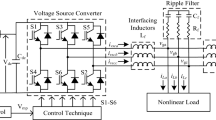
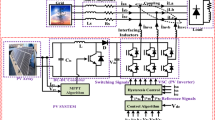
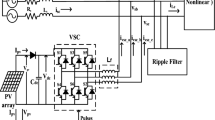
Abstract
The growing integration of distribution grid with solar energy (PV) has resulted in severe power quality (PQ) concerns, particularly in the case of a weak distribution grid. In order to improve the PQ, the effective development of a control algorithm for the solar energy (PV) conversion system, interfaced to the grid, is very vital. In this article, an adaptive robust least mean logarithmic square (RLMLS) filter-based control has been proposed to provide grid integration capabilities of a PV system, for optimal operation. Moreover, it supplies active power to the linear/nonlinear load and grid, along with power factor correction, load balancing, and harmonics mitigation. MATLAB/Simulink (2018a) is used for modelling and evaluation of the proposed system, under various loading scenarios, including nonlinear, unbalance, and load increment. It is also tested under severe grid voltage conditions, such as unbalanced and distorted grid voltage. The system’s performance has been verified as per IEEE-519 standard, showing that it is capable of grid integration and efficient in maintaining the PQ under non-ideal grid conditions characterized by a wide variety of load fluctuations, distortion, and unbalance with added benefits of faster convergence speed, reduced complexity, less sampling time, better accuracy, low dynamic oscillations/ripples in the estimation of active component, ease of implementation, and adaptability. Furthermore, a hardware prototype is developed for validation, and test results show that the system can operate efficiently under a wide variety of load fluctuations, distortion, and unbalance conditions.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- RLMLS:
-
Robust least mean logarithmic square
- PQ :
-
Power quality
- THD:
-
Total harmonic distortion
- LMS:
-
Least mean square
- PV :
-
Solar energy
- RES:
-
Renewable energy resources
- PCC :
-
Point of interconnection
- MPPT:
-
Maximum power point tracking
- \({\mathcal{U}}_{pa} , {\mathcal{U}}_{pb} ,{\mathcal{U}}_{pc}\) :
-
In-phase unit templates of voltages
- \({\mathcal{U}}_{qa} , {\mathcal{U}}_{qb} ,{\mathcal{U}}_{qc}\) :
-
Quadrature unit templates of voltages
- \(e_{pa} ,e_{pb} ,e_{pc} \) :
-
Estimation error of a, b, c phases
- \(w_{pa} ,w_{pb} ,w_{pc}\) :
-
Fundamental active weights’ component of load of a, b, c phases
- \(w_{lp}\) :
-
Averaging of the fundamental active component of load of a, b, c phases
- \(w_{qa} ,w_{qb} ,w_{qc}\) :
-
Fundamental reactive weights’ component of load of a, b, c phases
- \(w_{lq}\) :
-
Averaging of the fundamental reactive weight component of load of a, b, c phases
- \({\mathcal{V}}_{sa } ,{\mathcal{V}}_{sb } ,{\mathcal{V}}_{sc}\) :
-
Phase voltages of a, b, c phases
- \(V_{dc}\) :
-
DC-link voltage
- \(V_{dc}^{*}\) :
-
Reference DC-link Voltage
- \(K_{pd} , K_{id}\) :
-
Gains of PI controller of DC link
- \(K_{pa} , K_{ia}\) :
-
PI controller’s gain AC side
- \(w_{dc}\) :
-
DC loss weight
- \(w_{ac}\) :
-
AC loss weight
- \(G_{c} \left( S \right)\) :
-
Transfer function of the proposed control
- \(w_{ps}\) :
-
Total active weight component
- \(w_{qs}\) :
-
Total reactive weight component
- \(i_{pa}^{*} ; i_{pb}^{*} ;i_{pc}^{*}\) :
-
Active reference current
- \(i_{qa}^{*} ,i_{qb}^{*} ,i_{qc}^{*}\) :
-
Reactive reference components
- \(i_{sa}^{*} , i_{sb}^{*} ,i_{sc}^{*}\) :
-
Reference current
References
Singh B, Kumar S (2020) Grid interactive residential photovoltaic-battery based microgrid for rural electrification. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 56(4):4114–4123
Kumar N, Singh B, Panigrahi BK (2019) ANOVA kernel kalman filter for multi-objective grid integrated solar photovoltaic-distribution static compensator. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Regul Pap 66(11):4256–4264. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSI.2019.2922405
Patankar PP, Munshi MM, Deshmukh RR, Ballal MS (2021) A modified control method for grid connected multiple rooftop solar power plants. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 57(4):3306–3316. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2021.3075195
Arun R, Mohammed Gohar Latheef KS, Anandhakumar G (2015) Grid interconnection of renewable energy sources at the distribution level with power-quality improvement features. Int J Appl Eng Res 10(33):25622–25626. https://doi.org/10.23883/ijrter.conf.20171216.014.uylw8
Beniwal N, Hussain I, Singh B (2019) Second-order volterra-filter-based control of a solar PV-DSTATCOM system to achieve lyapunov’s stability. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 55(1):670–679. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2018.2867324
Shukl P, Singh B (2019) Grid integration of three-phase single-stage PV system using adaptive Laguerre filter based control algorithm under nonideal distribution system. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 55(6):6193–6202. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2019.2931504
Elgendy MA, Atkinson DJ, Zahawi B (2016) Experimental investigation of the incremental conductance maximum power point tracking algorithm at high perturbation rates. IET Renew Power Gener 10(2):133–139. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-rpg.2015.0132
Verma P, Garg R, Mahajan P (2020) Asymmetrical interval type-2 fuzzy logic control based MPPT tuning for PV system under partial shading condition. ISA Trans., no. January. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isatra.2020.01.009.
Gupta N, Garg R (2017) Tuning of asymmetrical fuzzy logic control algorithm for SPV system connected to grid. Int J Hydrogen Energy 42(26):16375–16385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.05.103
Choi W, Lee W, Han D, Sarlioglu B (2018) New configuration of multifunctional grid-connected inverter to improve both current-based and voltage-based power quality. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 54(6):6374–6382. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2018.2861737
IEEE (1993) IEEE recommended practices and requirements for harmonic control in electrical power systems, vol. 1992, June.
IEEE Std 1547:2003 (2003) IEEE standard for interconnecting distributed resources with electric power systems, IEEE Std 1547–2003, 2014, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1109/IEEESTD.2003.94285.
Verma P, Garg R, Mahajan P (2019) Asymmetrical fuzzy logic control based mppt algorithm for stand-alone photovoltaic system under partially shaded conditions. Int J Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.24200/SCI.2019.51737.2338
Trishan E, Patrick LC (2007) Comparison of photovoltaic array maximum power point tracking techniques. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 22(2):439–449. https://doi.org/10.1109/TEC.2006.874230
Jiang Y, Abu Qahouq JA, Haskew TA (2013) Adaptive step size with adaptive-perturbation-frequency digital MPPT controller for a single-sensor photovoltaic solar system. IEEE Trans Power Electron 28(7):3195–3205. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2012.2220158
Killi M, Samanta S (2015) Modified perturb and observe MPPT algorithm for drift avoidance in photovoltaic systems. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 62(9):5549–5559. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2015.2407854
Li H, Yang D, Su W, Lu J, Yu X (2019) An overall distribution particle swarm optimization MPPT algorithm for photovoltaic system under partial shading. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 66(1):265–275. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2018.2829668
Mohanty S, Subudhi B, Ray PK (2016) A new MPPT design using grey Wolf optimization technique for photovoltaic system under partial shading conditions. IEEE Trans Sustain Energy 7(1):181–188. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSTE.2015.2482120
Singh B, Chandra A, Al-Haddad K (2015) Power quality problems and mitigation techniques. Wiley . http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/book/10.1002/9781118922064, ISBN: 978–1–118–92205–7
Xiao F, Member S, Dong L, Li L, Lia X (2017) A frequency-fixed SOGI based PLL for single-phase grid-connected converters. IEEE Trans Power Electron 32(3):1713–1719. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2016.2606623
Wu F, Zhang L, Duan J (2015) A new two-phase stationary-frame-based enhanced PLL for three-phase grid synchronization. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst II Express Briefs 62(3):251–255. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSII.2014.2368257
Youssef TA, Mohammed O (2013) Adaptive SRF-PLL with reconfigurable controller for Microgrid in grid-connected and stand-alone modes. IEEE Power Energy Soc Gen Meet. https://doi.org/10.1109/PESMG.2013.6673028
Deo S, Jain C, Singh B (2015) A PLL-less scheme for single-phase grid interfaced load compensating solar PV generation system. IEEE Trans Ind Inform 11(3):692–699
Agarwal R, Hussain I, Singh B (2016) LMF based control algorithm for single stage three-phase grid integrated solar PV system. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 7(4):1379–1387
Li Z, Li D, Xu X, Zhang J (2019) normalized LMS adaptive filter with a variable regularization factor. J Syst Eng Electron 30(2):259–269. https://doi.org/10.21629/JSEE.2019.02.05
Sayin MO, Vanli ND, Kozat SS (2014) A novel family of adaptive filtering algorithms based on the logarithmic cost. IEEE Trans Signal Process 62(17):4411–4424. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSP.2014.2333559
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
1.1 Designed system parameters
Grid voltages (Vsabc): 415 V, Source impedances (Rs, Ls): 0.01Ω, 0.1mH, frequency (f): 50 Hz, Interfacing inductor (Rf, Lf): 0.01Ω,7mH, DC bus capacitor (Cdc): 1000 μF, Vdc: 750 V; scaling factor (α) = 0.0035; step size(µ) = 0.01; sampling time (Ts) = 5.5 μs; \(K_{pd} = 0.2, K_{id} = 20\);
1.2 Designed solar PV parameters
nominal voltage (Vmpp): 410 V, nominal current (Impp): 25 A, maximum power (Pmp):10.25 kW.; Designed boost converter parameters: Capacitor (C): 1000µF, Inductor (L): 0.5mH,, Duty cycle (D): 0.43, Switching frequency (fs): 10 kHz.
1.3 Experimental parameters
Ts = 40 μs; Vgrid (VLL) = 100 V(58 V/phase) (rms); Vdc = 200 V; inverter = 25 kVA, Interfacing inductor Lf = 5 mH; nonlinear load = three phase diode bridge rectifier with R load (R = 65-40Ω). \(K_{pd} = 0.5, K_{id} = 0.1\);
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, A., Garg, R. & Mahajan, P. Performance improvement of grid-integrated PV system using novel robust least mean logarithmic square control algorithm. Electr Eng 104, 3207–3224 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-022-01552-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-022-01552-1