Abstract
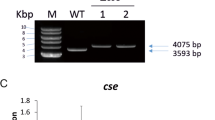
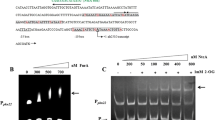
In the heterocyst-forming cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. PCC 7120 (also known as Nostoc sp. PCC 7120), it has been shown that spsB and susA, the genes coding for proteins related to sucrose synthesis and cleavage, respectively, exhibit converse expression regarding the nitrogen source. In the nitrogen-fixing filament, spsB expression is mostly localized to the heterocysts and susA is only expressed in vegetative cells. The aim of this work was to investigate the participation of NtcA, a global nitrogen regulator that operates in cyanobacteria, in the regulation of sucrose metabolism genes in Anabaena sp. PCC 7120. The induction of spsB expression observed in the filaments upon combined-nitrogen depletion was abolished in an NtcA-deficient mutant. In vitro experiments showed that NtcA binds specifically but with different affinities to two sites in the spsB promoter region. When susA expression was analyzed after a combined-nitrogen starvation, the levels of mRNA, polypeptide and activity increased in the mutant in comparison with the wild-type strain. Also, NtcA interacted with one site in the promoter region of susA. We conclude that sucrose metabolism is coordinated at the transcriptional level with nitrogen metabolism, suggesting a global metabolism regulating role for NtcA.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EMSA:
-
Electrophoretic mobility shift assay
- GST:
-
Glutathione S-transferase
- 2-OG:
-
2-Oxoglutarate
- Suc:
-
Sucrose
- Sps:
-
Sucrose-phosphate synthase
- Sus:
-
Sucrose synthase
References
Commichau FM, Forchhammer K, Stulke J (2006) Regulatory links between carbon and nitrogen metabolism. Curr Opin Microbiol 9:167–172
Cumino AC, Ekeroth CN, Salerno GL (2001) Sucrose-phosphate phosphatase from Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120: isolation of the protein and gene revealed significant structural differences from the higher-plant enzyme. Planta 214:250–256
Cumino A, Curatti L, Giarrocco L, Salerno GL (2002) Sucrose metabolism: Anabaena sucrose-phosphate synthase and sucrose-phosphate phosphatase define minimal functional domains shuffled during evolution. FEBS Lett 517:19–23
Cumino AC, Marcozzi C, Barreiro R, Salerno GL (2007) Carbon cycling in Anabaena sp. PCC 7120. Sucrose synthesis in the heterocysts and possible role in nitrogen fixation. Plant Physiol 143:1385–1397
Curatti L, Porchia AC, Herrera-Estrella L, Salerno GL (2000) A prokaryotic sucrose synthase gene (susA) isolated from a filamentous nitrogen-fixing cyanobacterium encodes a protein similar to those of plant. Planta 211:727–735
Curatti L, Flores E, Salerno GL (2002) Sucrose is involved in the diazotrophic metabolism of the heterocyst-forming cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. FEBS Lett 513:175–178
Curatti L, Giarrocco L, Salerno GL (2006) Sucrose synthase and RuBisCo expression is similarly regulated by the nitrogen source in the nitrogen-fixing cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. Planta 5:891–900
Frías JE, Flores E, Herrero A (1994) Requirement of the regulatory protein NtcA for the expression of nitrogen assimilation and heterocyst development genes in the cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. PCC 7120. Mol Microbiol 14:823–832
García-Domínguez M, Reyes JC, Florencio FJ (2000) NtcA represses transcription of gifA and gifB, genes that encode inhibitors of glutamine synthetase type I from Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Mol Microbiol 35:1192–1201
Herrero A, Muro-Pastor AM, Flores E (2001) Nitrogen control in cyanobacteria. J Bacteriol 183:411–425
Herrero A, Muro-Pastor AM, Valladares A, Flores E (2004) Cellular differentiation and the NtcA transcription factor in filamentous cyanobacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 28:469–487
Jiang F, Hellman U, Sroga GE, Bergman B, Mannervik B (1995) Cloning, sequencing, and regulation of the glutathione reductase gene from the cyanobacterium Anabaena PCC 7120. J Biol Chem 270:22882–22889
Jiang F, Mannervik B, Bergman B (1997) Evidence for redox regulation of the transcription factor NtcA, acting both as an activator and a repressor, in the cyanobacterium Anabaena PCC 7120. Biochem J 327:513–517
Jiang F, Wisén S, Widersten M, Bergman B, Mannervik B (2000) Examination of the transcription factor NtcA-binding motif by in vitro selection of DNA sequences from a random library. J Mol Biol 301:783–793
Khudyakov I, Wolk CP (1996) Evidence that the hanA gene coding for HU protein is essential for heterocyst differentiation and cyanophage A-4(L) sensitivity of, Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120. J Bacteriol 178:3572–3577
Korner H, Sofia HJ, Zumft WG (2003) Phylogeny of the bacterial superfamily of Crp-Fnr transcription regulators: exploiting the metabolic spectrum of controlling alternative gene programs. FEMS Microbiol Rev 27:559–592
Laurent S, Chen H, Bedu S, Ziarelli F, Peng L, Zhang CC (2005) Nonmetabolizable analogue of 2-OG elicits heterocyst differentiation under repressive conditions in Anabaena sp. PCC 7120. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:9907–9912
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−△△C T method. Methods 25:402–408
López-Gomollón S, Hernandez JA, Wolk CP, Peleato ML, Fillat MF (2007) Expression of furA is modulated by NtcA and strongly enhanced in heterocysts of Anabaena sp. PCC 7120. Microbiology 153:42–50
Luque I, Flores E, Herrero A (1994) Molecular mechanism for the operation of nitrogen control in cyanobacteria. EMBO J 13:2862–2869
Luque I, Zabulon G, Contreras A, Houmard J (2001) Convergence of two global transcriptional regulators on nitrogen induction of the stress acclimation gene nblA in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. PCC 7942. Mol Microbiol 1:937–947
Muro-Pastor MI, Reyes JC, Florencio FJ (2001) Cyanobacteria perceive nitrogen status by sensing intracellular 2-oxoglutarate levels. J Biol Chem 276:38320–38328
Olmedo-Verd E, Muro-Pastor AM, Flores E, Herrero A (2006) Localized induction of the ntcA regulatory gene in developing heterocysts of Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120. J Bacteriol 188:6694–6699
Porchia AC, Salerno GL (1996) Sucrose biosynthesis in a prokaryotic organism: presence of two sucrose-phosphate synthases in Anabaena with remarkable differences compared with the plant enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:13600–13604
Porchia AC, Curatti L, Salerno GL (1999) Sucrose metabolism in cyanobacteria: sucrose synthase from Anabaena sp PCC 7119 is remarkably different from the plant enzymes with respect to substrate affinity and amino-terminal sequence. Planta 210:34–40
Ramasubramanian TS, Wei TF, Golden JW (1994) Two Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120 DNA-binding factors interact with vegetative cell- and heterocyst-specific genes. J Bacteriol 176:1214–1223
Ramasubramanian TS, Wei TF, Oldham AK, Golden JW (1996) Transcription of the Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120 ntcA gene: multiple transcripts and NtcA binding. J Bacteriol 178:922–926
Rippka R, Deruelles J, Waterbury JB, Herdman M, Stanier RY (1979) Generic assignments, strain stories and properties of pure cultures of cyanobacteria. J Gen Microbiol 111:1–61
Salerno GL, Curatti L (2003) Origin of sucrose metabolism in higher plants: when, how and why? Trends Plant Sci 8:63–69
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Su Z, Olman V, Mao F, Xu Y (2005) Comparative genomics analysis of NtcA regulons in cyanobacteria: regulation of nitrogen assimilation and its coupling to photosynthesis. Nucleic Acids Res 33:5156–5171
Tanigawa R, Shirokane M, Maeda Si S, Omata T, Tanaka K, Takahashi H (2002) Transcriptional activation of the NtcA-dependent promoters of Synechococcus sp. PCC 7942 by 2-oxoglutarate in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:4251–4255
Vargas W, Cumino A, Salerno GL (2003) Cyanobacterial alkaline/neutral invertases. Origin of sucrose hydrolysis in the plant cytosol? Planta 216:951–960
Vázquez-Bermúdez MF, Flores E, Herrero A (2002a) Analysis of the binding sites for the nitrogen-control transcription factor NtcA in the promoters of Synechococcus nitrogen-regulated genes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1578:95–98
Vázquez-Bermúdez MF, Herrero A, Flores E (2002b) 2-Oxoglutarate increases the binding affinity of the NtcA (nitrogen control) transcription factor for the Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7942. FEMS Microbiol Lett 221:155–159
Vega-Palas MA, Flores E, Herrero A (1992) NtcA, a global nitrogen regulator from the cyanobacterium Synechococcus that belongs to the Crp family of transcriptional regulators. Mol Microbiol 6:1853–1859
Wisén S, Bergman B, Mannervik B (2004) Mutagenesis of the cysteine residues in the transcription factor NtcA from Anabaena PCC 7120 and its effects on DNA binding in vitro. Biopchim Biophys Acta 1679:156–163
Wolk CP, Ernst A, Elhai J (1994) Heterocyst metabolism and development. In: Bryant DA (ed) The molecular biology of cyanobacteria. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 769–823
Acknowledgments
We thank E. Flores for providing the CSE2 mutant and C. Fernández and L. Giarrocco for technical assistance. This work is part of C.M.’s PhD thesis (UNMdP) and supported by ANPCyT, CONICET, UNMdP and FIBA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Jack Meeks.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marcozzi, C., Cumino, A.C. & Salerno, G.L. Role of NtcA, a cyanobacterial global nitrogen regulator, in the regulation of sucrose metabolism gene expression in Anabaena sp. PCC 7120. Arch Microbiol 191, 255–263 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-008-0450-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-008-0450-y