Abstract
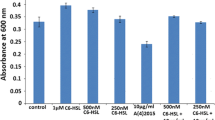
Listeria monocytogenes are Gram-positive well-known emerging food-borne pathogens causing listeriosis in humans. In the present study, we have isolated biofilm-forming Listeria sp. from utensils used by a local milk collection dairy society at Usgao Goa, which collects milk for Goa dairy. Through biochemical tests and 16S rRNA sequence analysis, the bacterium was confirmed to be L. monocytogenes and designated as strain BN3, having GenBank accession number MF095110. We report for the first time Gram-positive L. monocytogenes strain BN3 producing iron-chelating siderophores by chrome azurol S (CAS) agar test. Also, this is a first report which reveals that L. monocytogenes strain BN3 responds to N-hexanoyl-homoserine lactone molecule (C6-HSL) by gradual increase in their biofilm-forming potential with a gradual increase in AHL (C6-HSL) concentration (250, 500 nM–1 μM) as compared to control revealed by crystal violet assay (CV) in microtiter plate. These results were further confirmed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). A significant decrease in biofilm formation was observed when L. monocytogenes strain BN3 was treated with 10 µg/ml (R)-2-(2-hydroxynaphthalen-1-yl)thiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid, but when 250 and 500 nM AHL molecules were added, biofilm formation in strain BN3 was found to be enhanced as compared to control even in the presence of antibacterial compound, (R)-2-(2-hydroxynaphthalen-1-yl)thiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid. These results revealed that AHL molecules nullify the effect of antimicrobial compound and promote biofilm formation in L. monocytogenes strain BN3.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barchini E, Cowart RE (1996) Extracellular iron reductase activity produced by Listeria monocytogenes. Archiv Microbiol 166:51–57
Bauer AW, Kirby WMM, Sherris JC, Turck M (1966) Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disc method. Am J Clin Pathol 45:493–496
Biswa P, Doble M (2013) Production of acylated homoserine lactone by Gram-positive bacteria isolated from marine water. FEMS Microbiol Lett 343:34–41
Camejo A, Carvalho F, Reis O, Leitao E, Sousa S, Cabanes D (2011) The arsenal of virulence factors deployed by Listeria monocytogenes to promote its cell infection cycle. Virulence 2:379–394
Cherifi T, Jacques M, Quessy S, Fravalo P (2017) Impact of nutrient restriction on the structure of Listeria monocytogenes biofilm grown in a microfluidic system. Front Microbiol 8:864. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2017.00864
Doijad SP (2014) Biofilm forming ability and disinfectant resistance of Listeria species from food and food processing units. Shodhganga: a reservoir of Indian thesis, 1–221
Doijad SP, Vaidya V, Garg S, Kalekar S, Rodrigues J, D’Costa D, Bhosle SN, Barbuddhe SB (2010) Isolation and characterization of Listeria species from raw and processed meats. J Veter Pub Health 8:83–88
Doijad S, Barbuddhe SB, Garg S, Kalekar S, Rodrigues J, D’Costa D, Bhosle S, Chakraborty T (2011) Incidence and genetic variability of Listeria species from three milk processing plants. Food Control 22:1900–1904
Doijad SP, Barbuddhe SB, Garg S, Poharkar KV, Kalorey DR, Kurkure NV, Rawool DB, Chakraborthy T (2015) Biofilm-forming abilities of Listeria monocytogenes serotypes isolated from different sources. PLoS One 10(9):e0137046. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0137046
Dudhe NC, Chaudhary SP, Pantawane PB, Hirde VN, Ramees TP, Zade NN (2014) In-vitro characterization of Listeria monocytogenes isolates by haemolysis, CAMP, PIPLC assay with protein profiling and antibiotic resistance recovered from Nagpur region. Adv Anim Veter Sci 2:321–328
Eide MH, Homleid JP, Mattsson B (2003) Life cycle assessment (LCA) of cleaning-in-place processes in dairies. LWT Food Sci Technol 36:303–314
Farber JM, Peterkin PI (1991) Listeria monocytogenes, a food-borne pathogen. Microbiol Rev 55:476–511
Garmyn D, Gal L, Lemaitre J-P, Hartmann A, Piveteau P (2009) Communication and autoinduction in the species Listeria monocytogenes. Commun Integrat Biol 2:371–374
Gray B, Hall P, Gresham H (2013) Targeting agr- and agr-like quorum sensing systems for development of common therapeutics to treat multiple Gram-positive bacterial infections. Sensors 13:5130–5166
Irie Y, Parsek MR (2008) Quorum sensing and microbial biofilms. In: Romeo T. (ed) Bacterial biofilms. Curr Topics Microbiol Immunol 322: 67–84
Jain AB, Vaidya A, Ravichandran V, Kashaw SK, Agrawal RK (2012) Recent developments and biological activities of thiazolidinone derivatives: a review. Bioorg Med Chem 20:3378–3395
Lim Y, Ee R, Yin WF, Chan KG (2014) Quorum sensing activity of Aeromonas caviae strain YL12, a bacterium isolated from compost. Sensors 14:7026–7040
Low JC, Donachie W (1997) A review of Listeria monocytogenes and listeriosis. Veter J 153:9–29
Malik SVS, Barbuddhe SB, Chaudhari SP (2002) Listeric infections in humans and animals in Indian subcontinent: a review. Trop Anim Health Prod 34:359–381
Naik MM, Dubey SK (2011) Lead-enhanced siderophore production and alteration in cell morphology in a Pb-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain 4EA. Curr Microbiol 62:409–414
Novick RP, Muir TW (1999) Virulence gene regulation by peptides in staphylococci and other Gram positive bacteria. Curr Opin Microbiol 2:40–45
Oliveira MMM, Brugnera DF, Alves E, Piccoli RH (2010) Biofilm formation by Listeria monocytogenes on stainless steel surface and biotransfer potential. Braz J Microbiol 41:97–106
Qazi S, Middlenton B, Muharram SH, Cockayne A, Hill P, O’Shea P, Chhabra SR, Camera M, Williams P (2006) N-Acylhomoserine lactones antagonise virulence gene expression and quorum sensing in Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun 2006:910–919
Raorane AV, Doijad SP, Poharkar KV, Pathak A, Bhosle S, Barbuddhe SB (2015) Isolation and genotypic characterization of Listeria monocytogenes from pork and pork products. Internet J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 4:788–798
Schwyn B, Neilands JB (1987) Universal chemical assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Anal Biochem 160:47–56
Simon N, Coulanges V, Andre P, Vidom DJM (1995) Utilization of exogenous siderophores and natural catechols by Listeria monocytogenes. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:1643–1645
Sneath PHA, Mair NS, Sharpe ME, Holt JG (1986) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, vol 2. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore
Soyano A, Gomez M (1999) Role of iron in immunity and its relation with infections. Arch Latinoam Nutr 49:40S–46S
Swaminathan B, Gerner-Smidt P (2007) The epidemiology of human listeriosis. Microbes Infect 9:1236–1243
Vázquez-Boland JA, Kuhn M, Berche P, Chakraborthy T, Domínguez-Bernal G, Goebel W, González-Zorn B, Wehland J, Kreft J (2001) Listeria pathogenesis and molecular virulence determinants. Clin Microbiol Rev 14:584–640
Zetzmann M, Sanchez-Kopper A, Waidmann MS, Blombach B, Riedel CU (2016) Identification of agr peptide of Listeria monocytogenes. Front Microbiol 7:989. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2016.00989
Acknowledgements
Dr. Milind Mohan Naik thanks the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), Department of Science and Technology, Government of India, for financial support by the Young Scientist Project (File Number: YSS/2014/000258). We are thankful to Prof. S. K. Dubey, Department of Microbiology, Goa University, Dr. S. B. Barbuddhe, Principal Scientist, ICAR-National Institute of Biotic Stress Management, Baroda, Raipur, Chhattisgarh, India, and Mr. Satyajeet Kale, Ph.D. student, Department of Microbiology, Goa University, Goa. We are also thankful to Ms. Shivangi P Naik, M.Sc. Microbiology, Goa University, dissertation student, for her help during this research work and Dr. Shyamalina Haldar, postdoctoral fellow, Department of Microbiology, Goa University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naik, M.M., Bhangui, P. & Bhat, C. The first report on Listeria monocytogenes producing siderophores and responds positively to N-acyl homoserine lactone (AHL) molecules by enhanced biofilm formation. Arch Microbiol 199, 1409–1415 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-017-1416-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-017-1416-8