Abstract
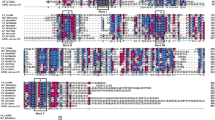
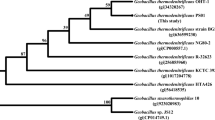
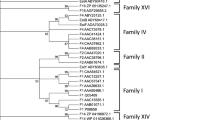
A psychrotrophic bacterium producing a cold-adapted esterase upon growth at low temperatures was isolated from the alimentary tract of Antarctic krill Euphasia superba Dana, and classified as Pseudoalteromonas sp. strain 643A. A genomic DNA library of strain 643A was introduced into Escherichia coli TOP10F’, and screening on tributyrin-containing agar plates led to the isolation of esterase gene. The esterase gene (estA, 621 bp) encoded a protein (EstA) of 207 amino acid residues with molecular mass of 23,036 Da. Analysis of the amino acid sequence of EstA suggests that it is a member of the GDSL-lipolytic enzymes family. The purification and characterization of native EstA esterase were performed. The enzyme displayed 20–50% of maximum activity at 0–20°C. The optimal temperature for EstA was 35°C. EstA was stable between pH 9 and 11.5. The enzyme showed activity for esters of short- to medium-chain (C4 and C10) fatty acids, and exhibited no activity for long-chain fatty acid esters like that of palmitate and stearate. EstA was strongly inhibited by phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, 2–mercaptoethanol, dithiothreitol and glutathione. Addition of selected divalent ions e.g. Mg2+, Co2+ and Cu2+ led to the reduction of enzymatic activity and the enzyme was slightly activated (∼30%) by Ca2+ ions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akoh CC, Lee GC, Liaw YC, Huang TH, Shaw JF (2004) GDSL family of serine esterases/lipases. Prog Lipid Res 43:534–552
Arpigny JL, Jaeger KE (1999) Bacterial lipolytic enzymes: classification and properties. Biochem J 343:177–183
Bendtsen JD, Nielsen H, Heijne G, Brunak S (2004) Improved prediction of signal peptides: signalP 3.0. J Mol Biol 340:783–795
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Cho H, Cronan Jr JE (1993) Escherichia coli thioesterase I, molecular cloning and sequencing of the structural gene and identification as a periplasmic enzyme. J Biol Chem 268:9238–9245
Cygler MJ, Schrag D, Sussman JL, Harel M, Silman I, Gentry MK, Doctor BP (1993) Relationship between sequence conservation and three-dimensional structure in a large family of esterases, lipases, and related proteins. Protein Sci 2:366–382
Davis BJ (1964) Disc electrophoresis. II. Methods and application to human serum protein. Ann N Y Acad Sci 121:404–427
Diaz P, Prim N, Javier Pastor FI (1999) Direct fluorescence-based lipase activity assay. BioTechniques 27:696–698
Flieger A, Neumeister B, Cianciotto NP (2002) Characterization of the gene encoding the major secreted lysophospholipase A of Legionella pneumophila and its role in detoxification of lysophosphatidylcholine. Infect Immun 70:6094–6106
Fojan P, Jonson PH, Petersen MTN, Petersen SB (2000) What distinguishes an esterase from a lipase: a novel structural approach. Biochimie 82:1033–1041
Gardy JL, Laird MR, Chen F, Rey S, Walsh CJ, Ester M, Brinkman FSL (2005) PSORTb v.2.0: expanded prediction of bacterial protein subcellular localization and insights gained from comparative proteome analysis. Bioinformatics 21:617–623
Jaeger KE, Reetz MT (1998) Microbial lipases form versatile tools for biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol 16:396–403
Jaeger KE, Eggert T (2002) Lipases for biotechnology. Curr Opin Biotechnol 13:390–397
Jaeger KE, Dijkstra BW, Reetz MT (1999) Bacterial biocatalysts: molecular biology, three-dimensional structures, and biotechnological applications of lipases. Annu Rev Microbiol 53:315–351
Kulakova L, Galkin A, Nakayama T, Nishino T, Esaki N (2004) Cold-active esterase from Psychrobacter sp. Ant300; gene cloning, characterization, and the effects of Gly→Pro substitution near the active site on its catalytic activity and stability. Biochim Biophys Acta 1696:59–65
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lo YC, Lin SC, Shaw JF, Liaw YC (2003) Crystal structure of Escherichia coli thioesterase I/protease I/lysophospholipases L1: consensus sequence blocks constitute the catalytic center of SGNH-hydrolases through a conserved hydrogen bond network. J Mol Biol 330:539–551
Margesin R, Schinner F (1994) Properties of cold-adapted microorganisms and their potential role in biotechnology. J Biotechnol 33:1–14
Ornstein L (1964) Disc electrophoresis. I. Background and theory. Ann N Y Acad Sci 121:321–349
Pandey A, Benjamin S, Soccol, Nigam P, Krieger N, Soccol VT (1999) The realm of microbial lipases in biotechnology. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 29:119–131
Rashid N, Shimada Y, Ezaki S, Atomi H, Imanaka T (2001) Low-temperature lipase from psychrotrophic Pseudomonas sp. strain KB700A. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:4064–4069
Ryu HS, Kim HK, Choi WC, Kim MH, Park SY, Han NS, Oh TK, Lee JK (2006) New cold-adapted lipase from Photobacterium lipolyticum sp. nov. that is closely related to filamentous fungal lipases. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 70:321–326
Sharma R, Chisti Y, Banerjee UC (2001) Production, purification, characterization, and application of lipases. Biotechnol Adv 19:627–662
Singh R, Gupta N, Goswami VK, Gupta R (2006) A simple activity staining protocol for lipases and esterases. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 70:679–682
Suzuki T, Nakayama T, Kurihara T, Nishino T, Esaki N (2002) A cold-active esterase with a substrate preference for vinyl esters from a psychrotroph, Acinetobacter sp. Strain no. 6 gene cloning, purification, and characterization. J Mol Catal B Enzym 16:255–263
Suzuki T, Nakayama T, Choo DW, Hirano Y, Kurihara T, Nishino T, Esaki N (2003) Cloning, heterologous expression, renaturation, and characterization of a cold-adapted esterase with unique primary structure from a psychrotroph Pseudomonas sp. strain B11–1. Protein Expr Purif 30:171–178
WeisburgWG, Barns SM, Pelletier DA, Lane DJ (1991) 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol 173:697–703
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Polish State Committee for Scientific Research Grant 2 P04B 018 30 to M.T. and N302 039 31/3427 to J.K.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Cieśliński Hubert and Białkowska Aneta contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cieśliński, H., Białkowska, A.M., Długołęcka, A. et al. A cold-adapted esterase from psychrotrophic Pseudoalteromas sp. strain 643A. Arch Microbiol 188, 27–36 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-007-0220-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-007-0220-2