Abstract
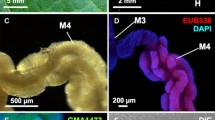
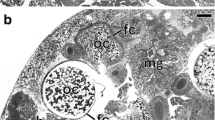
Spiroplasmas are bacteria in the Class Mollicutes that are frequently associated with insects and/or plants. Here, we describe the ultrastructure, localization, and occurrence of apparent commensal/symbiotic spiroplasma-like organisms (SLOs) in the midgut and hindgut of five leafhopper species from laboratory-reared colonies. Those found in Dalbulus elimatus, Endria inimica, and Macrosteles quadrilineatus were long and tubular shaped, whereas those in Dalbulus maidis and Graminella nigrifrons were shorter and mostly rod-shaped in their host organisms. These SLOs were found in great numbers in the gut lumen frequently associated with the gut microvilli, but unlike the plant-pathogenic mollicutes, they did not seem to invade the gut epithelium or other tissues in any of these five leafhopper species. Large accumulations of these gut-associated organisms were more commonly found by confocal laser scanning microscopy in males than in females and in crowded than in singly reared leafhoppers. Ultrastructural evidence suggests that these SLOs may be horizontally transmitted between leafhoppers by contamination of the mouth parts with leafhopper excretions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aksoy S (2000) Tsetse: a haven for microorganisms. Parasitol Today 16:114–118
Ammar E-D (1985) Internal morphology and ultrastructure of leafhoppers and planthoppers. In: Nault LR, Rodriguez JG (eds) Leafhoppers and planthoppers. Wiley, New York, pp 121–162
Ammar E-D, Hogenhout SA (2005) Use of immunofluorescence confocal laser scanning microscopy to study distribution of the bacterium corn stunt spiroplasma in vector leafhoppers (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae) and in host plants. Ann Entomol Soc Am 98:820–826
Ammar E-D, Hogenhout SA (2006) Mollicutes associated with arthropods and plants. In: Kostas B, Miller T (eds) Insect symbiosis, vol II. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 97–118
Ammar E-D, Nault LR (2002) Virus transmission by leafhoppers, planthoppers and treehoppers (Auchenorrhyncha, Homoptera). In: Plumb RT (ed) Interactions between plant viruses and their vectors, advances in botanical research, vol 36. Academic Press, New York, pp 141–167
Ammar ED, Gingery RE, Nault LR (1987) Interactions between Maize mosaic and Maize stripe viruses in their insect vector and host plant. Phytopathology 77:1051–1056
Ammar E-D, Fulton D, Bai X, Meulia T, Hogenhout SA (2004) An attachment tip and pili-like structures in insect- and plant-pathogenic spiroplasmas of the class Mollicutes. Arch Microbiol 181:97–105
Anbutsu H, Fukatsu T (2006) Tissue-specific infection dynamics of male-killing and nonmale-killing spiroplasmas in Drosophila melanogaster. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 57:40–46
Bové JM (1997) Spiroplasmas: infectious agents of plants, arthropods, and vertebrates. Wien Klin Wochenschr 109:604–612
Bové JM, Renaudin J, Saillard C, Foissac X, Garnier M (2003) Spiroplasma citri, a plant pathogenic mollicute: Relationships with Its Two Hosts, the plant and the leafhopper vector. Annu Rev Phytopathol 41:483–500
Clark TB (1982) Spiroplasmas: diversity of arthropod reservoirs and host-parasite relationships. Science 217:57–59
Dale C, Moran NA (2007) Molecular interactions between bacterial symbionts and their hosts. Cell 126:453–465
Dillon RJ, Dillon VM (2004) The gut bacteria of insects: nonpathogenic interactions. Annu Rev Entomol 49:71–92
Douglas AE (1998) Nutritional interactions in insect-microbial symbioses: aphids and their symbiotic bacteria Buchnera. Annu Rev Entomol 43:17–37
Ebbert MA, Jeffers DP, Harrison NA, Nault LR (2001) Lack of specificity in the interaction between two maize stunting pathogens and field collected Dalbulus leafhoppers. Entomol Exp Appl 101:49–57
Fletcher J, Melcher U, Wayadande A (2006) The phytopathogenic spiroplasmas. In: Dworkin M (ed) The prokaryotes, vol 4. Springer, New York, pp 905–947
Fukatsu T, Nikoh N (2000) Endosymbiotic microbiota of the bamboo pseudococcid Antonina crawii (Insecta, Homoptera). Appl Environ Microbiol 66:643–650
Fukatsu T, Tsuchida T, Nikoh N, Koga R (2001) Spiroplasma symbiont of the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum (Insecta: Homoptera). Appl Env Microbiol 67:1284–1291
Gasparich GE (2002) Spiroplasmas: evolution, adaptation and diversity. Frontiers in Bioscience 7:619–640
Gasparich GE, Whitcomb RF, Dodge D, French FE, Glass J, Williamson DL (2004) The genus Spiroplasma and its nonhelical descendants: phylogenetic classification, correlation with phenotype, and roots of the Mycoplasma mycoides clade. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:893–918
Hackett KJ, Whitcomb RF, Clark TB, Henegar RB, Lynn DE, Wagner AG, Tully JG, Gasparich GE, Rose DL, Carle P, Bove JM, Konai M, Clark EA, Adams JR, Williamson DL (1996) Spiroplasma leptinotarsae sp, nov, a mollicute uniquely adapted to its host, the Colorado potato beetle, Leptinotarsa decemlineata (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). Int J Syst Bacteriol 46:906–911
Hogenhout SA, Ammar E-D, Whitfield AE, Redinbaugh MG (2008) Insect vector interactions with persistently transmitted viruses. Ann Rev Phytopathol 46:327–359
Hurst GDD, Majerus MEN (1993) Why do maternally inherited microorganisms kill males? Heredity 71:81–95
Kwon M, Wayadande AC, Fletcher J (1999) Spiroplasma citri movement into the intestines and salivary glands of its leafhopper vector, Circulifer tenellus. Phytopathology 89:1144–1151
Lett JM, Granier M, Hippolyte I, Grondin M, Royer M, Blanc S, Reynaud B, Peterschmitt M (2002) Spatial and temporal distribution of geminiviruses in leafhoppers of the genus Cicadulina monitored by conventional and quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Phytopathology 92:65–74
Lundgren JG, Lehman RM, Sanford JC (2007) Bacterial communities within digestive tracts of ground beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae). Ann Entomol Soc Am 100:275–282
Markham PG, Townsend R (1979) Experimental vectors of spiroplasmas. In: Maramorosch K, Harris KF (eds) Leafhopper vectors and plant disease agents. Academic Press, New York, pp 413–445
Moya-Raygoza G, Nault LR (1998) Transmission biology of maize bushy stunt phytoplasma by the corn leafhopper (Homoptera: Cicadellidae). Ann Entomol Soc Am 91:668–676
Nault LR (1985) Evolutionary relationships between maize leafhoppers and their host plants. In: Nault LR, Rodriguez JG (eds) The leafhoppers and planthoppers. Wiley, New York, pp 309–330
Özbek E, Miller SA, Meulia T, Hogenhout SA (2003) Infection and replication sites of Spiroplasma kunkelii (Class: Mollicutes) in midgut and Malpighian tubules of the leafhopper Dalbulus maidis. J Invert Pathol 82:67–75
Purcell HP, Nault LR (1991) Interactions among plant-pathogenic prokaryotes, plants, and insect vectors. In: Barbosa P, Krischik VA, Jones CG (eds) Microbial mediation of plant-herbivore interactions. Wiley, New York, pp 383–405
Ratikov RA (1996) Post-moulting behavior associate with Malpighian tubule secretions in leafhoppers and treehoppers (Homoptera, Membracoidea). Eur J Entomol 93:167–184
Redinbaugh MG, Seifers DL, Meulia T, Abt JJ, Anderson RJ, Styer WE, Ackerman J, Salomon R, Houghton W, Creamer R, Gordon DT, Hogenhout SA (2002) Maize fine streak virus, a new leafhopper-transmitted maize rhabdovirus. Phytopathology 92:1167–1174
Stevens C, Tang AY, Jenkins E, Goins RL, Tully JG, Rose DL, Konai M, Williamson DL, Carle P, Bové JM, Hackett KJ, French FE, Wedincamp J, Henegar RB, Whitcomb RF (1997) Spiroplasma lampyridicola sp. nov, from the firefly beetle Photuris pennsylvanicus. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:709–712
Todd JC, Ammar ED, Redinbaugh MG, Hoy C, Hogenhout SA (2010) Plant host range and leafhopper transmission of Maize fine streak virus. Phytopathology 100:1138–1145
Tsai JH, Perrier JL (1996) Morphology of the digestive and reproductive systems of Dalbulus maidis and Graminella nigrifrons (Homoptera: Cicadellidae). Fla Entomol 79:563–578
Tsuchida T, Koga R, Shibao H, Matsumoto T, Fukatsu T (2002) Diversity and geographic distribution of secondary endosymbiotic bacteria in natural populations of the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum. Mol Ecol 11:2123–2135
Wedincamp J, French FE, Whitcomb RF, Henegar VM (1996) Spiroplasmas and entomoplasmas (Procaryotae: Mollicutes) associated with tabanids (Diptera: Tabanidae) and fireflies (Coleoptera: Lampyridae). J Invert Pathol 68:183–186
Williamson DL, Tully JG, Whitcomb RF (1989) The Genus Spiroplasma. In: Whitcomb RF, Tully JG (eds) The mycoplasmas, vol V. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 71–111
Zhang J, Hogenhout SA, Nault LR, Hoy CW, Miller SA (2004) Molecular and symptom analyses of phytoplasma strains from lettuce reveal a diverse population. Phytopathology 94:842–849
Acknowledgments
We thank Angela Strock and Tawheda Ammar (both formerly at the Entomology Department, OSU, OARDC) for their able technical assistance, and Tea Meulia and Dave Fulton (Molecular and Cellular Imaging Center, OSU, OARDC) for their advice on CLSM and SEM. Salaries and research support were provided by State and Federal funds appropriated to the OARDC, OSU. S.H. is supported by The John Innes Centre and The Gatsby Charitable Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Andreas Brune.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ammar, ED., Gasparich, G.E., Hall, D.G. et al. Spiroplasma-like organisms closely associated with the gut in five leafhopper species (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae). Arch Microbiol 193, 35–44 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-010-0637-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-010-0637-x