Abstract
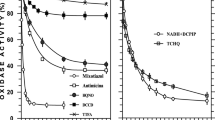
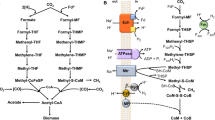
The variable cyanide-sensitivity of the iron-containing alcohol dehydrogenase isoenzyme (ADH II) of the ethanol-producing bacterium Zymomonas mobilis was studied. In aerobically grown permeabilized cells, cyanide caused gradual inhibition of ADH II, which was largely prevented by externally added NADH. Cyanide-sensitivity of ADH II was highest in cells grown under conditions of vigorous aeration, in which intracellular NADH concentration was low. Anaerobically grown bacteria, as well as those cultivated aerobically in the presence of cyanide, maintained higher intracellular NADH levels along with a more cyanide-resistant ADH II. It was demonstrated that cyanide acted as a competitive inhibitor of ADH II, competing with nicotinamide nucleotides. NADH increased both cyanide-resistance and oxygen-resistance of ADH II.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashcroft JR, Haddock BA (1975) Synthesis of alternative membrane—bound redox carriers during aerobic growth of Escherichia coli in the presence of potassium cyanide. Biochem J 148:349–352
Conway T, Sewell GW, Osman YA, Ingram LO (1987) Cloning and sequencing of the alcohol dehydrogenase II gene from Zymomonas mobilis. J Bacteriol 169:2591–2597
Delgado OD, Martinez MA, Abate CM, Sineriz F (2002) Chromosomal integration and expression of green fluorescent protein in Zymomonas mobilis. Biotechnol Lett 24:1285–1290
Dien BS, Cotta MA, Jeffries TW (2003) Bacteria engineered for fuel ethanol production: current status. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 63:258–266
DiMarco AA, Romano AH (1985) D-glucose transport system of Zymomonas mobilis. Appl Environ Microbiol 49:151–157
Dubey SK, Holmes DS (1995) Biological cyanide destruction mediated by microorganisms. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 11:257–265
Echave P, Esparza-Cerón MA, Cabiscol E, Tamarit J, Ros J, Membrillo-Hernández J, Lin ECC (2002) DnaK dependence of mutant ethanol oxidoreductases evolved for aerobic function and protective role of the chaperone against protein oxidative damage in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:4626–4631
Echave P, Tamarit J, Cabiscol E, Ros J (2003) Novel antioxidant role of alcohol dehydrogenase E from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 278:30193–30198
Francisco IA, Pinotti MHP (2000) Cyanogenic glycosides in plants. Braz Arch Biol Technol 43:487–492
Kalnenieks U, de Graaf AA, Bringer-Meyer S, Sahm H (1993) Oxidative phosphorylation in Zymomonas mobilis. Arch Microbiol 160:74–79
Kalnenieks U, Galinina N, Toma MM, Poole RK (2000) Cyanide inhibits respiration yet stimulates aerobic growth of Zymomonas mobilis. Microbiology 146:1259–1266
Kalnenieks U, Galinina N, Toma M, Marjutina U (2002) Ethanol cycle in an ethanologenic bacterium. FEBS Lett 522:6–8
Kalnenieks U, Toma MM, Galinina N, Poole RK (2003) The paradoxical cyanide- stimulated respiration of Zymomonas mobilis: cyanide sensitivity of alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH II). Microbiology 149:1739–1744
Karp MT, Raunio RP, Lővgren TN-E (1983) Simultaneous extraction and combined bioluminescent assay of NAD+ and NADH. Anal Biochem 128:175–180
Kinoshita S, Kakizono T, Kadota K, Kumudeswar D, Taguchi H (1985) Purification of two alcohol dehydrogenases from Zymomonas mobilis and their properties. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 22:249–254
Kita K, Konishi K, Anraku Y (1984) Terminal oxidases of Escherichia coli aerobic respiratory chain. II. Purification and properties of cytochrome b 558—d complex from cells grown with limited oxygen and evidence of branched electron—carrying systems. J Biol Chem 259:3375–3381
Knowles CJ (1976) Microorganisms and cyanide. Bacteriol Rev 40:652–680
Leonardo MR, Dailly Y, Clark DP (1996) Role of NAD in regulating the adhE gene of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 178:6013–6018
Membrillo-Hernández J, Lin ECC (1999) Regulation of expression of the adhE Gene, encoding ethanol oxidoreductase in Escherichia coli: transcription of a downstream promoter and regulation by Fnr and RpoS. J Bacteriol 181:7571–7579
Membrillo-Hernández J, Echave P, Cabiscol E, Tamarit J, Ros J, Lin ECC (2000) Evolution of the adhE gene product of Escherichia coli from a functional reductase to a dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem 275:33869–33875
Neale AD, Scopes RK, Kelly JM, Wettenhall REH (1986) The two alcohol dehydrogenases of Zymomonas mobilis. Purification by differential dye ligand chromatography, molecular characterisation and physiological roles. Eur J Biochem 154:119–124
O’Mullan PJ, Buchholz SE, Chase Jr T, Eveleigh DE (1995) Roles of alcohol dehydrogenases of Zymomonas mobilis (ZADH): characterization of a ZADH- 2-negative mutant. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 43:675–678
Osman YA, Conway T, Bonetti SJ, Ingram LO (1987) Glycolytic flux in Zymomonas mobilis: enzyme and metabolite levels during batch fermentation. J Bacteriol169:3726–3736
Rogers PLK, Lee J, Skotnicki ML, Tribe DE (1982) Ethanol production by Zymomonas mobilis. Adv Biochem Eng 23:37–84
Sprenger GA (1996) Carbohydrate metabolism in Zymomonas mobilis: a catabolic highway with some scenic routes. FEMS Microbiol Lett 145:301–307
Swings J, DeLey J (1977) The biology of Zymomonas. Bacteriol Rev 41:1–46
Tamarit J, Cabiscol E, Aguilar J, Ros J (1997) Differential inactivation of alcohol dehydrogenase isoenzymes in Zymomonas mobilis by oxygen. J Bacteriol 179:1102–1104
Wills C, Kratofil P, Londo D, Martin T (1981) Characterization of the two alcohol dehydrogenases of Zymomonas mobilis. Arch Biochem Biophys 210:775–785
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the grant 01.0401 of the Latvian Council of Science. We are grateful to Professor Robert K. Poole for stimulating discussions and support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalnenieks, U., Galinina, N. & Toma, M.M. Physiological regulation of the properties of alcohol dehydrogenase II (ADH II) of Zymomonas mobilis: NADH renders ADH II resistant to cyanide and aeration. Arch Microbiol 183, 450–456 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-005-0023-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-005-0023-2