Abstract
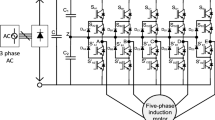
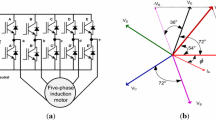
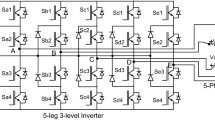
The torque ripple in five-phase induction motor (FP-IM) is reduced in the proposed direct torque control (DTC) drive scheme. The three-level five-phase inverter (TL-FPI) is utilized to feed the five-phase machine due to provision of availability of more switching states as compared to two-level five-phase inverter. The implemented 81 switching states among 243 available are distributed in 20 sectors each having 18° width. The 20-sector distribution gives more fine torque ripple slopes as compared to the 10-sector distribution by increasing the switchover frequency of the switching states. The main and intermediate switching states are alternately employed which maintain the torque slope (ripple) lower. An increase in changeover frequency of voltage vectors (VVs) decreases the sharpness of torque ripple, which keeps the magnitude of torque ripple lower. While reducing the torque ripple, the common-mode voltage (CMV) is controlled. Additionally, the phase current and stator flux are improved. The several results are provided with this paper to showcase the torque ripple reduction.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Takahashi I, Noguchi T (1986) A new quick response and high efficiency control strategy of an induction motor. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 22(5):820–827
Casadei D, Serra G (1997) Analytical investigation of torque and flux ripple in DTC schemes for induction motors. Proc IEEE IECON 97:552–556
Kang JK, Sul SK (1999) New direct torque control of induction motor for minimum torque ripple and constant switching frequency. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 35(5):1076–1082
Shyu K-K, Lin J-K, Pham VT, Yang M-J, Wang T-W (2010) Global minimum torque ripple design for direct torque control of induction motor drives. IEEE trans 57(9):3148–3155
Telford D, Dunnigan MW, Williams BW (2001) A novel torque-ripple reduction strategy for direct torque control of induction motor. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 48:867–870
Noguchi T, Yamamptp M, Kondo S, Takahashi I (1997) High frequency switching operation of pwm inverter for direct torque control of induction motor. IEEE Industry Appl Soc Ann Meet New Orleans 1:775–780
Idris NR, Yatim AH. (2000) Reduced torque ripple and constant torque switching frequency strategy for direct torque control of induction machine. InAPEC 2000. Fifteenth Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (Cat. No. 00CH37058) (Vol. 1, pp. 154-161). IEEE
Lee KB, Song JH, Choy I, Yoo JY (2002) Torque ripple reduction in DTC of induction motor driven by three-level inverter with low switching frequency. IEEE Trans Power Electron 17(2):255–263
Lee KB, Song JH, Choy I, Yoo JY (2001) Improvement of low speed operation performance of DTC for three-level inverter fed induction motors. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 48(5):255–264
Levi E (2008) Multiphase electric machines for variable-speed applications. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 55(5):1893–1909
Barrero F, Duran MJ (2016) Recent advances in the design, modeling, and control of multiphase machines—part I. IEEE Trans Industr Electron 63(1):449–458
Duran MJ, Barrero F (2016) Recent advances in the design, modeling, and control of multiphase machines—part II. IEEE Trans Industr Electron 63(1):459–468
Yang G et al (2021) A sequential direct torque control scheme for seven-phase induction machines based on virtual voltage vectors. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 57(4):3722–3734
Muduli UR, Chikondra B, Behera RK (2022) Space vector PWM based dtc scheme with reduced common mode voltage for five-phase induction motor drive. IEEE Trans Power Electron 37(1):114–124
Xu H, Toliyat HA, Petersen LJ (2002) Five-phase induction motor drives with DSP-based control system. IEEE Trans Power Electron 17(4):524–533
Zheng L, Fletcher JE, Williams BW, He X (2011) A novel direct torque control scheme for a sensorless five-phase induction motor drive. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 58(2):503–513
Gao L, Fletcher JE, Zheng L (2011) Low speed control improvements for a 2-level 5-phase inverter-fed induction machine using classic direct torque control. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 58(7):2744–2754
Payami S, Behera RK (2017) An improved DTC technique for low-speed operation of a five-phase induction motor. IEEE Trans Industr Electron 64(5):3513–3523
Riveros JA, Barrero F, Levi E, Duran MJ, Toral S, Jones M (2013) Variable-speed five-phase induction motor drive based on predictive torque control. Industrial Electron IEEE Trans 60(8):2957–2968
Bermudez M, Gonzalez-Prieto I, Barrero F et al (2018) An experimental assessment of open-phase fault-tolerant virtual-vector-based direct torque control in five-phase induction motor drives. IEEE Trans Power Electron 33(3):2774–2784
Bermudez M, Gonzalez-Prieto I, Barrero F et al (2017) Open-phase fault tolerant direct torque control technique for five-phase induction motor drives. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 64(2):902–911
Gao L, Fletcher JE (2010) A space vector switching strategy for Three-level five-phase inverter drives. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 57(7):2332–2343
Tatte Y, Aware M (2017) Direct torque control of five-phase induction motor with common-mode voltage and current harmonics reduction. IEEE Trans Power Electron 32(11):8644–8654
Payami S et al (2015) Common-mode voltage and vibration mitigation of a five-phase three-level NPC inverter-fed induction motor drive system. IEEE J Emerging Sel Top Power Electron 3(2):349–361
Chikondra B, Muduli UR, Behera RK (2022) Improved DTC Technique for THL-NPC VSI fed five-phase induction motor drive based on vvs assessment over a wide speed range. IEEE Trans Power Electron 37(2):1972–1981
Tatte YN, Aware MV, Pandit JK, Nemade R (2018) Performance improvement of three-level five-phase inverter-fed DTC controlled five-phase induction motor during low-speed operation. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 54(3):2349–2357
Garcia Entrambasaguas P, Gonzalez-Prieto I, Duran MJ, Bermudez M, Barrero F (2018) Fault tolerance in direct torque control with virtual voltage vectors. Revista Iberoamericana de Automatica e Informatica Industrial (RIAI). https://doi.org/10.4995/riai.2018.9288
Entrambasaguas PG, Prieto IG, Martínez MJ, Guzmán MB, García FJ (2018) Vectores Virtuales de Tensión en Control Directo de Par para una Máquina de Inducción de Seis Fases. Revista Iberoamericana de Automática e Informática industrial. 15(3):277–85
Masoumkhani H, Taheri A (2021) pi regulator-based duty cycle control to reduce torque and flux ripples in DTC of six-phase induction motor. IEEE J Emerg Selected Topics Power Electron 9(1):354–370
Holakooie MH, Iwanski G (2021) Virtual subspace-based DTC strategy for torque ripple minimization in six-phase induction motors. IEEE Access 9:154692–154703
Engku Ariff EAR, Dordevic O, Jones M (2016) Space vector PWM technique for a three-level six-phase drive. 8th IET International Conference on Power Electronics, Machines and Drives (PEMD 2016), 2016 1–6
He S, Sui X, Zhou D, Blaabjerg F. (2020) Torque ripple suppression of a five-phase induction motor under single-phase open. In: 2020 IEEE 9th international power electronics and motion control conference (IPEMC2020-ECCE Asia) pp 3470–3475. IEEE
Liu H, Wang D, Yi X, Meng F (2021) Torque ripple suppression under open-phase fault conditions in a five-phase induction motor with harmonic injection. IEEE J Emerg Selected Topics Power Electron 9(1):274–288
Tatte Y, Aware M (2017) Torque ripple and harmonic current reduction in three-level inverter fed direct torque controlled five-phase induction motor drive. IEEE Trans Industr Electron 64(7):5265–5275
Mäki-Ontto P, Luomi J, Kinnunen H (2006) Reduction of capacitive and induced shaft voltages in an induction motor drive using dual-bridge inverter approach. Electr Eng 88:465–472
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tatte, Y., Aware, M. & Khadse, C. Torque ripple reduction in three-level five-phase inverter-fed five-phase induction motor. Electr Eng 104, 3793–3805 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-022-01579-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-022-01579-4