM cellobiose and ~ 100 U (g cells)−1 for 2 mM pNPβG] and negligible periplasmic cellobiase activity. During batch fermentation, the strain with the best performance consumed all the available cellobiose in the first 18 h of the assay, producing 2.7 g L−1 of ethanol. Kinetics of its cellobiase activity demonstrated a high-affinity hydrolytic system inside cells, with Km of 12.4 mM. Our data suggest that, unlike other fungal species that hydrolyze cellobiose extracellularly, both analyzed strains transport it to the cytoplasm, where it is then hydrolyzed by high-affinity intracellular β-glucosidases. We believe this study increases the fund of knowledge regarding yeasts from Brazilian microbiomes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alves SL Jr, Herberts RA, Hollatz C, Miletti LC, Stambuk BU (2007) Maltose and maltotriose active transport and fermentation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Am Soc Brew Chem 65:99–104. https://doi.org/10.1094/ASBCJ-2007-0411-01
Alves SL Jr, Herberts RA, Hollatz C, Trichez D, Miletti LC, de Araujo PS, Stambuk BU (2008) Molecular analysis of maltotriose active transport and fermentation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae reveals a determinant role for the AGT1 permease. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:1494–1501. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02570-07
Alves SL Jr, Thevelein JM, Stambuk BU (2014) Expression of Saccharomyces cerevisiae α-glucoside transporters under different growth conditions. Braz J Chem Eng 31:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0104-66322014000100001
Alves SL Jr, Müller C, Camargo AF, Bonatto C, Scapini T, Fongaro G, Treichel H (2019) Bioprospecting Enzymes for 2G Ethanol through Metagenomics. In: Treichel H, Alves SL, Fongaro G, Müller C (eds) Ethanol as a green alternative fuel: insight and perspectives, 1st edn. Nova Science Publishers, Hauppauge, NY, pp 179–201
Amoikon TLS, Aké FM, Bakayoko M, Djéni TD, Mougo EBL, Djè MK (2018) Physiological profiles of indigenous yeasts isolated from raffia wine originated of côte d’ivoire. J Glob Biosci 7:5459–5474
Babič MN, Zalar P, Ženko B, Džeroski S, Gunde-Cimerman N (2016) Yeasts and yeast-like fungi in tap water and groundwater, and their transmission to household appliances. Fungal Ecol 20:30–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.funeco.2015.10.001
Baffi MA, Tobal T, Henrique J, Lago G, Leite RS, Boscolo M, Gomes E, Da-Silva R (2011) A novel β-glucosidase from Sporidiobolus pararoseus: characterization and application in winemaking. J Food Sci 76:997–1002. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-3841.2011.02293.x
Barbosa AM, Giese EC, Dekker RF, Borsato D, Briones Pérez AI, Ubeda Iranzo JF (2010) Extracellular β-glucosidase production by the yeast Debaryomyces pseudopolymorphus UCLM-NS7A: optimization using response surface methodology. N Biotechnol 27:374–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2010.05.013
Batista AS, Miletti LC, Stambuk BU (2004) Sucrose fermentation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae lacking hexose transport. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 8:26–33. https://doi.org/10.1159/000082078
Bazoti SF, Golunski S, Pereira Siqueira D, Scapini T, Barrilli ÉT, Alex Mayer D, Barros KO, Rosa CA, Stambuk BU, Alves SL Jr, Valério A, de Oliveira D, Treichel H (2017) Second-generation ethanol from non-detoxified sugarcane hydrolysate by a rotting wood isolated yeast strain. Bioresour Technol 244:582–587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.08.007
Buchta V, Bolehovská R, Hovorková E, Cornely OA, Seidel D, Žák P (2019) Saprochaete clavata invasive infections: a new threat to hematological-oncological patients. Front Microbiol 10:2196. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.02196
Cadete RM, Rosa CA (2018) The yeasts of the genus Spathaspora: potential candidates for second-generation biofuel production. Yeast 35:191–199. https://doi.org/10.1002/yea.3279
Cadete RM, Santos RO, Melo MA, Mouro A, Gonçalves DL, Stambuk BU, Gomes FC, Lachance MA, Rosa CA (2009) Spathaspora arborariae sp. nov., a d-xylose-fermenting yeast species isolated from rotting wood in Brazil. FEMS Yeast Res 9:1338–1342. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1567-1364.2009.00582.x
Castresana J (2000) Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol Biol Evol 17:540–552. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a026334
Casa-Villegas M, Polaina J, Marín-Navarro J (2018) Cellobiose fermentation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae: comparative analysis of intra versus extracellular sugar hydrolysis. Process Biochem 75:59–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2018.09.005
Dereeper A, Audic S, Claverie JM, Blanc G (2010) BLAST-EXPLORER helps you building datasets for phylogenetic analysis. BMC Evol Biol 10:8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-10-8
Dereeper A, Guignon V, Blanc G, Audic S, Buffet S, Chevenet F, Dufayard JF, Guindon S, Lefort V, Lescot M, Claverie JM, Gascuel O (2008) Phylogeny.fr: robust phylogenetic analysis for the non-specialist. Nucleic Acids Res 36:W465–W469. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn180
Duval EH, Alves SL Jr, Dunn B, Sherlock G, Stambuk BU (2010) Microarray karyotyping of maltose-fermenting Saccharomyces yeasts with differing maltotriose utilization profiles reveals copy number variation in genes involved in maltose and maltotriose utilization. J Appl Microbiol 109:248–259. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2009.04656.x
Eliodório KP, Cunha GCGE, Müller C, Lucaroni AC, Giudici R, Walker GM, Alves SL Jr, Basso TO (2019) Advances in yeast alcoholic fermentations for the production of bioethanol, beer and wine. Adv Appl Microbiol 109:61–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.aambs.2019.10.002
Feliciano RJ, Estilo EEC, Nakano H, Gabriel AA (2019) Ultraviolet-C resistance of selected spoilage yeasts in orange juice. Food Microbiol 78:73–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2018.10.003
Gancedo A (1998) Yeast carbon catabolite repression. Microbiol Mol Biol R 62:334–361
Guindon S, Dufayard JF, Lefort V, Anisimova M, Hordijk W, Gascuel O (2010) New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst Biol 59:307–321. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/syq010
Guo Z, Duquesne S, Bozonnet S, Cioci G, Nicaud JM, Marty A, O'Donohue MJ (2015) Development of cellobiose-degrading ability in Yarrowia lipolytica strain by overexpression of endogenous genes. Biotechnol Biofuels 8:109. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-015-0289-9
Hahn-Hägerdal B, Karhumaa K, Larsson CU, Gorwa-Grauslund M, Görgens J, van Zyl WH (2005) Role of cultivation media in the development of yeast strains for large scale industrial use. Microb Cell Fact 4:31. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-4-31
Hande A, Mahajan S, Prabhune A (2013) Evaluation of ethanol production by a new isolate of yeast during fermentation in synthetic medium and sugarcane bagasse hemicellulosic hydrolysate. Ann Microbiol 63:63–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-012-0445-4
Hollatz H, Stambuk BU (2001) Colorimetric determination of activeα-glucoside transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Microbiol Methods 146:253–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-7012(01)00281-0
Hoog GS, Smith MTh, Gueho E (1998) Galactomyces redhead and Malloch. In: Kurtzman CP, Fell JW (eds) The yeasts: a taxonomic study, 4th edn. Elsevier, New York, pp 209–213
Iwahara S, Takegawa K, Kawaguchi K, Okamoto G (1993) The presence of trehalose-containing oligosaccharides in yeast extract. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 57:1220–1221. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.57.1220
Kurtzman CP, Fell JW, Boekhout T, Robert V (2011) Methods for isolation phenotypic characterization and maintenance of yeasts. In: Kurtzman CP, Fell JW, Boekhout T (eds) The yeasts: a taxonomic study, 5th edn. Elsevier, NewYork, pp 87–110
Kurtzman CP, Hoog GS (2011) Cephaloascus Hanawa (1920). In: Kurtzman CP, Fell JW, Boekhout T (eds) The yeasts: a taxonomic study, 5th edn. Elsevier, New York, pp 341–344
Kurtzman CP, Robnett CJ (2013) Alloascoidea hylecoeti gen. nov., comb. nov., Alloascoidea africana comb. nov., Ascoidea tarda sp. nov., and Nadsonia starkeyi-henricii comb. nov., new members of the Saccharomycotina (Ascomycota). FEMS Yeast Res 13:423–432. https://doi.org/10.1111/1567-1364.12044
Kurtzman CP, Robnett CJ (1998) Identification and phylogeny of ascomycetous yeasts from analysis of nuclear large subunit (26S) ribosomal DNA partial sequences. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 73:331–371. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1001761008817
Lachance MA, Bowles JM, Starmer WT, Barker JS (1999) Kodamaea kakaduensis and Candida tolerans, two new ascomycetous yeast species from Australian Hibiscus flowers. Can J Microbiol 45:172–177. https://doi.org/10.1139/w98-225
Lagunas R (1993) Sugar transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS Microbiol Rev 10:229–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-1097(93)90598-v
Lefort V, Longueville JE, Gascuel O (2017) SMS: smart model selection in PhyML. Mol Biol Evol 34:2422–2424. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msx149
Limtong S, Kaewwichian R (2015) The diversity of culturable yeasts in the phylloplane of rice in Thailand. Ann Microbiol 65:667–675. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-014-0905-0
Lineaweaver H, Burk D (1934) The determination of enzyme dissociation constants. J Am Chem Soc 56:658–666. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01318a036
Liu D, Zhang R, Yang X, Zhang Z, Song S, Miao Y, Shen Q (2012) Characterization of a thermostable β-glucosidase from Aspergillus fumigatus Z5, and its functional expression in Pichia pastoris X33. Microb Cell Fact 11:25. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-11-25
Lopes MA, Lara CA, Moura MEF, Uetanabaro APT, Morais PB, Vital MJS, Rosa CA (2018) Characterisation of the diversity and physiology of cellobiose-fermenting yeasts isolated from rotting wood in Brazilian ecosystems. Fungal Biol 122:668–676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.funbio.2018.03.008
Maciel NO, Piló FB, Freitas LF, Gomes FC, Johann S, Nardi RM, Lachance MA, Rosa CA (2016) The diversity and antifungal susceptibility of the yeasts isolated from coconut water and reconstituted fruit juices in Brazil. Int J Food Microbiol 160:201–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2012.10.012
Marques WL, Raghavendran V, Stambuk BU, Gombert AK (2016) Sucrose and Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a relationship most sweet. FEMS Yeast Res 16:107. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsyr/fov107
Masoud W, Cesar LB, Jespersen L, Jakobsen M (2004) Yeast involved in fermentation of Coffea arabica in East Africa determined by genotyping and by direct denaturating gradient gel electrophoresis. Yeast 21:549–556. https://doi.org/10.1002/yea.1124
Miller MW, Phaff HJ (1998) Metschnikowia Kamienski. In: Kurtzman CP, Fell JW (eds) The yeasts: a taxonomic study, 4th edn. Elsevier, New York, pp 256–267
Molnárová J, Vadkertiová R, Stratilová E (2014) Extracellular enzymatic activities and physiological profiles of yeasts colonizing fruit trees. J Basic Microbiol 54:S74–S84. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.201300072
Nakase T, Komagata K, Fukazawa Y (1976) Candida pseudointermedia sp. nov., isolated from "kamaboko", a traditional fish-paste product in Japan. J Gen Appl Microbiol 22:177–182. https://doi.org/10.2323/jgam.22.177
O'Donnell K (1993) Fusarium and its near relatives. In: Reynolds DR, Taylor JW (eds) The fungal holomorph: mitotic, meiotic and pleomorphic speciation in fungal systematic. CAB International, Wallingford, pp 225–233
Parisutham V, Chandran SP, Mukhopadhyay A, Lee SK, Keasling JD (2017) Intracellular cellobiose metabolism and its applications in lignocellulose-based biorefineries. Bioresour Technol 239:496–506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.05.001
Peter G, Dlauchy D, Tóbiás A, Fülöp L, Podgoršek M, Čadež N (2017) Brettanomyces acidodurans sp. nov., a new acetic acid producing yeast species from olive oil. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 110:657–664. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-017-0832-8
Prillinger H, Molnár O, Eliskases-Lechner F, Lopandic K (1999) Phenotypic and genotypic identification of yeasts from cheese. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 75:267–283. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1001889917533
Putignani L, Del Chierico F, Onori M, Mancinelli L, Argentieri M, Bernaschi P, Coltella L, Lucignano B, Pansani L, Ranno S, Russo C, Urbani A, Federici G, Menichella D (2011) MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry proteomic phenotyping of clinically relevant fungi. Mol Biosyst 7:620–629. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0mb00138d
Reis AL, de Fátima R, de Souza R, Baptista Torres RR, Leite FC, Paiva PM, Vidal EE, de Morais MA (2014) Oxygen-limited cellobiose fermentation and the characterization of the cellobiase of an industrial Dekkera/Brettanomyces bruxellensis strain. Springerplus 3:38. https://doi.org/10.1186/2193-1801-3-38
Riley R, Haridas S, Wolfe KH, Lopes MR, Hittinger CT, Göker M, Salamov AA, Wisecaver JH, Long TM, Calvey CH, Aerts AL, Barry KW, Choi C, Clum A, Coughlan AY, Deshpande S, Douglass AP, Hanson SJ, Klenk HP, LaButti KM, Lapidus A, Lindquist EA, Lipzen AM, Meier-Kolthoff JP, Ohm RA, Otillar RP, Pangilinan JL, Peng Y, Rokas A, Rosa CA, Scheuner C, Sibirny AA, Slot JC, Stielow JB, Sun H, Kurtzman CP, Blackwell M, Grigoriev IV, Jeffries TW (2016) Comparative genomics of biotechnologically important yeasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:9882–9887. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1603941113
Ríos-Fránquez FJ, González-Bautista E, Ponce-Noyola T, Ramos-Valdivia AC, Poggi-Varaldo HM, García-Mena J, Martinez A (2017) Expression of a codon-optimized β-glucosidase from Cellulomonas flavigena PR-22 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae for bioethanol production from cellobiose. Arch Microbiol 199:605–611. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-016-1333-2
Rosa CA, Morais PB, Lachance MA, Santos RO, Melo WG, Viana RH, Bragança MA, Pimenta RS (2009) Wickerhamomyces queroliae sp. nov. and Candida jalapaonensis sp. nov., two yeast species isolated from Cerrado ecosystem in North Brazil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:1232–1236. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.006411-0
Rosa CA, Resende MA, Barbosa FAR, Morais PB, Franzot SP (1995) Yeast diversity in a mesotrophic lake on the karstic plateau of Lagoa Santa, MG-Brazil. Hydrobiologia 308:103–108. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00007394
Saha BC, Bothast RJ (1996) Production, purification, and characterization of a highly glucose tolerant novel β-glucosidase from Candida peltata. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:3165–3170
Santangelo GM (2006) Glucose signaling in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 70:253–282. https://doi.org/10.1128/MMBR.70.1.253-282.2006
Santos RO, Cadete RM, Badotti F, Mouro A, Wallheim DO, Gomes FC, Stambuk BU, Lachance MA, Rosa CA (2011) Candida queiroziae sp. nov., a cellobiose-fermenting yeast species isolated from rotting wood in Atlantic Rain Forest. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 99:635–642. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-010-9536-z
Shen XX, Opulente DA, Kominek J, Zhou X, Steenwyk JL, Buh KV, Haase MAB, Wisecaver JH, Wang M, Doering DT, Boudouris JT, Schneider RM, Langdon QK, Ohkuma M, Endoh R, Takashima M, Manabe RI, Čadež N, Libkind D, Rosa CA, DeVirgilio J, Hulfachor AB, Groenewald M, Kurtzman CP, Hittinger CT, Rokas A (2018) Tempo and mode of genome evolution in the budding yeast subphylum. Cell 175:1533–1545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.10.023
Silveira MCF, Carvajal E, Bon EPS (1996) Assay for in vivo yeast invertase activity using NaF. Anal Biochem 238:26–28. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1996.0244
Srivastava N, Srivastava M, Mishra PK, Gupta VK, Molina G, Rodriguez-Couto S, Manikanta A, Ramteke PW (2018) Applications of fungal cellulases in biofuel production: advances and limitations. Renew Sust Energ Rev 82:2379–2386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.08.074
Stambuk BU (1999) A simple experiment illustrating metabolic regulation: induction versus repression of yeast α-glucosidase. Biochem Educ 27:177–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0307-4412(98)00302-1
Suh SO, Blackwell M (2006) Three new asexual arthroconidial yeasts, Geotrichum carabidarum sp. nov., Geotrichum histeridarum sp. nov., and Geotrichum cucujoidarum sp. nov., isolated from the gut of insects. Mycol Res 110:220–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mycres.2005.08.008
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst197
Villena MA, Iranzo JFU, Gundllapalli SB, Otero RRC, Pérez AIB (2006) Characterization of an exocellular β-glucosidase from Debaryomyces pseudopolymorphus. Enzyme Microb Technol 39:229–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2005.10.018
Wallecha A, Mishra S (2003) Purification and characterization of two β-glucosidases from a thermo-tolerant yeast Pichia etchellsii. Biochim Biophys Acta 1649:74–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1570-9639(03)00163-8
Wang X, Liu ZL, Weber SA, Zhang X (2016) Two New Native β-Glucosidases from Clavispora NRRL Y-50464 Confer its dual function as cellobiose fermenting ethanologenic yeast. PLoS ONE 11:e0151293. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0151293
Wang Y, Ren YC, Li Y, Hui FL (2015) Molecular phylogeny and taxonomy of Yamadazyma dushanensis f.a., sp. nov., a cellobiose-fermenting yeast species from China. Curr Microbiol 71:268–273. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-015-0847-1
White TJ, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor J (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ (eds) PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 315–322
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq, Grant Numbers 454215/2014-2, 308627/2015-6 and 308389/2019-0) and Research and Innovation Support Foundation of Santa Catarina State (FAPESC, Grant Number 749/2016; T.O. 2016TR2188). ETB and VT are grateful to the Support Program for Scientific and Technological Initiation from Federal University of Fronteira Sul (PRO-ICT/UFFS), and CM to the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES), for scholarships. The authors also thank R. Philip Lindeman, MD, PhD (Liberty Medical Communications, LLC) for language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barrilli, É.T., Tadioto, V., Milani, L.M. et al. Biochemical analysis of cellobiose catabolism in Candida pseudointermedia strains isolated from rotten wood. Arch Microbiol 202, 1729–1739 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-020-01884-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-020-01884-1