Abstract
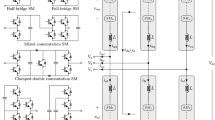
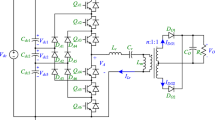
This paper focuses on sliding mode controller (SMC)-based master–slave parallel operation of DC–DC converters using a modified sliding manifold to achieve a fast dynamic response and very low steady-state error. The converter performance is analyzed in a novel way starting from a simple case of paralleling of two converters and then concept is extended for parallel operation of multiple converters. An investigation of the choice of the sliding surface on the performance of parallel converter is carried out in detail, and a mathematical design guideline for sliding coefficients for the proposed manifold for the master converter is derived to achieve stable operation. The proposed manifold ensures an improved dynamic response with an excellent steady-state accuracy in stand-alone mode. However, when it is incorporated with master–slave control for parallel operation with finite tie wire impedance, there is a degradation in the steady-state accuracy. In order to improve the steady-state performance of the sliding mode controller, two new hybrid (SMC + PI) controllers are proposed and implemented for parallel connected DC–DC converters. Finally, the proposed SMC techniques are verified through simulation study and through a scaled down experimental (laboratory) prototype.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choi B (1998) Comparative study on paralleling schemes of converter modules for distributed power applications. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 45(2):194–199
Liu Y, Han Y, Lin C, Yang P, Wang C (2019) Design and implementation of droop control strategy for DC microgrid based on multiple DC/DC converters. In: Proceedings of IEEE ISGT, Chengdu, China, pp 3896–3901
Ali S, Shengxue T, Jianyu Z, Ali A, Nawaz A (2019) An implementation of parallel buck converters for common load sharing in DC microgrid. Information 10:91
Wang JB (2012) Parallel DC/DC converters system with a novel primary droop current sharing control. IET Power Electron 5(8):1569–1580
Mazumder SK, Tahir M, Acharya K (2008) Master–slave current-sharing control of a parallel DC–DC converter system over an RF communication interface. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 55(1):59–66
Lai YM, Tan S-C, Tsang YM (2009) Wireless control of load current sharing information for parallel-connected DC/DC power converters. IET Power Electron 2(1):14–21
Rezkallah M, Sharma SK, Chandra A, Singh B, Rousse DR (2017) Lyapunov function and sliding mode control approach for the solar-PV grid interface system. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 64(1):785–795
Lopez M, de Vicuna LG, Castilla M, Gaya P, Lopez O (2004) Current distribution control design for paralleled DC/DC converters using sliding-mode control. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 51(2):419–428
Altin N, Ozdemir S, Komurcugil H, Sefa I (2019) Sliding-mode control in natural frame with reduced number of sensors for three-phase grid-tied LCL-interfaced inverters. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 66(4):2903–2913
Ling R, Shu Z, Hu Q, Song Y (2018) Second-order sliding-mode controlled three-level buck DC–DC converters. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 65(1):898–906
Bagheri F, Komurcugil H, Kukrer O, Guler N, Bayhan S (2020) Multi-input multi-output-based sliding-mode controller for single-phase quasi-Z-source inverters. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 67(8):6439–6449
He Y, Luo FL (2006) Sliding-mode control for DC–DC converters with constant switching frequency. Proc IEE Control Theory Appl 153(1):37–45
Petronijevic MP, Milosavljevic C, Veselic B et al (2021) Robust cascade control of electrical drives using discrete-time chattering-free sliding mode controllers with output saturation. Electr Eng 103:2181–2195
Goudarzian A, Khosravi A, Abjadi NR (2020) Input-output current regulation of Zeta converter using an optimized dual-loop current controller. Electr Eng 102:279–291
Al Zawaideh A, Boiko IM (2022) Analysis of stability and performance of a cascaded PI sliding-mode control DC–DC boost converter via LPRS. IEEE Trans Power Electron 37(9):10455–10465
Tan S-C, Lai YM, Tse CK (2005) Design of PWM based sliding mode voltage controller for DC–DC converters operating in continuous conduction mode. Proc ECPEA, Dresden, pp 1–10
Jazi HN, Goudarzian A, Pourbagher R, Derakhshandeh SY (2017) PI and PWM sliding mode control of POESLL converter. IEEE Trans Aerospace Electron Syst 53(5):2167–2177
Mohanty PR, Panda AK (2017) Fixed-frequency sliding-mode control scheme based on current control manifold for improved dynamic performance of boost PFC converter. IEEE J Emerg Sel Top Power Electron 5(1):576–586
Chincholkar SH, Jiang W, Chan C-Y (2018) An improved PWM-based sliding-mode controller for a DC–DC cascade boost converter. IEEE Trans Circ Syst II Express Briefs 65(11):1639–1643
Tan S, Lai YM, Tse CK (2008) Indirect sliding mode control of power converters via double integral sliding surface. IEEE Trans Power Electron 23(2):600–611
Chincholkar SH, Chan C-Y (2017) Design of fixed-frequency pulsewidth-modulation-based sliding-mode controllers for the quadratic boost converter. IEEE Trans Circ Syst II Express Briefs 64(1):51–55
Cao J, Chen Q, Zhang L, Quan S (2018) Sliding mode control of bidirectional DC/DC converter. In: Proceedings of YAC, Nanjing, pp 717–721
Tan S-C, Lai Y-M, Tse CK (2011) Sliding mode control of switching power converters. CRC Press, Cambridge
Lopez M, de Vicuna LG, Castilla M, Gaya P, Lopez O (2004) Current distribution control design for paralleled DC/DC converters using sliding-mode control. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 51(2):419–428
Mazumder SK, Tahir M, Acharya K (2008) Master–slave current-sharing control of a parallel DC–DC converter system over an RF communication interface. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 55(1):59–66
Rajagopalan J, Xing K, Guo Y, Lee FC, Manners B (1996) Modeling and dynamic analysis of paralleled DC/DC converters with master-slave current sharing control. In: Proceedings of APEC, CA, pp 678–684
Verma V, Talpur GG (2012) Decentralized master–slave operation of microgrid using current controlled distributed generation sources. In: Proceedings of IEEE PEDES, Bengaluru, pp 1–6
Chiang H-C, Jen K-K, You G-H (2016) Improved droop control method with precise current sharing and voltage regulation. IET Power Electron 9:789–800
Augustine S, Mishra MK, Lakshminarasamma N (2015) Adaptive droop control strategy for load sharing and circulating current minimization in low-voltage standalone DC microgrid. IEEE Trans Sustain Energy 6(1):132–141
Sadabadi MS (2021) A distributed control strategy for parallel DC–DC converters. IEEE Control Syst Lett 5(4):1231–1236
Renaudineau H et al (2014) Efficiency optimization through current-sharing for paralleled DC–DC boost converters with parameter estimation. IEEE Trans Power Electron 29(2):759–767
Chen S-Y, Yang B-C, Pu T-A, Chang C-H, Lin R-C (2019) Active current sharing of a parallel DC–DC converters system using bat algorithm optimized two-DOF PID control. IEEE Access 7:84757–84769
Du H, Jiang C, Wen G, Zhu W, Cheng Y (2019) Current sharing control for parallel DC–DC buck converters based on finite-time control technique. IEEE Trans Ind Inform 15(4):2186–2198
Chen H-C, Lu C-Y, Rout US (2018) Decoupled master–slave current balancing control for three-phase interleaved boost converters. IEEE Trans Power Electron 33(5):3683–3687
Long R, Quan S, Zhang L, Chen Q, Zeng C, Ma L (2015) Current sharing in parallel fuel cell generation system based on model predictive control. Int J Hydro Energy 40(35):11587–11594
Tomescu B, Vanlandingham HF (1999) Improved large-signal performance of paralleled DC–DC converters current sharing. IEEE Trans Power Electron 14(3):573–577
Keller G, Lascu D, Myrzik JMA (2005) State-space control structures for buck converters with/without input filter. In: Proceedings of ECPEA, Dresden, pp 1–10
Repecho V, Biel D, Ramos-Lara R, Vega PG (2018) Fixed-switching frequency interleaved sliding mode eight-phase synchronous buck converter. IEEE Trans Power Electron 33(1):676–688
Li M, Tse CK, Iu HHC, Ma X (2010) Unified equivalent modeling for stability analysis of parallel-connected DC/DC converters. IEEE Trans Circ Syst II Express Briefs 57(11):898–902
Repecho V, Biel D, Ramos-Lara R (2020) Robust ZAD sliding mode control for an 8-phase step-down converter. IEEE Trans Power Electron 35(2):2222–2232
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TRB, GS and DD designed the proposal. TRB, GS did the analysis, simulation and experimental studies and prepared the manuscript documentations. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests as defined by Springer, or other interests that might be perceived to influence the results and/or discussion reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Burle, T.R., Satpathy, G. & De, D. Hybrid controller configuration for master–slave paralleling of DC–DC converters with improved sliding manifold. Electr Eng 106, 79–91 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-023-01976-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-023-01976-3