Abstract
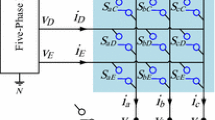
The given research article represents the voltage-fed quasi Z source direct matrix converter (QZSDMC) for three-phase to K-phase power conversion with the maximum constant boost control-modulation technique. To reduce the switching losses and to achieve high efficiency, a new PWM technique has been proposed. The technique controls both the rectifier side and inverter side of the matrix converter equivalent circuit. Compared with the ZSDMC, the voltage-fed QZSDMC has less effective components, is compact in size, and has higher efficiency and a wide range of controlled buck-boost operations. The proposed modulation technique provides lower harmonic contents in the output, poor switching current stresses, lower switching voltages and maximum voltage gain under the given modulation index. This paper discussed the relationship of the voltage gain to the modulation index and the relationship of the switching voltage stresses to the voltage gain have been analyzed. The proposed modulation technique was verified by simulation using MATLAB and also validated experimentally.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pipolo S, Formentini A, Trentin A, Zanchetta P, Calvini M, Venturini M (2021) A novel Matrix converter modulation with a reduced number of commutations. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 52:1
Thangavel MK, Ramasamy BK, Ponnusamy P (2020) Performance analysis of dual space vector modulation technique-based quasi z-source direct matrix converter. Electr Power Compon Syst 0(0):1–12
Krishnan S, Umasankar P, Mohana P (2020) A smart FPGA based design and implementation of grid-connected direct matrix converter with IoT communication. Microprocessor Microsyst 76:124
Yepes AG, Doval-Gandoy J (2021) Simple carrier-based PWM for prolonged high DC-link utilization for symmetrical and asymmetrical n-phase AC drives. IEEE Trans Power Electron 8993(c):1–1
Tawfiq KB, Mansour AS, Ibrahim MN (2020) Design, implementation and performance analysis of shunt active filter based on matrix converter. Int J Electron 0(0):52
Tawfiq KB, Ibrahim MN, EL-Kholy EE, Sergeant P (2021) Performance analysis of a five-phase synchronous reluctance motor connected to matrix converter. In: 2021 IEEE international electric machines & drives conference (IEMDC), pp 1–6
Malekjamshidi Z, Jafari M, Zhu J, Xiao D (2019) Bidirectional power flow control with stability analysis of the matrix converter for microgrid applications. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 110:725–736
Venkatasubramanian D, Shanthi B (2019) An efficient control method for PMSM drive using an optimized indirect matrix converter. Futur Gener Comput Syst 98:12–17
Siwek P, Urbanski K (2018) Improvement of the torque control dynamics of the PMSM drive using the FOC-controlled simple boost QZSDMC converter. In: 2018 23rd Int. Conf. Methods Model. Autom. Robot. MMAR 2018, pp 29–34
Guo M, Liu Y, Ge B, Abu-Rub H (2018) Optimum boost control of quasi-z source indirect matrix converter. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 65(10):8393–8404
DOF Philosophy, F. Of, and E. Engineering, “Z-source matrix converter for wind turbine driven permanent magnet generator submitted by,” no. March 2019
Moghadasi N, Esmaeli A, Soleymani S, Mozafari B (2018) Quasi-Z-source matrix converters to be used in PMSG-based WECS: modeling, control, and comparison. Int Trans Electr Energy Syst 28(6):1–27
Bozorgi AM, Hakemi A, Farasat M, Monfared M (2018) Modulation techniques for common-mode voltage reduction in the z-source ultra sparse matrix converters. IEEE Trans Power Electron 34(1):958–970
Sri Vidhya D, Venkatesan T (2018) Quasi-Z-source indirect matrix converter fed induction motor drive for flow control of dye in paper mill. IEEE Trans Power Electron 33(2):1476–1486
Li X, Sun Y, Zhang J, Su M, Huang S (2017) Modulation methods for indirect matrix converter extending the input reactive power range. IEEE Trans Power Electron 32(6):4852–4863
Alizadeh M, Kojori SS (2018) Small-signal stability analysis, and predictive control of Z-source Matrix Converter feeding a PMSG-WECS. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 95:601–616
Liu Y, Ge B, Abu-Rub H, Blaabjerg F (2018) Single-phase Z-source/quasi-Z-source inverters and converters. IEEE Ind Electron Mag 12(2):6–23
Liu Y, Liang W, Ge B, Abu-Rub H, Nie N (2018) Quasi-Z-source three-to-single-phase matrix converter and ripple power compensation based on model predictive control. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 65(6):5146–5156
Dabour SM, Abdel-Khalik AS, Ahmed S, Massoud AM, Allam SM (2018) Common-mode voltage reduction for space vector modulated three- to five-phase indirect matrix converter. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 95:266–274
Zhou M, Sun Y, Su M, Li X, Liu F, Liu Y (2018) A single-phase buck-boost AC-AC converter with three legs. J Electr Eng Technol 13(2):838–848
Saeed N, Ibrar A, Saeed A (2017) A review on industrial applications of Z-source inverter. J Power Energy Eng 05(09):14–31
M. Li, Y. Liu, and H. Abu-Rub, “Optimizing control strategy of quasi-Z source indirect matrix converter for induction motor drives,” IEEE Int. Symp. Ind. Electron., no. DMC, pp. 1663–1668, 2017.
Hakemi A, Monfared M (2017) Very high gain three-phase indirect matrix converter with two Z-source networks in its structure. IET Renew Power Gener 11(5):633–641
Alizadeh M, Kojori SS (2017) Modified predictive control for both normal and LVRT operations of a Quasi-Z-Source Matrix Converter based WECS. Control Eng Pract 68:1–14
Ellabban O, Abu-Rub H, Bayhan S (2016) Z-source matrix converter: an overview. IEEE Trans Power Electron 31(11):7436–7450
Pinto SF, Mendes PV, Fernando Silva J (2016) Modular matrix converter based solid state transformer for smart grids. Electr Power Syst Res 136:189–200
Liu S, Ge B, Liu Y, Abu-Rub H, Balog RS, Sun H (2016) Modeling, analysis, and parameters design of LC-filter-integrated quasi-Z-source indirect matrix converter. IEEE Trans Power Electron 31(11):7544–7555
Liu S, Ge B, You X, Jiang X, Abu-Rub H, Peng FZ (2015) A novel quasi-Z-source indirect matrix converter. Int J Circuit Theory Appl 43(4):438–454
Ellabban O, Abu-Rub H, Ge B (2015) A quasi-Z-source direct matrix converter feeding a vector controlled induction motor drive. IEEE J Emerg Sel Top Power Electron 3(2):339–348
Takahashi N, Liu S, Ge B, Jiang X, Abu-Rub H, Peng F (2014) Modeling, analysis, and motor drive application of quasi-Z-source indirect matrix converter. COMPEL Int J Comput Math Electr Electron Eng 52:487
Empringham L, Kolar JW, Rodriguez J, Wheeler PW, Clare JC (2013) Technological issues and industrial application of matrix converters: a review. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 60(10):4260–4271
Liu S, Ge B, Jiang X, Abu-Rub H, Peng FZ (2014) Comparative evaluation of three Z-source/quasi-Z-source indirect matrix converters. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 62(2):692–701
He L, Duan S, Peng F (2013) Safe-commutation strategy for the novel family of quasi-Z-source AC–AC converter. IEEE Trans Ind Inform 9(3):1538–1547
Friedli T, Kolar JW, Rodriguez J, Wheeler PW (2012) Comparative evaluation of three-phase AC–AC matrix converter and voltage DC-link back-to-back converter systems. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 59(12):4487–4510
Nguyen M, Lim Y, Kim Y (2012) A modified single-phase quasi-Z-source AC–AC converter. IEEE Trans Power Electron 27(1):201–210
BharaniKumar R, Adhisree VV, NirmalKumar A (2012) Performance analysis of Z-source matrix converter by implementing different PWM schemes. J Electr Eng 12(3):193–201
Liu X, Loh PC, Wang P, Han X (2012) Improved modulation schemes for indirect Z-source matrix converter with sinusoidal input and output waveforms. IEEE Trans Power Electron 27(9):4039–4050
Ge B, Lei Q, Qian W, Peng FZ (2012) A family of Z-source matrix converters. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 59(1):35–46
Perez MA, Rojas CA, Rodriguez J, Abu-Rub H (2012) A simple modulation scheme for a three-phase direct matrix converter. IEEE Int Symp Ind Electron 15:105–110
Rodriguez J, Rivera M, Kolar JW, Wheeler PW (2012) A review of control and modulation methods for matrix converters. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 59(1):58–70
Wheeler PW, Rodríguez J, Clare JC, Empringham L, Weinstein A (2002) Matrix converters: a technology review. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 49(2):276–288
Manivannan S, Saravanakumar N, Vijeyakumar KN (2021) Three-phase power conversion using quasi Z source direct matrix converter (QZSDMC) for fixed frequency to variable frequency using direct duty ratio based pulse width modulation technique. Int J Electron. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207217.2021.1966668
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manivannan, S., Saravanakumar, N. & Vijeyakumar, K.N. Three-phase to K-phase power conversion using voltage fed quasi Z source direct matrix converter with maximum constant boost control technique. Electr Eng 104, 3603–3617 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-022-01572-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-022-01572-x