Abstract
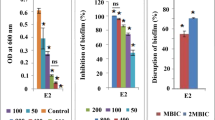
The aim of the work is to investigate the effect of marine bacterial culture supernatants on biofilm formation of Vibrio spp., a major menace in aquaculture industries. Vibrio spp. biofilm cause life-threatening infections in humans and animals. Forty-three marine bacterial culture supernatants were screened against the hydrophobicity index, initial attachment and biofilm formation in Vibrio spp. Twelve culture supernatants showed antibiofilm activity. The bacterial culture supernatants S8-07 (Bacillus pumilus) and S6-01 (B. indicus) inhibited the initial attachment, biofilm formation and dispersed the mature biofilm at 5% v/v concentration without inhibiting the growth. Analysis by light microscopy and confocal laser scanning microscopy showed that the architecture of the biofilm was destroyed by bacterial supernatants when compared to the control. The bacterial supernatants also reduce the surface hydrophobicity of Vibrio spp. which is one of the important requirements for biofilm formation. Further characterization of antibiofilm activity in S8-07 culture supernatant confirmed that it is an enzymatic activity and the size is more than 10 kDa and in S6-01, it is a heat-stable, non-protein compound. Furthermore, both the supernatants failed to show any biosurfactant activity. The culture supernatants of S8-07 and S6-01 with promising antibiofilm property have potential for application in medicine and marine aquaculture.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Annuk H, Hirmo S, Turi E, Mikelsaar M, Arak E, Wadstrom T (1999) Effect on cell surface hydrophobicity and susceptibility of Helicobacter pylori to medicinal plant extracts. FEMS Microbiol Lett 172:41–45
Bomchil N, Watnick P, Kolter R (2003) Identification and characterization of a Vibrio cholerae gene, mbaA, involved in maintenance of biofilm architecture. J Bacteriol 185:1384–1390
Brooun A, Liu S, Lewis K (2000) A dose-response study of antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 44:640–646
Brown MR, Collier PJ, Gilbert P (1990) Influence of growth rate on susceptibility to antimicrobial agents: modification of the cell envelope and batch and continuous culture studies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 34:1623–1628
Cai S, Simionato MR, Mayer MP, Novo NF, Zelante F (1994) Effects of subinhibitory concentrations of chemical agents on hydrophobicity and in vitro adherence of Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sanguis. Caries Res 28:335–341
Cerca N, Martins S, Pier GB, Oliveira R, Azeredo J (2005) The relationship between inhibition of bacterial adhesion to a solid surface by sub-MICs of antibiotics and subsequent development of a biofilm. Res Microbiol 156:650–655
Chao G et al. (2010) Distribution of genes encoding four pathogenicity islands (VPaIs), T6SS, biofilm, and type i pilus in food and clinical strains of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in China. Foodborne Pathog Dis. doi:10.1089/fpd.2009.0441
Davey ME, O’Toole GA (2000) Microbial biofilms: from ecology to molecular genetics. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 64:847–867
Defoirdt T, Crab R, Wood TK, Sorgeloos P, Verstraete W, Bossier P (2006) Quorum sensing-disrupting brominated furanones protect the gnotobiotic brine shrimp Artemia franciscana from pathogenic Vibrio harveyi, Vibrio campbellii, and Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolates. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:6419–6423
Dewanti R, Wong AC (1995) Influence of culture conditions on biofilm formation by Escherichia coli O157:H7. Int J Food Microbiol 26:147–164
Enos-Berlage JL, Guvener ZT, Keenan CE, McCarter LL (2005) Genetic determinants of biofilm development of opaque and translucent Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Mol Microbiol 55:1160–1182
Faruque SM et al (2006) Transmissibility of cholera: in vivo-formed biofilms and their relationship to infectivity and persistence in the environment. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:6350–6355
Hashimoto H (2001) Evaluation of the anti-biofilm effect of a new anti-bacterial silver citrate/lecithin coating in an in vitro experimental system using a modified Robbins device. Kansenshogaku Zasshi 75:678–685
Hawser S (1996) Adhesion of different Candida spp. to plastic: XTT formazan determinations. J Med Vet Mycol 34:407–410
Hell E, Giske CG, Nelson A, Romling U, Marchini G (2010) Human cathelicidin peptide LL37 inhibits both attachment capability and biofilm formation of Staphylococcus epidermidis. Lett Appl Microbiol 50:211–215
Johansson EM et al (2008) Inhibition and dispersion of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms by glycopeptide dendrimers targeting the fucose-specific lectin LecB. Chem Biol 15:1249–1257
Joseph LA, Wright AC (2004) Expression of Vibrio vulnificus capsular polysaccharide inhibits biofilm formation. J Bacteriol 186:889–893
Klueh U, Wagner V, Kelly S, Johnson A, Bryers JD (2000) Efficacy of silver-coated fabric to prevent bacterial colonization and subsequent device-based biofilm formation. J Biomed Mater Res 53:621–631
Kumar CG, Anand SK (1998) Significance of microbial biofilms in food industry: a review. Int J Food Microbiol 42:9–27
Li X, Yan Z, Xu J (2003) Quantitative variation of biofilms among strains in natural populations of Candida albicans. Microbiology 149:353–362
Nithya C, Pandian SK (2009) Isolation of heterotrophic bacteria from Palk Bay sediments showing heavy metal tolerance and antibiotic production. Microbiol Res. doi:10.1016/j.micres.2009.10.004
Nithya C, Aravindraja C, Pandian SK (2010) Bacillus pumilus of Palk Bay origin inhibits quorum sensing mediated virulence factors in Gram negative bacteria. Res Microbiol 161:293–304
Nithyanand P, Pandian SK (2009) Phylogenetic characterization of culturable bacterial diversity associated with the mucus and tissue of the coral Acropora digitifera from the Gulf of Mannar. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 69:384–394
Nithyanand P, Thenmozhi R, Rathna J, Pandian SK (2009) Inhibition of Streptococcus pyogenes biofilm formation by coral-associated actinomycetes. Curr Microbiol 60:454–460
Nostro A, Cannatelli MA, Crisafi G, Musolino AD, Procopio F, Alonzo V (2004) Modifications of hydrophobicity, in vitro adherence and cellular aggregation of Streptococcus mutans by Helichrysum italicum extract. Lett Appl Microbiol 38:423–427
Nyholm SV, Stabb EV, Ruby EG, McFall-Ngai MJ (2000) Establishment of an animal-bacterial association: recruiting symbiotic Vibrios from the environment. Proc Natl Acad Sci 97:10231–10235
Overhage J, Campisano A, Bains M, Torfs EC, Rehm BH, Hancock RE (2008) Human host defense peptide LL-37 prevents bacterial biofilm formation. Infect Immun 76:4176–4182
Ramage G, Bachmann S, Patterson TF, Wickes BL, Lopez-Ribot JL (2002) Investigation of multidrug efflux pumps in relation to fluconazole resistance in Candida albicans biofilms. J Antimicrob Chemother 49:973–980
Rasmussen TB et al (2005) Identity and effects of quorum-sensing inhibitors produced by Penicillium species. Microbiology 151:1325–1340
Razak FA, Othman RY, Rahim ZH (2006) The effect of Piper betle and Psidium guajava extracts on the cell-surface hydrophobicity of selected early settlers of dental plaque. J Oral Sci 48:71–75
Sandasi M, Leonard CM, Viljoen AM (2009) The in vitro antibiofilm activity of selected culinary herbs and medicinal plants against Listeria monocytogenes. Lett Appl Microbiol 50:30–35
Serebriakova EV, Darmov IV, Medvedev NP, Alekseev SA, Rybak SI (2002) Evaluation of the hydrophobicity of bacterial cells by measuring their adherence to chloroform drops. Mikrobiologiia 71:237–239
Sharon N, Ofek I (2000) Safe as mother’s milk: carbohydrates as future anti-adhesion drugs for bacterial diseases. Glycoconj J 17:659–664
Shi W, Sun H (2002) Type IV pilus-dependent motility and its possible role in bacterial pathogenesis. Infect Immun 70:1–4
Shime-Hattori A, Iida T, Arita M, Park KS, Kodama T, Honda T (2006) Two type IV pili of Vibrio parahaemolyticus play different roles in biofilm formation. FEMS Microbiol Lett 264:89–97
Sorum H (1999) Antibiotic resistance in aquaculture. Acta Vet Scand Suppl 92:29–36
Sousa C, Teixeira P, Oliveira R (2009) The role of extracellular polymers on Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm biomass and metabolic activity. J Basic Microbiol 49:363–370
Thenmozhi R, Nithyanand P, Rathna J, Pandian SK (2009) Antibiofilm activity of coral-associated bacteria against different clinical M serotypes of Streptococcus pyogenes. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 57:284–294
Thompson FL, Iida T, Swings J (2004) Biodiversity of vibrios. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 68:403–431
Turi M, Turi E, Koljalg S, Mikelsaar M (1997) Influence of aqueous extracts of medicinal plants on surface hydrophobicity of Escherichia coli strains of different origin. APMIS 105:956–962
Wai SN, Mizunoe Y, Takade A, Kawabata SI, Yoshida SI (1998) Vibrio cholerae O1 strain TSI-4 produces the exopolysaccharide materials that determine colony morphology, stress resistance, and biofilm formation. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:3648–3655
Watnick PI, Kolter R (1999) Steps in the development of a Vibrio cholerae El Tor biofilm. Mol Microbiol 34:586–595
Wong HC, Ting SH, Shieh WR (1992) Incidence of toxigenic vibrios in foods available in Taiwan. J Appl Bacteriol 73:197–202
Wong H-C, Chung YC, and Yu JA (2002) Attachment and inactivation of Vibrio parahaemolyticus on stainless steel and glass surface. Food Microbiol 19:341–305
Ye J, Ma Y, Liu Q, Zhao DL, Wang QY, Zhang YX (2008) Regulation of Vibrio alginolyticus virulence by the LuxS quorum-sensing system. J Fish Dis 31:161–169
Yildiz FH, Schoolnik GK (1999) Vibrio cholerae O1 El Tor: identification of a gene cluster required for the rugose colony type, exopolysaccharide production, chlorine resistance, and biofilm formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci 96:4028–4033
Yildiz FH, Visick KL (2009) Vibrio biofilms: so much the same yet so different. Trends Microbiol 17:109–118
Yip ES, Geszvain K, DeLoney-Marino CR, Visick KL (2006) The symbiosis regulator rscS controls the syp gene locus, biofilm formation and symbiotic aggregation by Vibrio fischeri. Mol Microbiol 62:1586–1600
You J et al (2007) Inhibition of Vibrio biofilm formation by a marine actinomycete strain A66. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76:1137–1144
Zhang Y, Miller RM (1992) Enhanced octadecane dispersion and biodegradation by a Pseudomonas rhamnolipid surfactant (biosurfactant). Appl Environ Microbiol 58:3276–3282
Zhu J, Mekalanos JJ (2003) Quorum sensing-dependent biofilms enhance colonization in Vibrio cholerae. Dev Cell 5:647–656
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the computational and bioinformatics facility provided by the Alagappa University Bioinformatics Infrastructure Facility (funded by DBT, GOI; Grant No. BT/BI/25/001/2006). Financial support provided to Chari Nithya by Alagappa University in the form of Research Fellowship is thankfully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Jan Roelof van der Meer.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nithya, C., Pandian, S.K. The in vitro antibiofilm activity of selected marine bacterial culture supernatants against Vibrio spp.. Arch Microbiol 192, 843–854 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-010-0612-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-010-0612-6