Abstract
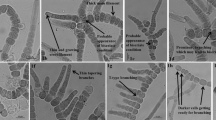
A phylogenetic analysis of selected symbiotic Nostoc strain sequences and available database 16S rDNA sequences of both symbiotic and free-living cyanobacteria was carried out using maximum likelihood and Bayesian inference techniques. Most of the symbiotic strains fell into well separated clades. One clade consisted of a mixture of symbiotic and free-living isolates. This clade includes Nostoc sp. strain PCC 73102, the reference strain proposed for Nostoc punctiforme. A separate symbiotic clade with isolates exclusively from Gunnera species was also obtained, suggesting that not all symbiotic Nostoc species can be assigned to N. punctiforme. Moreover, isolates from Azolla filiculoides and one from Gunnera dentata were well nested within a clade comprising most of the Anabaena sequences. This result supports the affiliation of the Azolla isolates with the genus Anabaena and shows that strains within this genus can form symbioses with additional hosts. Furthermore, these symbiotic strains produced hormogonia, thereby verifying that hormogonia formation is not absent in Anabaena and cannot be used as a criterion to distinguish it from Nostoc.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker JA, Entsch B, McKay DB (2003) The cyanobiont in an Azolla fern is neither Anabaena nor Nostoc. FEMS Microbiol Lett 229:43–47
Carpenter EJ, Foster RA (2002) Marine cyanobacterial symbiosis. In: Rai AN, Bergman B, Rasmussen U (eds) Cyanobacteria in symbioses. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 11–19
Costa JL, Paulsrud P, Lindblad P (1999) Cyanobiont diversity within coralloid roots of selected cycad species. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 28:85–91
Costa JL, Paulsrud P, Rikkinen J, Lindblad P (2001) Genetic diversity of Nostoc symbionts endophytically associated with two bryophyte species. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:4393–4396
Cummings MP, Handley SA, Myers DS, Reed DL, Rokas A, Winka K (2003) Comparing bootstrap and posterior probability values in the four-taxon case. Syst Biol 52:477–487
Enderlin CS, Meeks JC (1983) Pure culture and reconstitution of the Anthoceros-Nostoc symbiotic association. Planta 158:157–165
Golubic S, Seong-Joo L (1999) Early cyanobacterial fossil record: preservation, palaeoenvironments and identification. Eur J Phycol 34:339–348
Guevara R, Armesto JJ, Caru M (2002) Genetic diversity of Nostoc microsymbionts from Gunnera tinctoria revealed by PCR-STRR fingerprinting. Microb Ecol 44:127–136
Gugger M, Lyra C, Henriksen P, Coutė A, Humbert JF, Sivonen K (2002) Phylogenetic comparison of the cyanobacterial genera Anabaena and Aphanizomenon. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:1867–1880
Huelsenbeck JP, Ronquist F (2001a) MRBAYES: bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Biometrics 17:754–755
Huelsenbeck JP, Ronquist F (2001b) MrBayes: a program for the Bayesian inference of phylogeny, version 2.01. Computer Program distributed by the authors
Janson S (2002) Cyanobacteria in symbiosis with diatoms. In: Rai AN, Bergman B, Rasmussen U (eds) Cyanobacteria in symbioses. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 1–10
Johansson C, Bergman B (1994) Reconstitution of the symbiosis of Gunnera manicata Linden: cyanobacterial specificity. New Phytol 126:643–652
Kluge M, Mollenhauer D, Wolf E, Schüβler A (2002) The Nostoc-Geosiphon endocytobiosis. In: Rai AN, Bergman B, Rasmussen U (eds) Cyanobacteria in symbioses. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 19–30
Lachance M-A (1981) Genetic relatedness of heterocystous cyanobacteria by deoxyribonucleic acid-deoxyribonucleic acid reassociation. Int J Syst Bacteriol 31:139–147
Lewis PO (2001) Phylogenetic systematics turns over a new leaf. Trends Ecol Evol 16:30–37
Lumpkin TA, Plucknett DL (1980) Azolla: botany, physiology, and use as a green manure. Econ Bot 34:111–153
Lyra C, Soumalainen S, Gugger M, Vezie C, Sundman P, Paulin L, Sivonen K (2001) Molecular characterization of planctonic cyanobacteria of Anabaena, Aphanizomenon, Microcystis and Planktothrix genera. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:513–526
Maddison DR, Swofford DL, Maddison WP (1997) NEXUS: an extensible file format for systematic information. Syst Biol 46:590–621
Mazel D, Houmard J, Castets AM, Tandeau de Marsac N (1990) Highly repetitive DNA sequences in cyanobacterial genomes. J Bacteriol 172:2755–2761
Meeks JC, Elhai J, Thiel T, Potts M, Larimer F, Lamerdin J, Predki P, Atlas R (2001) An overview of the genome of Nostoc punctiforme, a multicellular, symbiotic cyanobacterium. Photosynth Res 70:85–106
Mollenhauer D, Mollenhauer R, Kluge M (1996) Studies on the initiation and development of the partner association in Geosiphon pyriforme (Kütz.) v. Wettstein, a unique endocytobiotic system of a fungus (Glomales) and the cyanobacterium Nostoc punctiforme (Kütz.). Hariot Protoplasma 193:3–9
Moor AW (1969) Azolla: biology and agronomic significance. Bot Rev 35:17–34
Nilsson M, Bergman B, Rasmussen U (2000) Cyanobacterial diversity in geographically related and distant host plants of the genus Gunnera. Arch Microbiol 173:97–102
Nübel U, Garcia-Pichel F, Muyzer G (1997) PCR primers to amplify 16S rRNA genes from cyanobacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:3327–3332
Nylander JAA (2001) MrModeltest, version 1.1b. Distributed by the author
Oksanen I, Lohtander K, Sivonen K, Rikkinen J (2004) Repeat-type distribution in trnL intron does not correspond with species phylogeny: comparison of the genetic markers 16S rRNA and trnL intron in heterocystous cyanobacteria. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:765–772
Paulsrud P, Lindblad P (1998) Sequence variation of the tRNA Leu intron as a marker for genetic diversity and specificity of symbiotic cyanobacteria in some lichens. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:310–315
Paulsrud P, Rikkinen J, Lindblad P (1998) Cyanobiont specificity in some Nostoc-containing lichens and in a Peltigera aphthosa photosymbiodeme. New Phytol 139:517–524
Plazinski J, Zheng Q, Taylor R, Croft L, Rolfe BG, Gunning BES (1990) DNA probes show genetic variation in cyanobacterial symbionts of the Azolla fern and a closer relationship to free-living Nostoc strains than to Anabaena strains. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:1263–1270
Posada D, Crandall KA (1998) Modeltest: testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 14:817–818
Rai AN, Söderbäck E, Bergman B (2000) Cyanobacterium-plant symbioses. Transley review 116. New Phytol 147:449–481
Rambaut A (1996) Se-Al. Sequence Alignment Editor, version 1.0a1. Distributed by the author, Department of Zoology, University of Oxford
Rannala B, Yang Z (1996) Probability distribution of molecular evolutionary trees: a new method of phylogenetic inference. J Mol Evol 43:304–311
Rasmussen U, Svenning MM (1998) Fingerprinting of cyanobacteria based on PCR with primers derived from short and long tandemly repeated repetitive sequences. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:265–272
Rasmussen U, Svenning MM (2001) Characterization by genotypic methods of symbiotic Nostoc strains isolated from five species of Gunnera. Arch Microbiol 179:204–210
Raven JA (2002) Evolution of cyanobacterial symbioses. In: Rai AN, Bergman B, Rasmussen U (eds) Cyanobacteria in symbioses. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 329–346
Rikkinen J, Oksanen I, Lohtander K (2002) Lichen guilds share related cyanobacterial symbionts. Science 297:357
Rippka R (1988) Recognition and identification of cyanobacteria. Methods Enzymol 167:28–67
Rippka R, Herdman M (1992) Pasteur culture collection of cyanobacterial strains in axenic culture. Catalogue and taxonomic handbook, vol I: Catalog of strains, 1992/1993. Institute Pasteur, Paris
Rippka R, Deruelles J, Waterbury JB, Herdman M, Stanier RY (1979) Generic assignments, strain histories and properties of pure cultures of cyanobacteria. J Gen Microbiol 111:1–61
Schopf JW (2000) The fossil record: tracing the roots of the cyanobacterial linage. In: Whitton BA, Potts M (eds) The ecology of cyanobacteria. Their diversity in time and space. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 13–35
Staden R (1996) The Staden sequence analysis package. Mol Biotech 5:233–241
Stanier RY, Kunisawa R, Mandel M, Cohen-Bazire G (1971) Purification and properties of unicellular blue-green algae (order Chroococcales). Bacteriol Rev 35:171–205
Swofford DL (2001) PAUP* Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony and other methods, version 4.0. Sinauer
Tamas I, Svircev Z, Andersson SGE (2000) Determinative value of a portion of the nifH sequence for the genera Nostoc and Anabaena (Cyanobacteria). Curr Microbiol 41:197–200
Weisburg WG, Barns SM, Pelletier DA, Lane DJ (1991) 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol 173:697–703
West NJ, Adams DG (1997) Phenotypic and genotypic comparison of symbiotic and free-living cyanobacteria from a single field site. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:4479–4484
Wilmotte A, Herdman M (2001) Phylogenetic relationships among the cyanobacteria based on 16S rRNA sequences. In: Boone DR, Castenholz RW, Garrity GM (eds) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 487–514
Wright D, Prickett T, Helm RF, Potts M (2001) Form species Nostoc commune (Cyanobacteria). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:1839–1852
Zheng WW, Nilsson M, Bergman B, Rasmussen U (2002) Genetic diversity and classification of cyanobacteria in different Azolla species by the use of PCR fingerprinting. Theor Appl Genet 99:1187–1193
Zimmerman WJ, Culley DE (1991) Genetic variation at the apcAB, gvpAi, and nifH loci and in the DNA methylation among N2-fixing cyanobacteria designated Nostoc punctiforme. Microb Ecol 21:199–209
Zimmerman WJ, Rosen BH (1992) Cyanobiont diversity within and among cycads on one field site. Can J Microbiol 38:1324–1328
Acknowledgements
Coby Weber and Björn Hansen are thanked for technical assistance. This work was supported by grants from Carl Tryggers Foundation and Nordic Academy for Advanced Study to U.R.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The GenBank accession numbers for the cyanobacterial 16S rRNA gene sequences determined in this study are AY742447-AY742454.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Svenning, M.M., Eriksson, T. & Rasmussen, U. Phylogeny of symbiotic cyanobacteria within the genus Nostoc based on 16S rDNA sequence analyses. Arch Microbiol 183, 19–26 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-004-0740-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-004-0740-y