Abstract
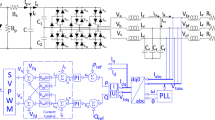
Three-phase grid-connected voltage-source inverters (VSIs) are widely used for renewable energies integration. Cost reduction and suitable operation under nonideal grid conditions are their important technical challenges. Accordingly, this paper proposes an efficient adaptive neural filter-based virtual flux (ANF-VF) estimator for sensorless control of a grid-connected VSI under unbalanced and distorted grid conditions. To perform sensorless predictive direct power control (PDPC), the grid voltage sensors are substituted by the ANF-VF estimator. This estimator includes an emulated ideal integrator in series with two simple ANFs. Lyapunov’s theory-based convergence analysis is conducted for its optimal tuning. This is resulted in an accurate extraction of VF fundamental components. For more effectiveness under unbalanced grid conditions, an extension of original instantaneous power theory is introduced in the proposed VF-based PDPC (VF-PDPC). Effectiveness of the VF-PDPC is verified through simulation and experimental tests. A direct and smooth startup without initialization is accomplished under unbalanced grid conditions. Superiority of the VF-PDPC compared to the conventional PDPC is demonstrated. The proposal presents sinusoidal grid currents with low total harmonic distortion under unbalanced and distorted grid conditions. Moreover, the ANF-VF estimator illustrates best performances compared to the second-order generalized integrator-based VF estimator that uses measured grid voltages under nonideal grid conditions.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
International Energy Agency (2020), Renewables 2020, IEA, Paris. https://www.iea.org/reports/renewables-2020. Accessed 10 February 2021
Vijay AS, Doolla S, Chandorkar M (2020) Unbalance mitigation strategies in microgrids. IET Power Elect 13(9):1687–1710. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-pel.2019.1080
Singh M, Khadkikar V, Chandra A, Varma RK (2011) Grid interconnection of renewable energy sources at the distribution level with power-quality improvement features. IEEE Trans Power Del 26(1):307–315. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPWRD.2010.2081384
Villanueva I, Rosales A, Ponce P, Molina A (2018) Grid-voltage-oriented sliding mode control for DFIG under balanced and unbalanced grid faults. IEEE Trans Sustain Energy 9(3):1090–1098. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSTE.2017.2769062
AlShabi M, Elnady A (2020) Recursive smooth variable structure filter for estimation processes in direct power control scheme under balanced and unbalanced power grid. IEEE Syst J 14(1):971–982. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSYST.2019.2919792
Zhang Z, Xu H, Xue M, Chen Z, Sun T, Kennel R, Hackl CM (2015) Predictive control with novel virtual-flux estimation for back-to-back power converters. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 62(5):2823–2834. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2014.2361802
Zhang Y, Liu J, Yang H, Gao J (2018) Direct power control of pulse-width modulated rectifiers without DC voltage oscillations under unbalanced grid conditions. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 65(10):7900–7910. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2018.2807421
Bouafia A, Gaubert JP, Krim F (2010) Predictive direct power control of three-phase pulse width modulation (PWM) rectifier using space vector modulation (SVM). IEEE Trans Power Electron 25(1):228–236. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2009.2028731
Zhang Y, Qu C (2015) Direct power control of a pulse width modulation rectifier using space vector modulation under unbalanced grid voltages. IEEE Trans Power Electron 30(10):5892–5901. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2014.2371469
Mehreganfar M, Saeedinia MH, Davari SA, Garcia C, Rodriguez J (2019) Sensorless predictive control of AFE rectifier with robust adaptive inductance estimation. IEEE Trans Ind Informat 15(6):3420–3431. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2018.2879060
Cho Y, Lee KB (2016) Virtual-flux-based predictive direct power control of three-phase PWM rectifiers with fast dynamic response. IEEE Trans Power Electron 31(4):3348–3359. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2015.2453129
Xiao X, Zhang Y, Song X, Yildirim T, Zhang F (2018) Virtual flux direct power control for PWM rectifiers based on an adaptive sliding mode observer. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 54(5):5196–5205. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2018.2832122
Judewicz MG, González SA, Fischer JR, Martínez JF, Carrica DO (2018) Inverter-side current control of grid-connected voltage source inverters with LCL filter based on generalized predictive control. IEEE J Emerg Sel Topics Power Electron 6(4):1732–1743. https://doi.org/10.1109/JESTPE.2018.2826365
Zeng Q, Chang L (2008) An advanced SVPWM-based predictive current controller for three-phase inverters in distributed generation systems. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 55(3):1235–1246. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2007.907674
Komatsu Y, Kawabata T (1995) A control method of active power filter where system voltage contains negative-phase-sequence components or zero-phase-sequence component. In: Proc Int Power Electron Derive Syst Conf. pp 583–586. https://doi.org/10.1109/PEDS.1995.405004
Bechouche A, Seddiki H, Ould Abdeslam D, Rahoui A, Triki Y, Wira P (2018) Predictive direct power control with virtual-flux estimation of three-phase PWM rectifiers under nonideal grid voltages. In: Proc IEEE Int Conf Ind Technol (ICIT 2018). Lyon, France. pp 806–811. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIT.2018.8352281
Fantino RA, Busada CA, Solsona JA (2019) Observer-based grid-voltage sensorless synchronization and control of a VSI-LCL tied to an unbalanced grid. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 66(7):4972–4981. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2018.2868255
Ahmed M, Abdelrahem M, Kennel R (2020) Highly efficient and robust grid connected photovoltaic system based model predictive control with kalman filtering capability. Sustainability 12(11):4542. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12114542
Liu T, Xia C, Shi T (2014) Robust model predictive current control of grid-connected converter without alternating current voltage sensors. IET Power Electron 7(12):2934–2944. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-pel.2013.0304
Lee KJ, Park BG, Kim RY, Hyun DS (2012) Robust predictive current controller based on a disturbance estimator in a three-phase grid-connected inverter. IEEE Trans Power Electron 27(1):276–283. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2011.2157706
Yang H, Zhang Y, Liang J, Gao J, Walker P, Zhang N (2018) Sliding mode observer based voltage-sensorless model predictive power control of PWM rectifier under unbalanced grid condition. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 65(7):5550–5560. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2017.2774730
Malinowski M, Kazmierkowski MP, Hansen S, Blaabjerg F, Marques GD (2001) Virtual-flux-based direct power control of three-phase PWM rectifiers. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 37(4):1019–1027. https://doi.org/10.1109/28.936392
Norniella JG, Cano JM, Orcajo GA, Rojas CH, Pedrayes JF, Cabanas MF, Melero MG (2014) Improving the dynamics of virtual flux-based control of three-phase active rectifiers. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 61(1):177–187. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2013.2245614
Malinowski M, Marques G, Cichowlas M, Kazmierkowski MP (2003) New direct power control of three-phase PWM boost rectifiers under distorted and imbalanced line voltage conditions. In: Proc IEEE Int Symp Ind Electron. Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. pp 438–443. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISIE.2003.1267289
Cichowlas M, Malinowski M, Kazmierkowski MP, Sobczuk DL, Rodriguez P, Pou J (2005) Active filtering function of three-phase PWM boost rectifier under different line voltage conditions. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 52(2):410–419. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2005.843915
Ketzer MB, Jacobina CB (2016) Virtual flux sensorless control for shunt active power filters with quasi-resonant compensators. IEEE Trans Power Electron 31(7):4818–4830. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2015.2487298
Kulka A (2009) Sensorless digital control of grid connected three phase converters for renewable sources. PhD dissertation. Norwegian Univ Sci Technol. Trondheim, Norway
Suul JA, Luna A, Rodriguez P, Undeland T (2012) Voltage sensorless synchronization to unbalanced grids by frequency-adaptive virtual flux estimation. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 59(7):2910–2923. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2011.2168793
Pinto JOP, Bose BK, De Silva LEB (2001) A stator-flux-oriented vector-controlled induction motor drive with space-vector PWM and flux-vector synthesis by neural network. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 37(5):1308–1318. https://doi.org/10.1109/28.952506
Cirrincione M, Pucci M, Cirrincione G, Capolino GA (2004) A new adaptive integration methodology for estimating flux in induction machine drives. IEEE Trans Power Electron 19(1):25–34. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2003.820565
Zhao R, Xin Z, Loh PC, Blaabjerg F (2017) A novel flux estimator based on multiple second- order generalized integrators and frequency-locked loop for induction motor drives. IEEE Trans Power Electron 32(8):6286–6296. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2016.2620428
Akagi H, Kanazawa Y, Nabae A (1984) Instantaneous reactive power compensators comprising switching devices without energy storage components. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 20(3):625–630. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIA.1984.4504460
IEEE recommended practice and requirements for harmonic control in electric power systems, IEEE Std 519–2014 (revision of IEEE Std 519–1992), 2014. https://doi.org/10.1109/IEEESTD.2014.6826459
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Triki, Y., Bechouche, A., Seddiki, H. et al. Sensorless predictive control of voltage source inverters for renewable energies integration under unbalanced and distorted grid conditions. Electr Eng 104, 1781–1796 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-021-01432-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-021-01432-0