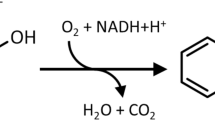
Abstract
Pseudomonas fluorescens ST is a styrene degrading microorganism that, by the sequential oxidation of the vinyl side chain, converts styrene to phenylacetic acid. The cluster of styrene upper pathway catabolic genes (sty genes) has been previously localized on a chromosomal region. This report describes the isolation, sequencing and analysis of a new chromosomal fragment deriving from the ST strain genomic bank that contains the styrene lower degradative pathway genes (paa genes), involved in the metabolism of phenylacetic acid. Analysis of the paa gene cluster led to the description of 14 putative genes: a gene encoding a phenylacetyl-CoA ligase (paaF), the enzyme required for the activation of phenylacetic acid; five ORFs encoding the subunits of a ring hydroxylation multienzymatic system (paaGHIJK); the gene paaW encoding a membrane protein of unknown function; five genes for a β-oxidation-like system (paaABCDE), involved in the steps following the aromatic ring cleavage; a gene encoding a putative permease (paaL) and a gene (paaN) probably involved in the aromatic ring cleavage. The function of some of the isolated genes has been proved by means of biotransformation experiments.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso S, Bartolome’-Martin D, del Alamo M, Diaz E, Garcia JL, Perera J (2003) Genetic characterization of the styrene lower catabolic pathway of Pseudomonas sp. strain Y2. Gene 319:71–83
Bartolome’-Martin D, Martinez-Garcia E, Mascaraque V, Rubio J, Perera J, Alonso S (2004) Characterization of a second functional gene cluster for the catabolism of phenylacetic acid in Pseudomonas sp. strain Y2. Gene 341:167–179
Beltrametti F, Marconi AM, Bestetti G, Colombo C, Galli E, Ruzzi M, Zennaro E (1997) Sequencing and functional analysis of styrene catabolic genes from Pseudomonas fluorescens ST. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:2232–2239
Bestetti G, Di Gennaro P, Colmegna A, Ronco I, Galli E, Sello G (2004) Characterization of styrene catabolic pathway in Pseudomonas fluorescens ST. Int Biodet Biodeg 54:183–187
Bond JA (1989) Review of the toxicology of styrene. Crit Rev Toxicol 19:227–249
Di Gennaro P, Colmegna A, Galli E, Sello G, Pelizzoni F, Bestetti G (1999) A new biocatalyst for production of optically pure aryl epoxides by styrene monooxygenase from Pseudomonas fluorescens ST. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:2794–2797
Ferrandez A, Minanbres B, Garcia B, Olivera ER, Luengo JM, Garcia JL, Diaz E (1998) Catabolism of phenylacetic acid in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 273:25974–25986
Fu MH, Alexander M (1992) Biodegradation of styrene in samples of natural environments. Environ Sci Technol 26:1540–1544
Geissler JF, Harwood CS, Gibson J (1988) Purification and properties of benzoate-coenzymeA ligase, a Rhodopseudomonas palustris enzyme involved in the aerobic degradation of benzoate. J Bacteriol 170:1709–1714
Gescher G, Ismail W, Olgeschlager E, Eisenreich W, Worth J, Fuchs G (2006) Aerobic benzoyl-Coenzyme A (CoA) catabolic pathway in Azoarcus evansii: conversion of ring cleavage product by 3,4-dehydroadipyl-CoA semialdehyde dehydrogenase. J Bacteriol 188:2919–2927
Hansen JH, Olsen RH (1978) Isolation of large bacterial plasmids and characterization of the P2 incompatibility group plasmids pMG1 and pMG5. J Bacteriol 135:227–238
Holmes DS, Quigley M (1981) A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem 114:193–199
Ismail W, El-Said Mohamed M, Wanner BL, Datsenko KA, Eisenreich W, Rohdich F, Bacher A, Fuchs G (2003) Functional genomics by NMR spectroscopy phenylacetate catabolism in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem 270:3047–3054
Jimenez JI, Minambres B, Garcia JL, Diaz E (2002) Genomic analysis of the aromatic catabolic pathways from Pseudomonas putida KT2440. Environ Microbiol 4:824–841
Liese A, Filho MV (1999) Production of fine chemicals using biocatalysis. Curr Opin Biotechnol 10:595–603
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Olivera ER, Reglero A, Martinez-Blanco H, Fernandez-Medarde A, Moreno MA, Luengo JM (1994) Catabolism of aromatics in Pseudomonas putida U. Formal demonstration that phenylacetic acid and 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid are catabolized by two unrelated pathways. Eur J Biochem 221:375–381
Olivera ER, Miñambres B, García B, Muñiz C, Moreno MA, Ferrández A, Diaz E, García JL, Luengo JM (1998) Molecular characterization of the phenylacetic acid catabolic pathway in Pseudomonas putida U: the phenylacetyl-CoA catabolon. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:6419–6424
Pearson WR, Lipman DJ (1988) Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:2444–2448
Sambrook J, Russell D (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. C.S.H.L. Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Schulze B, Wubbolts MG (1999) Biocatalysis for industrial production of fine chemicals. Curr Opin Biotechnol 10:609–615
Sugino H, Sasaki M, Azakami H, Yamashita M, Murooka Y (1992) A monoamine-regulated Klebsiella aerogenes operon containing the monoamine oxidase structural gene maoA and maoC gene. J Bacteriol 174:2485–2492
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTALW improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting position-specific gappen alties and weight matrix choic. Nucleic Acid Res 22:4673–4680
Velasco A, Alonso S, Garcia JL, Perera J, Diaz E (1998) Genetic and functional analysis of styrene catabolic cluster of Pseudomonas sp. strain Y2. J Bacteriol 180:1063–1071
Warhurst AM, Fewson CA (1994) Microbial metabolism and biotransformation of styrene. J Appl Bacteriol 77:597–606
Yanisch-Perron C, Vieira J, Messing J (1985) Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene 33:103–119
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grants from MIUR-PRIN 2004 “Biocatalytic process development to produce bioproducts of interest” and ISPESL (National Institute of Occupational Safety and Prevention).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Di Gennaro, P., Ferrara, S., Ronco, I. et al. Styrene lower catabolic pathway in Pseudomonas fluorescens ST: identification and characterization of genes for phenylacetic acid degradation. Arch Microbiol 188, 117–125 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-007-0226-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-007-0226-9