Abstract
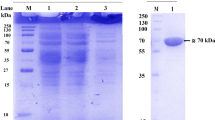
Our fungal culture collection was screened for fructosyl peptide oxidase, an enzyme that could be used for the determination of glycated hemoglobin in diabetic subjects with hyperglycemia. Fructosyl peptide oxidases were found in strains of eight genera: Achaetomiella, Achaetomium, Chaetomium, Coniochaeta, Eupenicillium, Gelasinospora, Microascus and Thielavia. By their substrate specificity toward N α-fructosyl valyl-histidine (α-keto-amine) and N ε-fructosyl lysine (ε-keto-amine), fructosyl peptide oxidases could be categorized into two groups: (1) enzymes that oxidize both α-keto-amine and ε-keto-amine, and (2) enzymes that preferably oxidize α-keto-amine. A fructosyl peptide oxidase from Achaetomiella virescens ATCC 32393, active toward both N α-fructosyl valyl-histidine and N ε-fructosyl lysine, was purified to homogeneity and characterized. The enzyme was monomeric (M r=50,000), was most active at 40 °C and pH 8.0, and had a covalently bound flavin as a prosthetic group. Apparent K m values for N α-fructosyl valyl-histidine and N ε-fructosyl lysine were 2.30 and 1.69 mM, respectively. N α-fructosyl valyl-histidine was consumed and the same molar amount of valyl-histidine was produced by the fructosyl peptide oxidase reaction. This enzyme could be useful for the measurement of hemoglobin A1C, the N-terminal valine residue of the β-subunit of which is glycated.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HbA 1C :
-
Hemoglobin A1C
- FPOX :
-
Fructosyl peptide oxidase
- FAOX :
-
Fructosyl amino acid oxidase
- Fru-ValHis :
-
N α-fructosyl valyl-histidine
- Fru-Val :
-
N α-fructosyl valine
- εFru-Lys :
-
N ε-fructosyl lysine
- Fru-Gly :
-
Fructosyl glycine
- TOOS :
-
N-ethyl-N-(2-hydroxy-3-sulfopropyl)-3-methylaniline, sodium salt
References
Bookchin RM, Gallop PM (1968) Structure of hemoglobin AIc: nature of the N-terminal beta chain blocking group. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 32:86–93
Bunn HF, Gabbay KH, Gallop PM (1978) The glycosylation of hemoglobin: relevance to diabetes mellitus. Science 200:21–27
Hirokawa K, Kajiyama N (2002) Recombinant Agrobacterium AgaE-like protein with fructosyl amino acid oxidase activity. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 66:2323–2329
Horiuchi T, Kurokawa T, Saito N (1989) Purification and properties of fructosyl-amino acid oxidase from Corynebacterium sp. 2-4-1. Agric Biol Chem 53:103–110
Jeong HY, Song MH, Back JH, Han DM, Wu X, Monnier V, Jahng KY, Chae KS (2002)The veA gene is necessary for the inducible expression by fructosyl amines of the Aspergillus nidulans faoA gene encoding fructosyl amino acid oxidase (amadoriase, EC 1.5.3). Arch Microbiol 178:344–350
Kennedy L, Mehl TD, Riley WJ, Merimee TJ (1981) Non-enzymatically glycosylated serum protein in diabetes mellitus: an index of short-term glycaemia. Diabetologia 21:94–98
Kim K-S, Chilton WS, Farrand SK (1996) A Ti plasmid-encoded enzyme required for degradation of mannopine is functionally homologous to the T-region-encoded enzyme required for synthesis of this opine in crown gall tumors. J Bacteriol 178:3285–3292
Kobold U, Jeppsson JO, Dulffer T, Finke A, Hoelzel W, Miedema K (1997) Candidate reference methods for hemoglobin A1C based on peptide mapping. Clin Chem 43:1944–1951
Sakai Y, Yoshida N, Isogai A, Tani Y, Kato N (1995) Purification and properties of fructosyl lysine oxidase from Fusarium oxysporum S-1F4. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 59:487–491
Sakaue R, Hiruma M, Kajiyama N, Koyama Y (2002) Cloning and expression of Fructosyl-amino acid oxidase gene from Corynebacterium sp. 2-4-1 in Escherichia coli. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 66:1256–1261
Sakurabayashi I, Watano T, Yonehara S, Ishimaru K, Hirai K, Komori T, Yagi M (2003) New enzymatic assay for glycohemoglobin. Clin Chem 49:269–274
Sode K, Ishimura F, Tsugawa W (2001) Screening and characterization of fructosyl-valine utilizing marine microorganism. Mar Biotechnol 3:126–132
Staniford JM, Power JA, Lovelady JA, (July 27, 1992) European Patent 0526150
Takahashi M, Pischetsrieder M, Monnier VM (1997) Molecular cloning and expression of amadoriase isoenzyme (fructosyl amine:oxygen oxidoreductase, EC 1.5.3) from Aspergillus fumigatus. J Biol Chem 272:12505–12507
Wu X, Palfey BA, Mossine VV, Monnier VM (2001) Kinetic studies, mechanism, and substrate specificity of amadoriase I from Aspergillus sp. Biochemistry 40:12886–12895
Yoshida N, Sakai Y, Serata M, Tani Y, Kato N (1995) Distribution and properties of fructosyl amino acid oxidase in fungi. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:4487–4489
Yoshida N, Sakai Y, Isogai A, Fukuya H, Yagi M, Tani Y, Kato N (1996) Primary structures of fungal fructosyl amino acid oxidases and their application to the measurement of glycated proteins. Eur J Biochem 242:499–505
Acknowledgements
We thank N. Yamaji, A. Arai, R. Sakaue and Y. Senoh for various suggestions; T. Izumi and A. Sano for substrate synthesis; M. Moromachi and F. Tatsumi for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hirokawa, K., Gomi, K., Bakke, M. et al. Distribution and properties of novel deglycating enzymes for fructosyl peptide in fungi. Arch Microbiol 180, 227–231 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-003-0584-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-003-0584-x